The Haas Effect, also known as the precedence effect or the law of the first wavefront, is a psychoacoustic phenomenon that determines how humans perceive sound based on the timing and direction of arrival. This effect plays a crucial role in audio perception and is widely used in audio engineering to create a sense of width and spaciousness in recordings. In this article, we will explore the Haas Effect, its concept, and its impact on our audio perception.
The Concept of the Haas Effect
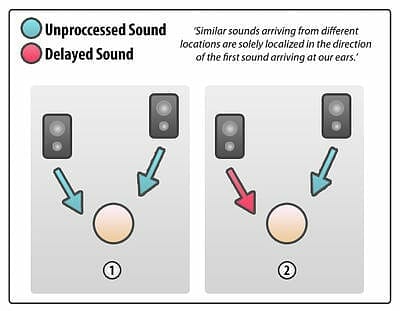
The Haas Effect is based on the idea that when two identical sounds are played simultaneously to a listener, with a slight time delay between them, the listener perceives only one sound source. The delayed sound, called the “preceding sound,” has a shorter delay time of up to approximately 30 milliseconds (ms), while the second sound, called the “following sound,” arrives within this time frame or with a longer delay. The listener predominantly localizes the perceived sound source based on the direction and timing of the preceding sound, rather than considering the following sound. This phenomenon is known as the Haas Effect.
To elaborate further, the Haas Effect states that if a sound reaches the listener’s ear within that short delay time of up to 30 ms, the listener perceives it as originating from the direction of the first sound. However, if the delay time exceeds 30 ms, the listener starts to perceive the sound as an echo or a separate sound source.
Impact on Audio Perception
The Haas Effect has a significant impact on how humans perceive audio, particularly in stereo audio recordings and sound reinforcement systems. By utilizing the Haas Effect, audio engineers can create a wideness or spaciousness effect, adding depth and realism to the sound experience. This effect helps to simulate a more natural and immersive environment, enhancing the audio quality.
Audio engineers often implement the Haas Effect by introducing a slight delay to one of the stereo channels. This creates a perceived localization of sound that is wider than the physical separation of the speakers. By manipulating the delay time and the panning position of the sound sources, engineers can control the perceived width and depth of the audio image.
Furthermore, the Haas Effect is extensively used in sound reinforcement systems to enhance the intelligibility of audio in large venues or outdoor settings. By time-aligning speakers and utilizing delay speakers, engineers can reduce echo and improve sound localization, ensuring that the sound arrives at the listener’s ears within the Haas Effect time frame. This allows for a clear and accurate sound reproduction, enhancing the overall audio perception for the audience.
Credit: output.com
Considerations and Limitations
Despite its benefits, the Haas Effect does come with some considerations and limitations that audio engineers and professionals need to be aware of. One significant consideration is the potential for phase cancellation when combining delayed and non-delayed signals. If the audio signals are not handled correctly, phase cancellation can occur, leading to a negative impact on the audio quality and the perceived stereo image.
Additionally, it is important to note that the Haas Effect can vary depending on various factors such as the listener’s environment, the sound level, and the frequency of the audio signals. Excessive use of the Haas Effect or incorporating long delay times can result in a loss of clarity and precise localization. Therefore, it is crucial for audio engineers to carefully consider these factors and use the Haas Effect sparingly and effectively.
Credit: www.eurekalert.org
In Conclusion
The Haas Effect is a psychoacoustic phenomenon that significantly impacts audio perception. By understanding and implementing this effect in audio engineering, professionals can create a sense of width, spaciousness, and immersion in stereo audio recordings and sound reinforcement systems. However, it is crucial to consider its limitations and use it judiciously to ensure optimal audio quality and localization. The Haas Effect is just one of many tools audio engineers have at their disposal to enhance the overall listening experience.
Frequently Asked Questions For What Is The Haas Effect And How Does It Impact Audio Perception?
What Is The Haas Effect?
The Haas Effect refers to the human ear’s ability to perceive a single sound as two distinct sources when heard with a slight delay.
How Does The Haas Effect Impact Audio Perception?
The Haas Effect affects the localization and spaciousness of audio, enhancing stereo imaging and creating a sense of depth in sound.