Music publishing is a crucial aspect of the music industry that deals with the administration and management of songs. It involves the acquisition of rights, licensing, royalty collection, and distribution of musical compositions. In this article, we will delve deeper into music publishing and explore how it works.

Credit: www.soundonsound.com
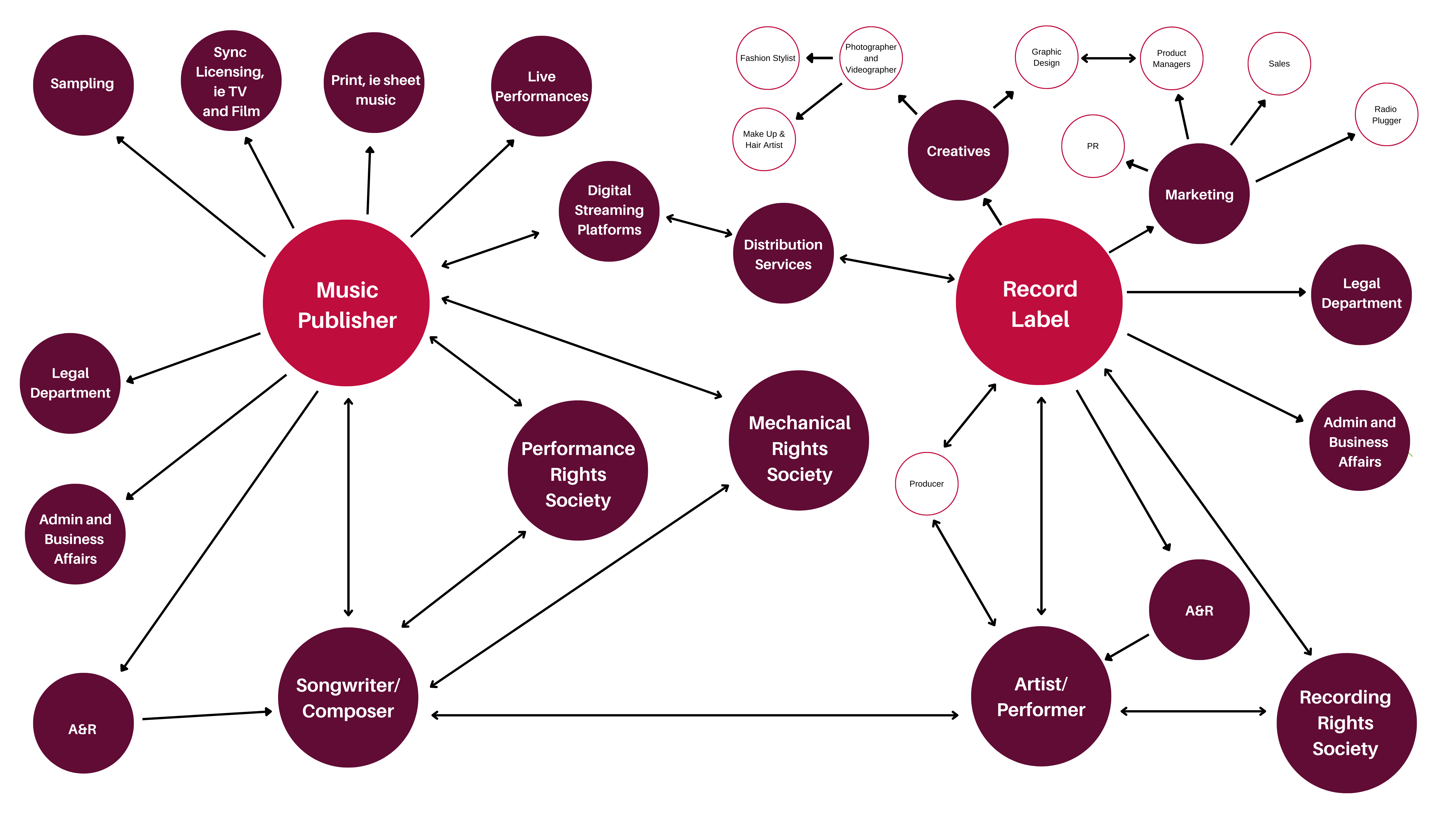
The Role of a Music Publisher
A music publisher serves as the intermediary between songwriters and artists, connecting them with opportunities to generate income from their compositions. Publishers actively promote the work of songwriters by pitching songs to recording artists, film and TV producers, and other media outlets.
Acquiring Music Rights
When a songwriter creates a song, they automatically own the copyright to that composition. However, they can choose to enter into a publishing agreement with a music publisher to handle the administrative tasks and exploit the commercial potential of their work. In exchange, the publisher secures a share of the revenue generated by the song.
Types of Music Publishing Agreements
There are various types of music publishing agreements, including:
- Administration Deals: The songwriter retains ownership of their copyrights but grants the publisher the rights to administer and collect royalties for a specified term.
- Co-publishing Deals: The songwriter and publisher share ownership of the copyrights and split the revenue generated from the exploitation of the composition.
- Sub-publishing Deals: In international markets, publishers often enter into sub-publishing agreements with local publishers, granting them the rights to administer and exploit a composition in a specific territory.
Credit: www.anarapublishing.com
Music Licensing and Royalty Collection
Music publishers play a crucial role in licensing songs for various purposes, such as recordings, synchronization in movies and TV shows, or performances in live venues. They negotiate licensing agreements and collect royalties on behalf of the songwriters.
Revenue Streams for Music Publishers
Music publishers generate revenue from various sources, including:
- Performance Royalties: Earned when a composition is publicly performed, whether on radio, television, or live performances.
- Mechanical Royalties: Generated from the sale or reproduction of a composition, such as digital downloads, CDs, or vinyl records.
- Synchronization Fees: Obtained from licensing songs for use in films, TV shows, commercials, and video games.
- Print Music Income: Accrued from the sale of sheet music and scores.
How Music Publishers Work with Royalty Collection Organizations
Music publishers work closely with performing rights organizations (PROs), such as ASCAP, BMI, and SESAC, to collect performance royalties and ensure that songwriters receive their fair share of the revenue generated by their compositions.
Frequently Asked Questions For What Is Music Publishing And How Does It Work?
What Is The Role Of A Music Publisher In The Music Industry?
A music publisher helps songwriters manage copyrights, collect royalties, and license their music.
How Do Music Publishers Generate Revenue From Songs?
Music publishers earn through licensing and royalties, such as synchronization, performance, and mechanical.
Why Do Musicians Need To Work With Music Publishers?
Musicians collaborate with music publishers to protect their music, secure deals, and maximize earnings.
How Does Music Publishing Benefit Emerging Artists In The Industry?
Music publishing provides emerging artists with opportunities for exposure, guidance, and financial stability.
Conclusion
Music publishing is an essential part of the music industry, providing songwriters with the necessary support and expertise to generate revenue from their compositions. Publishers handle licensing, royalty collection, and promotional efforts, enabling songwriters to focus on their creative endeavors.