Dither is a technique used in digital audio processing to improve sound quality by adding low-level noise. This noise helps reduce distortion and quantization errors in audio signals.
In the world of digital audio processing, dither plays a crucial role in enhancing the quality of sound output. By introducing a controlled amount of noise to the audio signal, dither minimizes the impact of quantization errors that can occur during the conversion of analog signals to digital format.
Understanding the concept of dither and its application in digital audio technology is essential for ensuring high fidelity sound reproduction. Let’s delve deeper into the significance of dither in audio processing and explore how this technique contributes to the overall audio quality.

Credit: fastercapital.com
The Basics Of Dithering
Dithering is a technique used to reduce quantization error in digital audio. Dither adds low-level noise to the signal, improving the overall sound quality. It helps to minimize distortion and create a more natural and pleasant listening experience.
Dithering is a technique used in digital audio and imaging to reduce quantization error and improve quality.What Is Dithering?
Dithering is the process of adding low-level noise to a signal before quantizing it to a lower bit depth.How Dithering Works
1. Dithering helps prevent distortions that can occur when reducing the bit depth. 2. Low-level noise added during dithering masks quantization errors. 3. Noise is carefully controlled to ensure it does not affect the overall quality of the signal. 4. Dithering is essential in maintaining smooth gradations in images and audio. 5. By adding noise, dithering allows for more accurate representation of subtle details. 6. The human ear and eye are less sensitive to random noise than to quantization errors. 7. Dithering is a crucial step in the digital conversion process.Types Of Dithering Algorithms
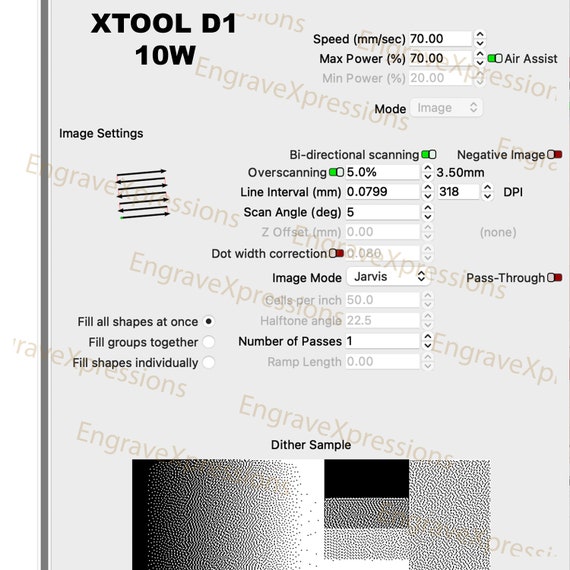
Dithering is a technique used in digital imaging to reduce color banding and improve image quality. There are different types of dithering algorithms that help achieve this. Two popular algorithms include:
Ordered Dithering
Ordered dithering divides the image into a grid pattern and assigns specific colors to each grid cell to simulate additional colors.
Error Diffusion Dithering
Error diffusion dithering distributes color errors from each pixel to neighboring pixels, creating a more visually appealing dithered image.
Applications Of Dithering
Dithering is a technique used in various digital processes to improve the quality of digital images, audio, and printed materials. The applications of dithering are diverse, making it a vital tool in many industries.
Digital Imaging
Dithering plays a crucial role in digital imaging, especially when it comes to reducing the visual artifacts caused by limited color palettes. It helps in creating smooth transitions between colors, making images appear more realistic. By introducing noise, dithering minimizes banding and creates the illusion of additional colors, enhancing the overall visual quality of digital images.
Audio Processing
In audio processing, dithering is used to mask quantization noise, which occurs during the digitization of analog audio signals. By adding low-level noise, dithering reduces distortion and maintains the dynamic range, resulting in a more natural and transparent sound reproduction. It is particularly beneficial when converting high-resolution audio to lower bit depths.
Printing
Dithering is an essential aspect of printing, especially for devices with limited color capabilities such as inkjet and laser printers. By diffusing colors using patterns of dots, dithering enables printers to replicate a broader range of hues, creating the illusion of additional colors and improving the overall print quality. This technique is particularly valuable in producing detailed images and graphics with smoother color transitions.
Advantages And Limitations
Dither is a technique used to reduce quantization errors in digital audio. The advantages include improved audio quality and reduced distortion. However, dither adds a small amount of noise, which may not be desirable in certain situations.
Advantages Of Dithering
Dithering is a technique frequently used in digital images and audio to reduce banding and improve the visual or audio quality, making it an essential tool for professionals. There are several significant advantages to dithering that make it a valuable process in various industries.
Here are some key advantages of dithering:
- Noisy Pattern: Dithering introduces a random, low-level noise pattern to mask the discontinuities in a digital image or audio file. This noise pattern helps to reduce the noticeable color or sound errors. By incorporating this noise pattern, dithering effectively minimizes banding or quantization artifacts that may occur during the conversion process.
- Improved Smoothness: Dithering enhances the overall smoothness and gradient transitions in an image or audio file. By adding slight variations to the visual or audio elements, dithering creates a more pleasing and natural progression between colors or sounds, resulting in a smoother and more realistic output.
- Increased Bit Depth: Dithering allows for a perceived increase in the bit depth of an image or audio file. By distributing the quantization errors across a larger range, dithering effectively increases the apparent resolution and details in the final output, even if the actual bit depth remains the same.
- Preserving Details: Dithering helps in preserving fine details during the quantization process. Instead of losing minute details due to rounding errors, dithering redistributes the errors across adjacent pixels or samples, ensuring crucial details are retained.
Limitations Of Dithering
While dithering offers several advantages, it’s essential to consider its limitations to ensure its appropriate use. Understanding the limitations of dithering helps in determining when and how to apply this technique effectively.
Here are some notable limitations of dithering:
- Increased Noise: Dithering introduces a certain level of noise into the image or audio file. While this noise is often imperceptible, it can become noticeable with certain compression or playback methods that amplify noise. Hence, dithering may not be suitable in situations where noise needs to be minimized, such as in some medical or scientific applications.
- Processing Time: Implementing dithering can increase the processing time for converting or rendering digital files. The randomization and distribution of quantization errors require additional computational resources, especially for large or complex images or audio files. Therefore, it’s important to consider the trade-off between processing time and the desired quality improvement.
- Color or Sound Accuracy: Dithering, while effective in reducing banding, may introduce some loss of color or sound accuracy. The random noise pattern added during the dithering process can slightly alter the original colors or sounds, particularly in highly sensitive applications such as scientific or professional color grading.
Best Practices For Dithering
When it comes to optimizing image quality, dithering plays a crucial role. Dithering is the process of adding noise or patterns to an image in order to reduce banding and create the illusion of more colors than what the image format supports. By strategically applying dithering techniques, you can achieve smoother gradients and enhance the visual appeal of your images. In this section, we will explore the best practices for dithering, including choosing the right technique and optimizing image quality.
Choosing The Right Dithering Technique
There are various dithering techniques available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. It is essential to choose the right technique based on the specific requirements of your image. Here are a few popular dithering techniques to consider:
- Ordered Dithering: This technique uses a pre-defined matrix of threshold values to distribute the error of color quantization. It creates a structured and predictable pattern, ideal for images with a high level of detail.
- Error Diffusion Dithering: Unlike ordered dithering, error diffusion distributes the quantization error across neighboring pixels, resulting in smoother gradients and a more natural appearance.
- Random Dithering: This technique introduces randomness into the dithering process, which can be useful for reducing pattern artifacts and achieving a more organic look.
- Hybrid Dithering: As the name suggests, hybrid dithering combines the strengths of multiple techniques to create a custom dithering algorithm. This approach allows for fine-tuning and achieving the desired outcome.
Optimizing Image Quality
While dithering can enhance the visual appeal of your images, it is important to optimize the image quality to strike a balance between file size and visual fidelity. Here are a few best practices to keep in mind:
- Avoid excessive dithering: Applying too much dithering can result in a noisy and unnatural appearance. Use dithering sparingly and adjust the intensity based on the desired effect.
- Consider image format: Different image formats have varying support for dithering. For example, GIF and PNG-8 are well-suited for dithering, while JPEG and PNG-24 may not offer the same level of support. Choose the appropriate format accordingly.
- Experiment and preview: Dithering can sometimes introduce unexpected artifacts or color shifts. It is important to experiment with different dithering techniques and preview the results to ensure the desired visual outcome is achieved.
- Finalize with compression: After applying dithering, compress the image using appropriate compression techniques to ensure efficient file size without compromising image quality. This will help to reduce bandwidth and improve website load times.
Credit: www.etsy.com

Credit: www.pi-usa.us
Frequently Asked Questions On What Is Dither
What Is Dither And How Does It Work?
Dither is a technique used in digital imaging to reduce color banding and improve image quality. It works by adding random noise to smooth out gradients and create the illusion of more colors. Dithering helps to achieve smoother transitions between colors and make images appear more natural and visually appealing.
Why Is Dithering Important In Digital Graphics?
Dithering plays a crucial role in digital graphics by mitigating the limited color palette of display devices. Without dithering, images with subtle color gradients may appear blocky and suffer from color banding artifacts. By introducing noise, dithering enables smoother color transitions, resulting in better visual representation and avoiding distracting artifacts.
Can Dithering Be Customized For Specific Applications?
Yes, dithering can be customized to suit different applications and requirements. The level of dithering or the amount of noise introduced can be adjusted to achieve a desired effect. For instance, in situations where file size is a concern, minimal dithering may be applied, while high-quality printing may require more sophisticated dithering algorithms for optimal results.
Does Dithering Have Any Drawbacks?
While dithering improves image quality in many cases, it does have some limitations. Dithering adds random noise, which can introduce a grainy texture to the image. Additionally, the dithering process may slightly alter the original colors in order to smooth out gradients.
However, these drawbacks are generally outweighed by the benefits of reducing color banding and enhancing overall visual quality.
Conclusion
Understanding the concept of dither is essential for anyone involved in digital image or audio production. Its ability to reduce distortion and enhance the perception of quality makes it a valuable tool in the modern field. Mastering dithering techniques can lead to significant improvements in the final product’s overall performance and professional appeal.