Digital sound refers to sound that has been converted into digital format, allowing it to be manipulated and stored as digital data. Digital sound is created by converting analog sound waves into digital data through a process called sampling.
In today’s world, digital sound has become an integral part of our daily lives. It can be found in everything from music to movies to phone calls and video games. The use of digital sound has revolutionized the entertainment industry, allowing for higher quality audio and greater accessibility.
With the rise of digital technology, sound can be easily shared and distributed across the world, making it easier than ever for people to connect and enjoy their favorite content. Understanding digital sound and its capabilities is essential for anyone looking to create or consume digital media.

Credit: www.linkedin.com
The Evolution Of Sound
The Evolution of Sound is as fascinating as music or any other auditory arts. Sound which was first recorded in 1857 has come a long way today. From the simple phonographs to today’s digital sound, the quality of sound has improved tremendously. In this blog post, we will discuss the evolution of sound from analog to digital, and how it has impacted the way we listen to music today.
From Analog To Digital
In the early days, sound was recorded using analog technology. This involved using a needle which would etch the sound waves onto a vinyl record. As the years passed, this technology was replaced with magnetic tape. This tape could be easily edited and was more portable than the earlier method.
However, analog sound systems had certain limitations. The quality of sound would degrade with each subsequent copy. Additionally, analog sound was more susceptible to noise interference, and could be easily damaged or destroyed. These limitations gave rise to the need for a new technology that could overcome these drawbacks.
The Digital Revolution
The digital revolution in sound recording began in the 1970s. Digital sound recordings used computers to convert sound waves into binary code, which could then be edited and stored on various digital media. The benefits of digital sound were numerous – it was cleaner, had higher fidelity, and could be easily edited without quality loss.
With digital sound, new possibilities emerged. Music production became more affordable, as one could record and edit music with a computer. Artists had more creative freedom to experiment as they could edit, rearrange and manipulate sounds as they wished. As a result, the music industry as we know it today was born.
The Impact Of Digital Sound
Over the years, digital sound has become the preferred choice of recording for the music industry. The quality of sound has improved tremendously, and we can now listen to music in crystal-clear quality. Additionally, digital sound has paved the way for new ways of listening to music, from online streaming to portable music players.
Furthermore, digital sound has impacted other fields like movies and gaming. Today, 3D sound and surround sound technologies create immersive experiences that were once only a dream. In conclusion, the evolution from analog to digital sound has been a fascinating journey – and we can only hope that it will continue to progress.
Understanding Digital Sound
Digital sound is the sound that has been converted into digital format. It is the representation of sound in the form of zeros and ones. Digital sound is widely used today as it ensures high-quality sound without any distortion or noise. Almost all music that people listen to today is in digital format as it is easy to store, distribute, and manipulate.
Definition Of Digital Sound
Digital sound can be defined as sound that has been converted into numerical data that can be stored, processed, and transmitted through digital communication channels. In simple terms, digital sound refers to any sound that has been digitized, allowing it to be easily transferred and manipulated by electronic devices.
What Makes Sound Digital?
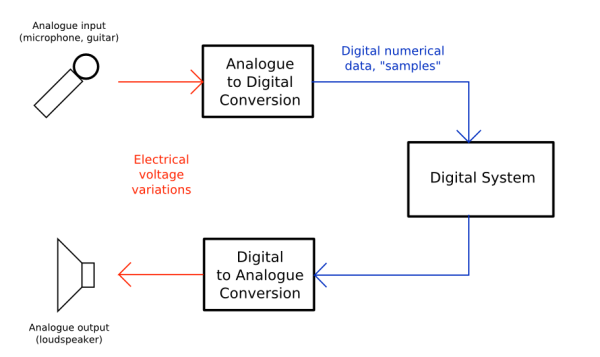
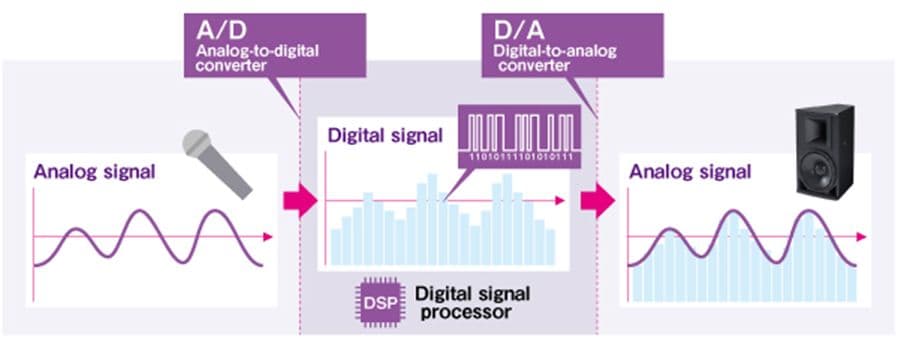
Sound is made digital through a process called digital audio conversion, which involves converting an analog audio signal into a digital format using an analog-to-digital converter (ADC).
Once the sound is digitized, it is transmitted and stored using binary code consisting of zeros and ones. This binary code can be easily processed and manipulated by a computer or any other digital device, allowing for various effects such as filtering, equalization, and compression, among others.
Digitally recorded sound is of higher quality and clarity than its analog counterpart. Digital recording allows for better signal-to-noise ratios, wider frequency responses, and greater dynamic range, all of which contribute to a more realistic and immersive listening experience.
Conclusion
Digital sound has revolutionized the way people listen to music and consume audio content. Understanding digital sound and its benefits is critical for anyone who wants to appreciate high-quality audio in today’s digital age.
Benefits Of Digital Sound
Digital sound is the process of converting analog sound waves into digital signals that improve the sound quality and clarity. With the benefits of clearer sound, wider frequency range, and higher fidelity, digital sound is becoming increasingly popular in various applications such as music recording, movie production, and streaming services.
Quality
Digital sound technology has revolutionized the way we listen to music, watch movies and play games. Unlike traditional analog recordings, digital sound recordings offer exceptional audio quality. The elimination of noise and distortion results in crystal clear sound that is both immersive and enjoyable.
Accessibility
The rise of digital sound technology has made it possible to access a wide range of music and audio content at the click of a button, from all around the world. With digital sound, you can conveniently stream or download your favorite tracks and play them on various devices such as smartphones, laptops, and mp3 players, anytime, anywhere.
Portability
Digital sound technology has shrunk the size of recording devices while increasing storage capacity. This has made it more convenient and practical to carry around vast libraries of music and other audio content within a single device. You can enjoy high-quality sound wherever you go, whether you’re working out, traveling, or just relaxing at home.
In conclusion, digital sound technology has transformed the way we experience sound. With its crystal clear quality, easy accessibility, and portability, we can enjoy immersive and enhanced audio experiences from almost any location.
How Digital Sound Works
Have you ever wondered how music is recorded and played back digitally? Well, in simple terms, digital sound is created when analog sound waves are converted into a series of binary code that a computer can read and reproduce. Sounds interesting, right? In this post, we will delve deeper into how digital sound works.
Recording Sound Digitally
The process of recording digital sound involves capturing analog sound waves using a microphone and converting them to digital signals using an analog-to-digital converter (ADC). The ADC samples the analog sound waves at regular intervals and converts them into a digital format, which can be stored on a computer or other digital device. The quality of the digital recording is determined by the sampling rate and the bit depth used during the conversion process.
Converting Analog To Digital
Converting analog sound into digital sound is a complex process that involves several steps. The first step is to sample the analog sound waves at a fixed rate, usually between 44,100 and 192,000 times per second, which is known as the sampling rate. The higher the sampling rate, the greater the detail and accuracy of the digital sound.
The next step is to convert the analog sound waves into a series of binary digits using an ADC. The ADC essentially measures the amplitude of the analog sound wave at each sample point and assigns a binary code to represent that amplitude. The number of digits used to represent each sample is known as the bit depth, which determines the dynamic range of the digital sound. The more bits that are used, the greater the dynamic range, which means that the digital sound can capture a wider range of volume levels.
Conclusion
Now that you understand how digital sound works, you can appreciate the technical wizardry that goes into recording and reproducing your favorite songs. Whether you’re mixing beats in a recording studio or streaming music from your phone, digital sound is an integral part of our modern lives.
Different Types Of Digital Audio Files
Digital sound comes in different file types, including MP3, WAV, AIFF, FLAC, and AAC. Each of these file types delivers unique audio quality and compression levels, making them suitable for specific purposes.
Different Types of Digital Audio Files Digital sound refers to audio that has been converted into a digital format and stored on a digital device. Different types of digital audio files have emerged over the years, with varying properties that affect sound quality, compatibility, and storage size. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at lossy vs. lossless formats and the most common file formats used for digital sound. H3: Lossy vs. Lossless Formats Lossy and lossless are two basic digital audio file formats. Lossy audio files are designed to reduce storage space by removing some of the audio data that is deemed less important. This compression, however, results in a decrease in sound quality as some of the data that makes up the original sound signal is lost. Popular lossy audio formats include MP3, Ogg Vorbis, and AAC. In contrast, lossless audio uses a compression algorithm that preserves all of the original audio data. This ensures that no audio information is lost, which minimizes any reduction in audio quality. FLAC, ALAC, and WAV are some examples of lossless audio file formats commonly used in digital audio production. H3: Common File Formats Although there are many different digital audio file formats available, a few are considered the most common and widely used. These formats include: – MP3: The most popular digital audio file format in the world, MP3, is known for its small file size and compatibility with a wide range of devices. – AAC: Developed as a successor to MP3, AAC provides better sound quality at lower bitrates and is widely used for streaming media. – FLAC: An open-source lossless compression format that provides CD-quality sound, FLAC is a popular choice among audiophiles. – WAV: An uncompressed lossless audio format, WAV is commonly used in professional audio production due to its superior sound quality. – AIFF: Developed by Apple, AIFF is a lossless audio format that is commonly used for storing high-quality audio on macOS systems. In summary, choosing the right digital audio file format depends on various factors, including storage, compatibility, and sound quality. When it comes to choosing between lossy vs. lossless formats, it’s essential to weigh the need for storage space savings against the desire for superior sound quality.
Applications Of Digital Sound
Digital sound is the process of electronically recording, storing, and reproducing sound. It is widely used in various fields, including music, television, and films, due to its high-quality sound and ease of manipulation. Digital sound technology has also enabled many new applications that were not possible with traditional analog audio systems.
Digital sound is sound that has been converted into a digital format, allowing it to be manipulated and reproduced using computer technology. With the advancement of technology, digital sound has become an essential part of various industries such as music, film and television, and video games. In this section, we will discuss the applications of digital sound in these industries.
In Music Production
Digital sound has revolutionized the music industry, transforming the way music is recorded, produced, and distributed. The use of digital audio workstations (DAW) has made it possible for musicians and producers to manipulate and edit sound with the help of software tools. The use of digital sound has also enabled the creation of electronic music, enabling musicians to create sounds that were not previously possible with analog technology.
In Film And Television
In the film and television industry, digital sound has replaced analog sound, making it easier to manipulate sound with precision and accuracy. Digital sound has made it possible to create immersive soundscapes that add to the overall cinematic experience. With the use of surround sound technology, digital sound can be used to create a sense of depth and space, providing a more realistic and engaging viewing experience for the audience.
In Video Games
Digital sound has played a significant role in the development of video games, enabling developers to create immersive and realistic environments for players. With the use of digital sound, video game developers can create unique sound effects, background music, and voice acting, enhancing the overall gaming experience. Digital sound has also made it possible for games to provide directional sound, allowing players to locate enemies and object with greater ease. Overall, the applications of digital sound are vast and varied, and it is clear that digital sound technology will continue to play a significant role in various industries in the future.
Future Of Digital Sound
In this digital age, sound technology is evolving at a rapid pace. The future of digital sound looks extremely bright, as we can witness advancements in audio technology that always brings better sound quality and listening experience. With this progress, we can assume that digital sound will become more accessible, clear, and immersive. In this article, we will explain how digital sound is evolving, and how it impacts various aspects of sound.
High-resolution Audio
High-resolution audio refers to audio files that have a higher sampling rate and/or bit depth than the standard CD quality. These files capture more of the original sound and offer a better listening experience. The demand for high-res audio is increasing because of its superior quality, making it one of the most significant trends in digital sound. By 2024, the high-res audio market is expected to reach $7.1 billion. High-res audio offers an extensive range of options to music lovers and audiophiles, bringing them closer to the music they love.
Immersive Audio Technologies
Immersive audio technologies aim to give the listener an experience like they’re present in the performance venue. These technologies can position and transport sounds in 3D space, creating an immersive experience. With virtual reality and augmented reality gaining market share, the demand for immersive audio is growing too. The technology creates an experience where people can perceive sound, just like they perceive it in the real world. Immersive audio technologies are no longer limited to music; they are now used in movies, gaming, and even virtual events. With the evolution of this technology, the future of digital sound seems exceptionally promising.
Conclusion
Digital sound is the future, and it’s exciting to see how it’s evolving. From high-resolution audio to immersive audio, technology is making sound better, more realistic, and more accessible. In conclusion, digital sound has changed the way we listen to music, and it seems we are yet to witness the full potential of digital sound. Exciting times await us!
Credit: brunoruviaro.github.io
Credit: usa.yamaha.com
Frequently Asked Questions On What Is Digital Sound
What Is Digitally Sound?
Digitally sound refers to the production, recording, and reproduction of high-quality audio using digital technology. It involves the use of digital devices and software to capture and process sound, resulting in better sound quality and clarity.
What Are The Examples Of Digital Sound?
Digital sound examples include MP3 files, internet streaming audio, CDs, and digital audio files used in movie soundtracks, video games, and television commercials.
What Is The Difference Between Analog And Digital Sound?
Analog sound is continuous, while digital sound is represented by discrete values. Analog sound converts sound waves into electrical signals and stores them in an analog format. Digital sound transforms sound waves into numerical codes and stores them in a digital format.
What Is The Difference Between Audio And Digital Audio?
Audio refers to sounds that we can hear with our ears, while digital audio involves converting sound into digital signals that can be stored or manipulated by electronic devices. The key difference is that audio is analog, while digital audio is quantized into digital data.
Conclusion
In this age of technology, digital sound has become an integral part of our lives. It has revolutionized the way we create and listen to music, enjoy movies and communicate with one another. From its inception to the modern-day advancements, digital sound continues to push the boundaries of audio quality.
With the promise of better quality and convenience, the future of digital sound is undoubtedly fascinating. As we embrace the digital era, it’s safe to say that digital sound is here to stay.