Analog warmth refers to the pleasant, natural sound produced by analog equipment, while harmonic distortion is the intentional introduction of subtle distortion to audio signals to enhance their character and warmth. These techniques are commonly used in audio production and are sought after by many enthusiasts who prefer the warmer, richer sounds produced by analog technology.
The use of harmonic distortion can also help to overcome the often sterile and digital-sounding audio produced by modern equipment, giving recordings a more natural, organic feel. We will explore the concept of analog warmth and harmonic distortion, discussing how they are achieved, what effects they have on sound quality, and how they are commonly used in audio production.
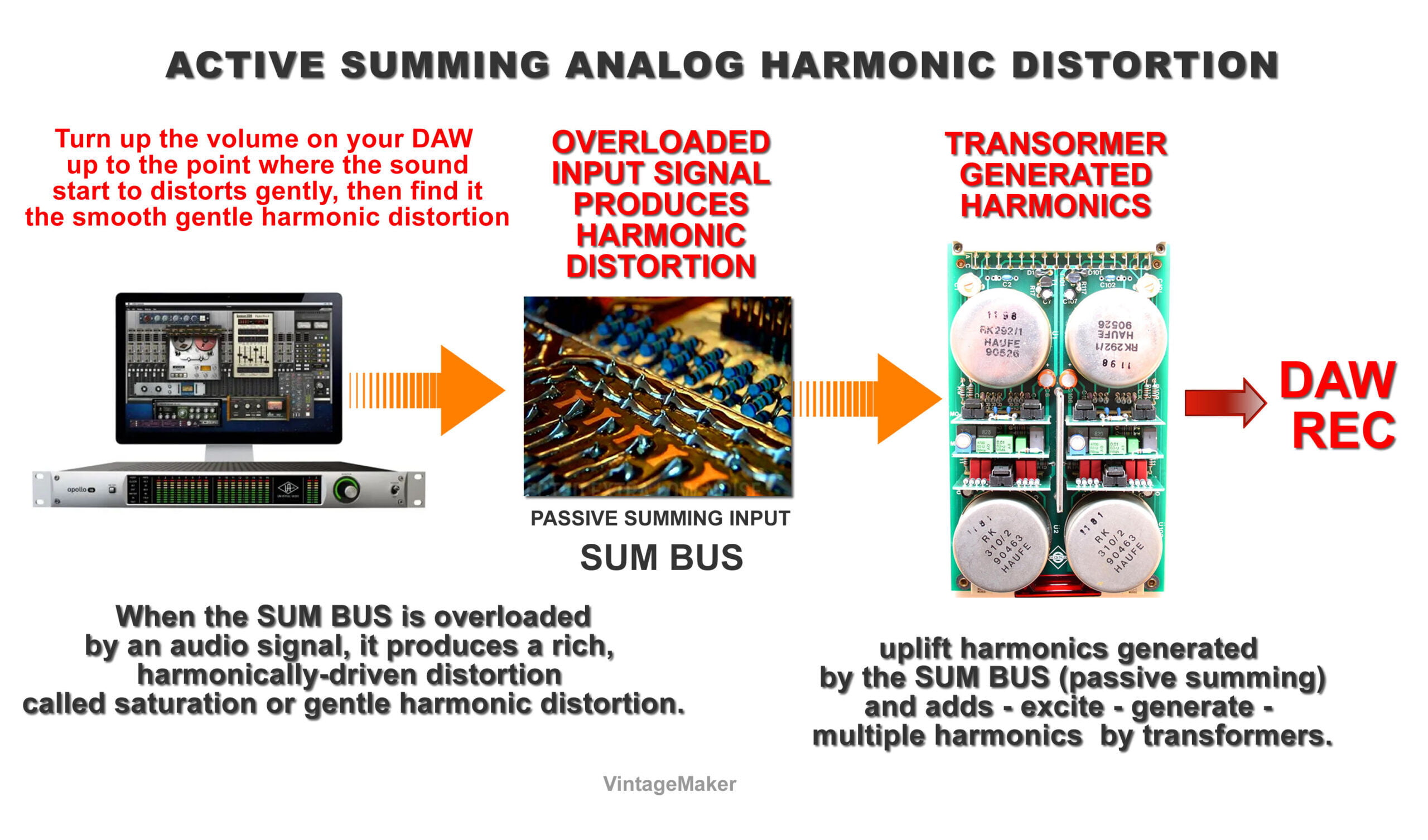
Credit: vintagemaker.net
What Is Analog Warmth?
Analog warmth refers to the pleasing sound qualities produced by older analog audio equipment. This type of sound is characterized by a subtle distortion known as harmonic distortion, which adds richness and fullness to the sound.
Analog warmth is a term frequently used in music production but what does it actually mean? If you are one of those who are curious to learn about it, then you have come to the right place! In this article, we will discuss the definition, explanation, and examples of analog warmth. Let’s dive into it, shall we?
Definition And Explanation Of Analog Warmth
In simple terms, analog warmth refers to the pleasing sound quality produced by analog audio equipment. Analog equipment, unlike digital, adds a slight distortion to the audio signal that can be perceived as warm, rich, and full-bodied. The distortion is caused due to various factors such as harmonics, noise, and other imperfections in the circuitry of the analog equipment. This distortion creates a pleasant sound quality that is often favored by music producers and audiophiles for its unique character and warmth.
Examples Of Analog Warmth In Music Production
Analog warmth can be found in various genres of music from classic rock to modern pop. This pleasing sound quality can be achieved through the use of analog equipment such as vintage tube amplifiers, reel-to-reel tape machines, and analog mixing consoles. Here are some examples of how analog warmth can be heard in music production:
- The slight distortion in the guitar solo of Led Zeppelin’s “Stairway to Heaven”
- The full-bodied sound of the kick drum in Michael Jackson’s “Billie Jean”
- The tape hiss and warmth of the vocals in The Beatles’ “Come Together”
In conclusion, analog warmth is a unique sound quality that can be achieved through the use of analog equipment. This pleasing distortion adds character and richness to the audio signal and is often favored by music producers and audiophiles.
Introduction To Harmonic Distortion
Harmonic distortion is an audio effect that gives analog warmth to music. It occurs when additional frequencies are introduced into the sound, creating a warmer, smoother tone. Harmonic distortion is often used in music production to add character and depth to recordings.
Harmonic distortion is an effect that is highly desired by music producers, especially when it comes to mixing and mastering audio tracks. In simple words, it’s an audio effect that occurs when the music signal passes through an amplifier or sound processor, and the resulting audio output contains harmonics that are not found in the original signal. This effect, when done correctly, can add warmth and character to the music, which is commonly referred to as ‘analog warmth’. This article will explore the types of harmonic distortion, examples of harmonic distortion in music production and an explanation of harmonic distortion.
Explanation Of Harmonic Distortion
Harmonic distortion happens when a non-linear device, such as an amplifier or processor, is applied in an audio signal chain. It occurs because the device amplifies or modifies the input signal disproportionately.The amount of harmonic distortion increases when the input signal’s amplitude strengthens, resulting in the distortion of the original signal. The resulting signal contains harmonics that were not present in the original signal. These harmonics can be odd or even and are multiples of the fundamental frequencies present in the original signal.
Types Of Harmonic Distortion
There are several types of harmonic distortion that audio engineers commonly use:
| Type of Harmonic Distortion | Description |
|---|---|
| Odd Order Harmonics | Harmonics that are presented in odd multiples of the fundamental frequencies. |
| Even Order Harmonics | Harmonics that are presented in even multiples of the fundamental frequencies. |
| Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) | The total measure of harmonic distortion that includes both odd and even harmonics of the original signal. |
Examples Of Harmonic Distortion In Music Production
Harmonic distortion is extensively used in music production to add character and warmth to the music. The following are some examples of harmonic distortion applications in music production:
- Overdriving guitar amps to create desirable harmonics, widely found in rock music.
- Distorting vocal on a chorus to add a bit of grit needed to cut through the mix.
- Artificially introducing distortion in synthesizer patches to add richness and movement to the sound.
In conclusion, harmonic distortion is the unique sound produced by nonlinear devices that contain harmonics that are not present in the original signal. This effect is highly desirable in music production, as it adds a unique warmth and character to the music. Distortion should be used correctly and judiciously to achieve the desired effect, as the excessive use can lead to harsh results.
Frequently Asked Questions Of What Is Analog Warmth Introduction To Harmonic Distortion
What Is Analogue Warmth?
Analogue warmth refers to the unique and natural sound that is created when audio is processed or recorded using analogue equipment instead of digital. This is due to the subtle distortions and imperfections in the analogue signal that can add depth and character to the sound.
It is especially preferred by audio professionals in music production to achieve a more authentic and warmer sound.
What Is Analogue Distortion?
Analogue distortion is a type of sound distortion that occurs in analogue audio signals. It can create warm, gritty, or fuzzy effects in audio recordings, but can also produce unwanted noise and distortion. This is different from digital distortion which occurs in digital audio signals.
What Is Analog Sound In Music?
Analog sound in music refers to the sounds that were recorded or produced using non-digital methods. It involves capturing sound waves directly onto physical media, such as vinyl records, cassette tapes, or reel-to-reel tapes. Analog sound tends to have a warmer, richer, and more natural sound compared to digital recordings.
What Level Of Thd Is Audible?
The level of Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) that is audible varies depending on the application. Generally, THD below 1% is perceived as clean and distortion-free in audio systems. However, sensitive listeners can detect THD levels as low as 0. 1%.
The higher the THD value, the more audible the distortion will be.
Conclusion
Analog warmth and harmonic distortion have become buzzwords in the music industry, and for good reason. These concepts can significantly impact the overall sound quality of your recordings. By understanding how they work and utilizing them in your production process, you can achieve a more natural, warm, and organic sound that listeners will love.
Incorporating analog warmth and harmonic distortion into your music production is not just a trend, it’s becoming a necessity for artists looking to stand out in the digital age.