Dither is a technique used in digital audio processing to prevent distortion or noise. It matters because it can minimize the negative effects of quantization errors in digital audio.
The advancement of technology in recent years has led to remarkable growth in digital audio processing. With the widespread use of digital audio technology, the problem of quantization errors has gained more attention. Dithering is one of the techniques used to reduce the negative impact of quantization errors in digital audio.
We will discuss what dither is, how it works, and why it matters in the world of digital audio. Additionally, we will look at the different types of dithering techniques and their applications. By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of dither and its essential role in digital audio processing.

Credit: www.masteringthemix.com
What Is Dither?
Dither is a process of adding random noise to an audio signal to reduce distortion. It is commonly used in digital audio to improve the quality of sound. Whether it matters or not depends on the specific context and requirements of the audio project.
What is dither? Dither is an image processing technique that is used to minimize or eliminate quantization errors, thereby improving the overall quality of digital images. Essentially, dithering involves adding small amounts of noise to an image to smooth out the transitions between pixels and reduce the appearance of banding. But there’s more to it than that. Let’s explore a clarification on the definition of dither and some examples of dither in action.
A Clarification On The Definition Of Dither
Dither is often described as a process of adding noise to an image to improve its quality. However, this oversimplification can be misleading. Dither does involve adding noise, but it’s not just any noise. The noise is carefully generated and applied in a way that minimizes visual artifacts and improves the overall appearance of the image. Additionally, dither is not a one-size-fits-all solution. The type and amount of dither used will depend on the specific requirements of the image and the context in which it will be used.
Examples Of Dither In Action
To better understand the role of dither in image processing, let’s look at some examples of dither in action.
| A noisy gradient without dither | The same gradient with dither |
In the example above, you can see the effect of dither on a gradient. Without dither, the gradient is blocky and exhibits visible banding. However, adding dither to the image smooths out the transitions between colors and makes the gradient appear much smoother.
Summary
In summary, dither is an image processing technique that involves adding carefully-generated noise to an image to improve its quality. While it may seem counterintuitive to add noise to an image, dither can actually help to smooth out pixel transitions and reduce visual artifacts like banding. By carefully selecting the type and amount of dither applied, you can achieve better-looking images that are better suited for their intended use.

Credit: www.masteringthemix.com
Why Does It Matter?
If you work with audio, you may have come across the term “dither.” Dither is a technique used to reduce quantization errors, which occur when digital audio signals are converted from analog to digital. But why does it matter?
The Problem With Quantization Error
When an analog signal is converted to digital, the signal is divided into a series of binary numbers called “samples.” The samples are then quantized to a specific bit depth, which determines the number of possible values that each sample can have. For example, a 16-bit audio signal has 65,536 possible values per sample.
The problem with quantization is that it can introduce errors into the audio signal. This is because each sample can only have one of a limited number of values, so there will always be some rounding error or “quantization noise” as the signal is converted from analog to digital.
How Dither Reduces Quantization Error
Dither is a technique used to reduce quantization errors by adding a small amount of noise to the signal before quantization. This noise is carefully chosen to be random and uncorrelated with the original audio signal, so it effectively masks the quantization noise and makes it less audible.
The idea behind dither is that by adding a small amount of noise to the signal, the quantization errors become less noticeable to the human ear. This means that the audio signal sounds smoother and more natural, even though it has been digitally processed.
The Audible Difference
So, does dither actually make a noticeable difference? The answer depends on a few factors, such as the bit depth of the audio signal and the dynamic range of the content. In general, dither can help to improve the quality of audio recordings, especially when they are being reduced in bit depth or dynamically compressed.
However, it’s worth noting that dither is not a magic solution that can fix all audio problems. It’s just one tool in the audio engineer’s toolbox, and it should be used judiciously and with knowledge of its effects.
The Science Behind Dithering
Dithering is a technique used to reduce the impact of quantization errors when converting digital signals to analog. It adds random noise to a signal to create a more natural and smoother sound or image. While its impact may not be noticeable to everyone, certain professionals such as audio engineers rely on it for high-quality outputs.
Dithering is the process of adding noise to a signal to mask distortion that can occur during digital processing. While it might sound counterintuitive to add noise to a signal, it’s actually crucial to achieving high-quality audio. The science behind dithering involves a combination of mathematics, physics, and psychoacoustic research.
How Noise Shaping Works
When a signal is encoded to digital, there is a finite number of bits available to represent the signal, resulting in quantizing errors. Noise shaping is a technique that redistributes the quantization error to frequency regions that are less audible to the human ear. Essentially, it shifts the distortion to where it’s less noticeable, creating a more pleasing sound. This technique relies on dithering to be effective.
Different Types Of Dither
There are various types of dither available, including simple dither, shaped dither, and noise-shaped dither. Simple dither is pure noise added to the signal, while shaped dither uses a predetermined pattern of noise that can reduce the audibility of artifacts. Noise-shaped dither is more advanced and utilizes psychoacoustic models to calculate the amount and shape of the noise added to the signal. Each type of dither has its own benefits and drawbacks, and knowing which to use in a particular situation is crucial to achieving optimal results.
When To Use Dithering
Dithering is a technique used in digital audio and visual processing to reduce color banding and distortion. It is mainly used when converting digital signals with a lower bit depth into a higher bit depth, as it adds a small amount of noise that masks any quantization errors caused by the conversion process.
Different Scenarios Where Dither Is Beneficial
Dither is a technique used in digital image processing to minimize distortion and increase the quality of digital audio or visual signals. While dithering is not necessary in every scenario, it is beneficial in some situations. Here are some different scenarios where dithering is beneficial:
- Low-bit Depth Audio: Dithering is used when the final output of the digital audio contains fewer bits than during processing. Examples include 16-bit audio files converted to 8-bit or when a 24-bit audio file is played on a 16-bit playback system.
- Image processing: Dithering can help to minimize the visual artifacts or banding which may appear in images, particularly when the image is encoded with fewer bits than may be needed for high-quality output.
- Video processing: In low bit-rate video, dithering can be used to reduce unwanted visual artifacts in gradients or singular color patches throughout the video.
When Not To Use Dither
While dither is useful in some audio and visual scenarios, it’s not necessary in all circumstances. Dithering is not recommended when:
- Audio recordings are already high-quality, lossless or have enough bits depth for high-resolution output, such as 24-bit audio files or when the production environment is high-end and high quality.
- In video production, dithering should be avoided in high-resolution formats such as 4K when the playback system where it is going to be played is high-end.
- In image processing, dithering should be avoided when the final output is printed and when the image has enough bits depth to render the image with a high resolution.
Conclusion
Dithering is an important technique that can help to improve the quality of digital audio and visual signals. However, it should only be used in certain scenarios and not applied universally. By understanding when dithering is beneficial and when it’s better to avoid, you can optimize the quality of your digital outputs.
Tools For Dithering
Dithering is a technique that adds artificial noise to audio recordings before they get converted into a digital format. The human ear can’t pick up those small variations, but they are essential for creating a high-quality digital sound. Dithering tools ensure that the audio remains clean and consistent, getting rid of any noise or distortion that might distort the sound.
Dither is a technique used to minimize artifacts while converting audio from one bit depth to another. It helps to maintain the sound quality when reducing the bit depth, making it a crucial part of the music industry. There are various tools available for dithering, including software and hardware options.
Software Options For Dithering
There are various software options to choose from when it comes to dithering, each with its unique features. Among the software tools for dithering are Waves L3 Multimaximizer, iZotope Ozone, and FabFilter Pro-L 2. These software tools offer high-quality dithering and allow the user to customize the dithering settings according to their needs.
Hardware Options For Dithering
Hardware options for dithering include standalone units like the Weiss Saracon and the Crane Song HEDD. These units provide high-quality dithering solutions, and some are equipped with advanced features like sample rate conversion. Additionally, some audio interfaces have built-in dithering capabilities, like the Universal Audio Apollo series.
In Conclusion
Dithering is an essential technique in the world of audio engineering, and it ensures that the sound quality remains consistent when converting audio from one bit depth to another. With the software and hardware options available for dithering, audio engineers can choose the best tool that suits their needs and preferences.
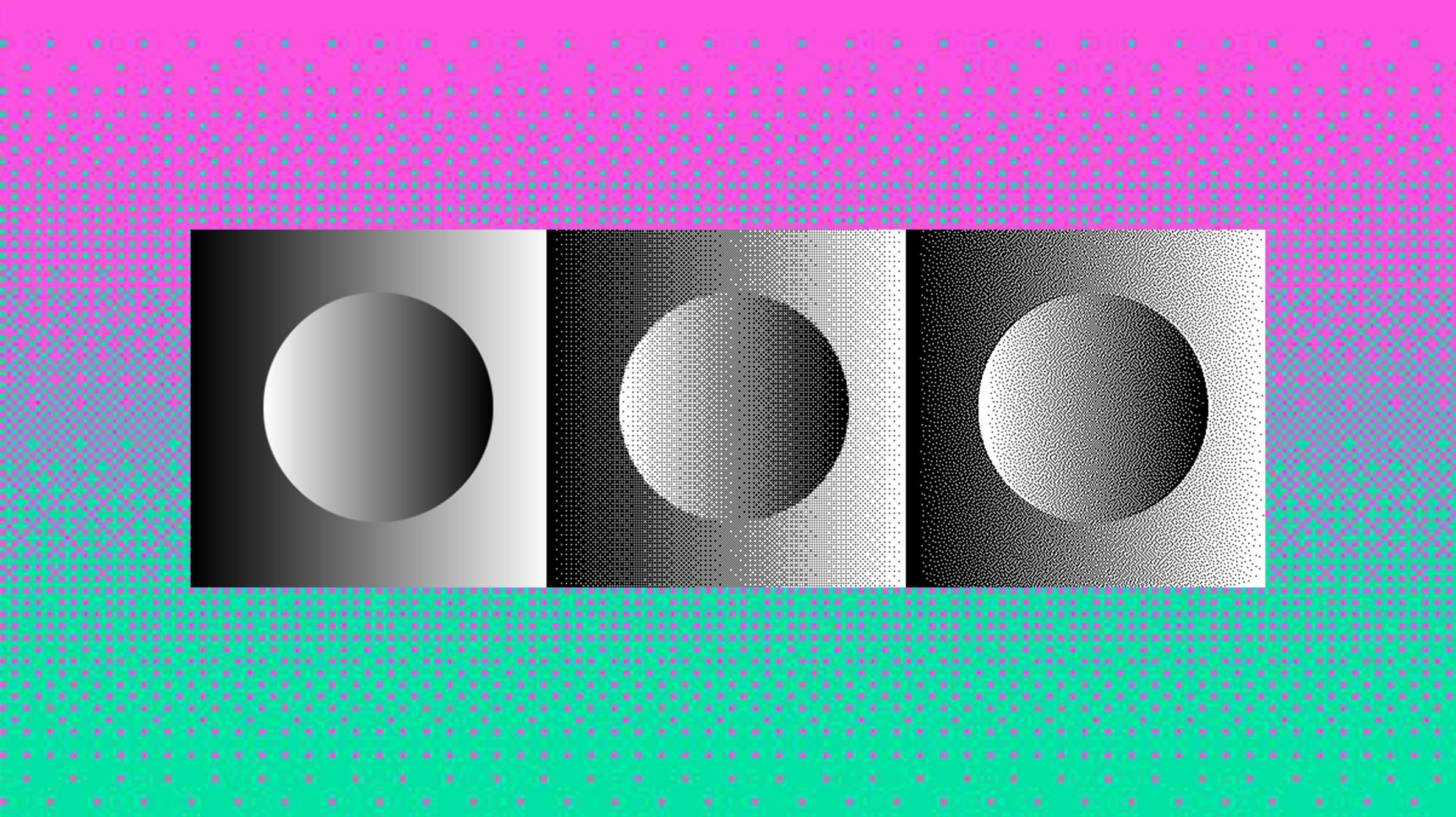
Credit: wavmonopoly.com
Frequently Asked Questions For What Is Dither And Does It Matter
Is It Necessary To Dither?
Dithering is not always necessary but can be used in certain situations. It is a technique used to minimize potential color banding in digital images and music. Dithering adds random noise to smooth out the gradient transition and create a more natural-looking image or sound.
Its use depends on the intended application, such as high-quality photography or music production.
Does Dithering Make A Difference?
Dithering can make a difference in certain situations. It helps to reduce color banding and produces smooth tonal transitions. However, in some cases, it may not be necessary or noticeable, especially on high-quality displays.
Does Dithering Improve Quality?
Yes, dithering can improve the quality of images and audio. It adds noise to the signal which reduces the noticeable effects of some types of errors, leading to smoother and more accurate reproduction.
What Is Dithering And Why Is It Important?
Dithering is the process of adding noise to a digital signal to improve its overall quality. It’s important in digital audio, photography and video to minimize color banding and distortion. By adding random noise, dithering can improve the accuracy and smoothness of gradients and fine details in a digital file, resulting in a higher-quality end product.
Conclusion
To conclude, dither is an essential technique that is used to minimize the distortion of digital signals at low amplitudes. It works by adding random noise to the signal, which helps to create the illusion of higher precision. While it may not be necessary for everyday use, dither is crucial when it comes to high-quality audio or visual work.
So, the next time you’re working on a project that requires top-notch quality, make sure to keep dither in mind.