RMS in audio world refers to Root Mean Square which indicates the average power of a signal over a certain period of time. It is used as a metric to measure the loudness of an audio signal.
RMS is an important criterion in understanding how audio signals are perceived by listeners. Whether you are working in music production, sound engineering or any other audio-related field, knowing the RMS value of an audio signal is crucial. It helps in maintaining the uniformity of sound levels, making sure they are not too loud or too low.
In addition, it helps in controlling distortion, especially when processing or amplifying audio signals. Therefore, if you are working with audio files, understanding what RMS means can help you produce better quality audio and improve your overall sound experience.
Defining Rms
Defining RMS means explaining the acronym ‘Root Mean Square.’ It is the most commonly used term in audio and electronics to measure the power or amplitude of a waveform.
Explaining The Acronym
‘Root Mean Square’ or RMS is a statistical term used to find the average values of a set of numbers. In the audio world, it refers to the measurement of the steady-state power an amplifier can output without distortion.
RMS is a method to calculate the AC voltage or current levels and is used as an indicator to measure the amplifier’s power rating.
When Is Rms Used In Audio
RMS measurement is not limited to audio equipment. However, in the audio world, it is used to measure the power handling capacity of an amplifier or speaker.
When comparing audio equipment, manufacturers often use RMS measurement as the benchmark for power output instead of instantaneous peak power. It helps to specify the continuous power output and makes it easier to compare different models of amplifiers or speakers.
Why Is Rms Important In Audio
RMS measurement provides a more accurate reading of an amplifier or speaker’s true power output capacity. A speaker’s power rating is usually based on how much power it can take at its maximum without distortion
However, that maximum power rating is not sustainable, and the speaker or amplifier can be damaged if pushed to its limits for an extended time. In contrast, RMS measurement provides a more accurate reading of the amplifier or speaker’s power handling capacity, making it a reliable indicator of the device’s quality and performance.

Credit: www.amazon.com
Understanding Rms And Audio Signals
Understanding RMS and Audio Signals is vital to the audio world. One of the most essential concepts in this field is RMS, which refers to the root mean square. RMS plays a significant role in calculating the amplitude of an audio signal, which is crucial in producing high-quality sound. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of what RMS is, how it works, and how it relates to audio signals.
What Is An Audio Signal?
An audio signal is an electrical representation of sound that is used to transmit sound through electrical devices. It is a waveform that varies in amplitude and frequency over time and can be captured by a microphone. In the audio world, a signal is considered to be an electrical representation of sound that is processed through devices like amplifiers and speakers.
Amplitude And Power Of An Audio Signal
The amplitude of an audio signal refers to the amount of electrical energy that is carried by the signal. It is the measure of the signal’s strength or loudness and is measured in decibels (dB). The power of an audio signal is the rate at which electrical energy is delivered to a device, and it is measured in watts (W). In the audio world, the power of an audio signal is typically measured in terms of its root mean square (RMS) value.
How Rms Calculates The Amplitude Of An Audio Signal
The RMS value of an audio signal is calculated by averaging the squared values of the signal over a period of time, taking the square root of the result. This calculation results in a value that represents the equivalent AC voltage that would produce the same amount of heat in a resistor as the audio signal power. In simple terms, RMS is a measure of the average power of an audio signal and is used to determine the maximum power that an amplifier can deliver to a speaker without damaging it.
| RMS Calculation Example | |
| Audio Signal Values | Squared Values |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| -1 | 1 |
| 2 | 4 |
| -2 | 4 |
| 3 | 9 |
| -3 | 9 |
For example, if an audio signal has values of 1, -1, 2, -2, 3, and -3, the RMS calculation would be:
- Square each value: 1, 1, 4, 4, 9, and 9.
- Average these squared values: (1+1+4+4+9+9) / 6 = 4.33.
- Calculate the square root of this result: sqrt(4.33) = 2.08.
The resulting value of 2.08 represents the RMS value of the audio signal, which is used to calculate the maximum power an amplifier can deliver to a speaker. By understanding RMS, audio engineers can ensure that their audio signals are properly amplified and reproduce high-quality sound.
Rms Vs. Peak Measurement
RMS or Root Mean Square is a measurement of the average power an audio signal carries. It depicts the effective power of an audio signal over a given time, while peak measurement indicates the highest point of a sound wave.
RMS is an essential factor for measuring audio equipment’s quality and performance accurately.
What Is RMS In Audio World – RMS vs. Peak Measurement When it comes to measuring and analyzing audio signals, there are two types of measurements that are commonly used: root mean square (RMS) and peak. While both measurements have their uses, they are fundamentally different from each other. In this section, we will explore the differences between RMS and peak measurements, the accuracy of peak measurements, and how RMS and peak measurements are used in the audio world. Differences Between RMS and Peak RMS is a type of measurement that represents the average power of an audio signal over a period of time. It takes into account both the positive and negative values of the waveform, making it a more accurate representation of the loudness of the signal. On the other hand, peak measurement simply measures the highest point of the waveform, regardless of the duration of the peak. This means that peak measurements can sometimes be misleading, as a short, high peak may not accurately represent the overall loudness of the signal. Why Peak Measurement is Not Always Accurate Peak measurement is commonly used to measure the maximum level of an audio signal, but it can sometimes be misleading. This is because it only measures the highest point of the waveform, which might not be representative of the overall loudness of the signal. For example, a short, high peak might be followed by a long period of silence, which would not be reflected in the peak measurement. This is where RMS measurement comes in, as it provides a more accurate representation of the overall loudness of the signal. Examples of How RMS and Peak Measurements are Used RMS and peak measurements are used in a variety of applications in the audio world. For example, in music production and mastering, RMS measurement is used to ensure that the overall loudness of a track is consistent, while peak measurement is used to prevent distortion. In live sound reinforcement, peak measurement is used to prevent the sound system from clipping, while RMS measurement is used to ensure that the overall loudness of the sound is appropriate for the venue. In short, both RMS and peak measurements have their uses in the audio world and are essential tools for anyone working with audio signals. In conclusion, understanding the differences between RMS and peak measurements is essential for anyone working with audio signals. While both measurements have their uses, it is important to use the appropriate measurement for the task at hand. Whether you are a musician, sound engineer, or audio enthusiast, knowing how to use these measurements effectively can help you achieve the best results in your work.
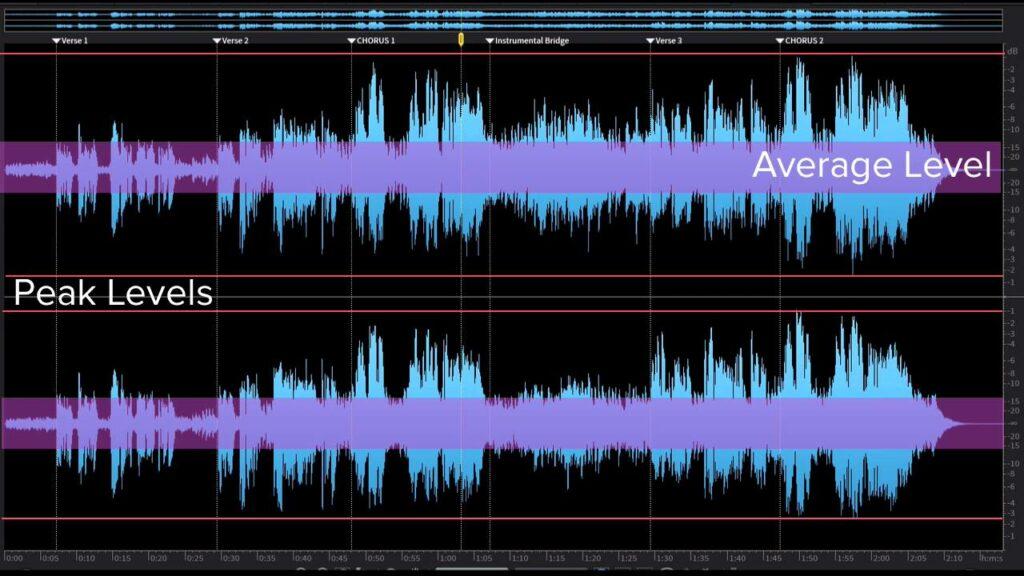
Credit: majormixing.com
Applying Rms In Audio Processing
Root Mean Square (RMS) is a measurement of the average amplitude of a signal. In the audio world, RMS is used to determine the energy level of a sound signal. It is a crucial tool in audio processing and is used for setting audio levels, compression, and measuring loudness. Let’s explore how RMS is applied in audio processing.
Using Rms To Set Audio Levels
Setting audio levels is a crucial element in producing high-quality audio. This is where RMS comes into play. RMS is used to measure the energy level of an audio signal to ensure that the sound is clear. By setting the audio levels using RMS, you can prevent the audio from sounding too loud or too soft, which can be unpleasant for the ears.
How Rms Is Used In Audio Compression
RMS is also used in audio compression to balance the dynamic range of an audio signal. Audio compression is the process of reducing the dynamic range of a sound signal, which makes the quiet parts louder and the loud parts quieter. This is done to make the audio sound more even and consistent. RMS is used in this process to determine the energy level of the signal, which helps the compressor to work more effectively.
Using Rms To Measure Loudness
RMS is also used to measure loudness. Loudness is a subjective measure of how loud a sound seems to be to the human ear. By using RMS, you can measure the energy level of a sound signal, which gives you an indication of how loud the sound will be. This is important in broadcasting and other applications where the sound needs to be consistent and at a predetermined level.
Techniques For Rms Measurement
Root Mean Square (RMS) is a measure of the average power of an audio signal over time and is used to calculate the amplitude of an audio waveform accurately. Measuring the RMS level of a signal is an essential aspect of audio engineering, as it helps in maintaining the quality of audio recordings.
Hardware Vs. Software Rms Measurement
Hardware and software are two primary methods used for measuring RMS. Hardware measuring devices are stand-alone units that come with their own display and built-in software for measuring the RMS values. In contrast, software-based RMS measurement tools are installed on a computer or mobile device and rely on an audio interface or soundcard to capture and analyze the audio signal.
Peak Metering Vs. Rms Metering
Peak metering measures the signal’s instantaneous peak amplitude, while RMS metering calculates the average signal level over time. Although peak metering is useful for identifying clipping or distortion, RMS metering provides a more accurate measurement of the perceived loudness of the signal. Hence it is preferred for mastering tasks.
Best Practices For Accurate Rms Measurement
- Ensure that the audio source used for measurement has a constant volume level.
- Use a calibrated measurement device to ensure accurate results.
- Measure the RMS level of the entire audio signal, rather than a specific part, for better accuracy.
- Set the averaging time to match the audio signal’s duration. A shorter averaging time is appropriate for signals with fast peak levels, while a longer averaging time is suitable for signals with slow dynamics.
The proper use of RMS measurement techniques can ensure that an audio signal’s level is consistent and does not produce unwanted distortion or clipping. Hence, it is essential to use reliable equipment and appropriate techniques to achieve accurate RMS measurements.

Credit: www.reddit.com
Frequently Asked Questions Of What Is Rms In Audio World
What Is A Good Rms Level?
A good RMS level depends on the specific audio application and the desired loudness. In general, a level between -16 and -20 dBFS is commonly used for music, while speech and dialogue usually require a lower level of -23 to -27 dBFS.
It’s important to measure and adjust levels to prevent distortion and ensure the best listening experience.
What Is Rms For Audio?
RMS for audio refers to Root Mean Square, which measures the average power of an audio signal. It is commonly used to determine the loudness of audio and is important for ensuring that audio stays within safe levels that do not cause damage to equipment or the human ear.
Does Higher Rms Mean Louder?
RMS (Root Mean Square) is a measure of the average power of an electrical signal, whereas loudness is a measure of the perceived volume of sound. A higher RMS value does not necessarily mean that the sound is louder. Other factors, such as the efficiency of the speaker and the characteristics of the room, also impact the loudness.
How Much Rms Is Good For Speakers?
The RMS power handling of speakers depends on their type, size, and intended use. Generally, speakers with an RMS of 50-100 watts are good for average home use. However, for larger rooms and louder volumes, speakers with 150W RMS or higher may be needed.
It’s important to match the RMS power of speakers with the output power of the amplifier to avoid damage.
Conclusion
Understanding RMS in audio is crucial to producing high quality sound. RMS is a measurement of the power used by audio equipment to produce sound. It provides a more accurate representation of how loud a sound is, as opposed to peak measurements.
By knowing how to calculate and use RMS, you can ensure that your audio is consistent and professional. Incorporating RMS into your audio setup can help you achieve a true representation of sound and improve the overall quality of your content.