Vocal Eq compression enhances the quality of vocals by balancing loudness and reducing dynamic range. This technique minimizes inconsistencies in vocal performance and results in a polished, professional sound.
Vocal EQ compression is a popular audio engineering technique used to improve the quality and clarity of recorded vocals. By using a combination of equalization and compression, sound engineers and producers can balance the loudness and reduce the dynamic range of a vocal track.
This process helps to minimize any inconsistencies in the vocal performance, resulting in a polished and professional sound. EQ compression can be used to add warmth, depth, and character to a vocal recording and is an essential tool for any audio professional. We’ll delve deeper into vocal EQ compression and discover how this technique can help you achieve a better-sounding recording.
Understanding Vocal Eq
Vocal EQ compression is an essential technique for enhancing the quality of recorded vocals. By balancing the frequencies and dynamics of the vocal track, you can achieve a polished, professional sound that stands out in any mix. With the right equipment and a good ear, anyone can learn how to use EQ compression effectively.
Understanding Vocal EQ Vocal EQ is an essential aspect of music production, which involves tweaking the frequency of the recorded vocals to enhance clarity, intelligibility, and tone. It helps to balance the sound and make the vocals sit perfectly in a mix. Vocal EQ can help remove unwanted frequencies, add presence and warmth, or shape the timbre of the singer’s voice to achieve the desired effect. In this post, we’ll discuss what vocal EQ is, its importance in music production, and how to use it effectively. Defining Vocal EQ In music production, EQ stands for equalization, which is a tool used to adjust the volume of individual frequencies in an audio signal. Vocal EQ refers to the process of using an equalizer to alter specific frequencies in the range of a human voice. For instance, boosting the mid-range frequencies of a vocal track can help bring out the clarity and detail in the vocals. Similarly, cutting out the low frequencies can remove rumble and other unwanted noises in the recording. Importance of Vocal EQ in Music Production Vocal EQ is crucial in music production because it helps to enhance the quality of the vocals and make them stand out in the mix. Proper EQ can provide the necessary balance and separation between different elements of the track and contribute to the overall clarity and intelligibility of the mix. When vocals are not well EQ’d, they can sound muffled, muddy, or lost in the mix, thus affecting the overall quality of the track. Using Vocal EQ for Tonal Shaping Vocal EQ can also be used for tonal shaping, which involves fine-tuning the frequency response of a singer’s voice to achieve the desired effect. For instance, boosting the high frequencies can add airiness and brightness to the vocals, while attenuating the mid-range can create a warm, silky tone. Conversely, a drastic cut in the high frequencies can create a dull, muted sound, while boosting the low-end can add depth and body to the vocals. Conclusion In conclusion, vocal EQ is an essential tool in music production, which can help enhance the quality of the vocals and make them sit perfectly in the mix. By understanding the basics of vocal EQ, you can achieve more significant control over the frequency response of a singer’s voice and create more professional-sounding tracks. Remember that each voice is unique, and finding the right EQ settings may take some experimentation. Practice, listen, and adjust until you find the perfect vocal EQ for your project.

Credit: www.audio-issues.com
Types Of Vocal Eq
Equalization, or EQ for short, is a valuable tool when it comes to tweaking the sound of vocals. By adjusting the balance between different frequency ranges, you can add warmth, clarity, and depth to a recording. There are three main types of EQ used with vocals: graphic EQ, parametric EQ, and dynamic EQ. Each of these types of EQ has its own strengths and weaknesses, so let’s explore them in more detail.
Graphic Eq
Graphic EQ is perhaps the most well-known type of equalizer. It displays a set of fixed frequency bands, typically ranging from around 20 Hz to 20 kHz, on a visual graph. Each band can be adjusted individually, allowing you to boost or cut a specific range of frequencies. Graphic EQ is particularly useful when you need to tackle broad tonal issues, such as removing unwanted low-end rumble or taming harsh high frequencies.
Parametric Eq
With parametric EQ, you have more control over which frequencies you adjust and how you adjust them. Instead of preset frequency bands, parametric EQ lets you set the center frequency, bandwidth, and gain of each individual filter. This level of precision makes it ideal for fine-tuning the vocal sound. You can isolate and boost specific harmonics, notch out resonances, or shape the overall tone in subtle ways. Parametric EQ can also help you combat issues such as sibilance or boomyness.
Dynamic Eq
While graphic and parametric EQ can help shape the tone of a sound, dynamic EQ can help control the level of individual frequencies. Using a dynamic EQ, you can set a threshold and ratio as you would with a compressor, but instead of compressing the entire signal, you only compress the specific frequency ranges that exceed the threshold. This can be helpful for taming harsh notes or controlling vocals that are too resonant. Dynamic EQ can also be used to add presence or sparkle to a vocal by boosting certain frequencies when they are not prominent enough.
Tips For Vocal Eq
Achieving the perfect vocal EQ is crucial for producing quality music. When it comes to vocal EQ compression, it’s important to find the right balance between keeping the vocals upfront and preventing harshness or sibilance. Proper use of EQ can add warmth and definition to a vocal performance.
When it comes to mixing vocals, achieving a balanced sound can be a challenge. But with the right EQ settings, you can improve the clarity, tone and presence of the vocals in your mix. Here are some essential tips for Vocal EQ that can make a big difference to your mixes.
Identifying The Problem Frequencies
One of the most crucial steps in vocal EQ is identifying the problematic frequencies. Analyze the vocal track and identify the frequencies that make it sound muddy, too bright or harsh. Use frequency analyzer plugins to help you identify the frequencies causing issues in the vocal track.
Using High-pass Filter To Reduce Muddiness
Muddiness is a common problem in vocal recordings, and high-pass filtering is an effective solution to tackle this issue. Set the high-pass filter around 100 Hz, and gradually increase until the muddiness is gone. Be careful not to remove too many low-end frequencies, which can result in a thin-sounding vocal.
Using Low-pass Filter To Control Harshness
If your vocal track sounds harsh or sibilant, you can use a low-pass filter to control the high-end frequencies. Set the low-pass filter around 8 kHz and adjust until the harshness is reduced. Be careful not to cut too much high-end, which can result in a dull vocal sound.
Cutting And Boosting Specific Frequencies
Cutting and boosting specific frequencies can help you achieve a well-balanced vocal sound. Cut the frequencies that are causing issues in the vocal track, and boost the frequencies that need more emphasis. Use a narrow Q setting to avoid affecting surrounding frequencies. In conclusion, by following these tips for Vocal EQ, you can achieve a smooth, balanced and clear vocal sound in your mixes. Remember, it’s essential to approach vocal EQ with a critical ear, patience, and attention to detail to achieve the desired results.
Types Of Vocal Compression
Vocal Eq compression involves adjusting the levels of different frequency ranges in a singer’s voice, enabling the vocal performance to sound more balanced. Eq compression is instrumental to cut through robust mixes while maintaining clarity, preserving the vocals at the mix’s forefront.
Types of Vocal Compression Compression is one of the most used techniques in music production, and it’s essential to understand the different types of vocal compressions available. Depending on the type of compressor, you’ll get different responses and varying degrees of control over the sound. In this section, we’ll discuss the three main types of vocal compressions: Optical Compression, VCA Compression, and FET Compression. Optical Compression Optical compressors use a light-dependent resistor (LDR) to control the gain reduction of the signal. They’re known for their smooth, transparent sound and are popular for gently taming vocal dynamics. Optical compressors are ideal for adding warmth and character to a vocal without altering its tone. They’re easy to use, and many of them feature a single knob that controls the amount of compression applied. VCA Compression Voltage-controlled amplifiers (VCAs) are the backbone of most compressors, and they’re found in digital, analog, and hardware units. VCA compressors are known for their accuracy and fast response times, making them ideal for controlling loud and percussive vocals. They’re also known for their transparent sound, which makes them ideal for subtle compression adjustments. VCA compressors have several controls, including ratio, threshold, attack, release, and makeup gain. FET Compression Field-effect transistor (FET) compressors use a FET to control the gain reduction of the signal. They’re popular for their aggressive, upfront sound, and are ideal for adding punch and character to vocals. FET compressors have a fast attack time, which helps capture the initial transient of a vocal. They’re also known for their warm, vintage character and are often used on rock and pop vocals. FET compressors typically have controls for ratio, threshold, attack, release, and makeup gain. In conclusion, understanding the different types of vocal compressions available is essential for achieving the desired sound. Each type of compressor has its unique characteristics and applications, and choosing the right one will depend on the vocal performance and the desired result. Whether you go for the smooth, transparent sound of an optical compressor, the accuracy of a VCA compressor, or the aggression of an FET compressor, your vocals will benefit greatly from the right type of compression.
Tips For Vocal Compression
Achieving the perfect vocal sound can be a challenge, but using vocal EQ compression can help. Start by setting a low ratio and applying gentle compression, then adjust the attack and release times to smooth out the vocal.
vocal EQ compression to enhance the quality of your recordings. In this post, we’ll focus on some essential tips for vocal compression, including controlling dynamics, avoiding over-compression, and using sidechain compression for optimal vocal clarity.
Using Compression To Control Dynamics
Compression helps in controlling the dynamics of vocals, which is critical for a polished sound. One of the best ways to achieve this is by using a low ratio compression setting. This is because a lower ratio setting offers a gentle compression effect, which leaves the overall dynamic range more intact.
Avoiding Over-compression
When compressing vocals, it’s essential to avoid over-compression. When too much compression is applied, vocals can sound too compressed and lose clarity. As a general rule, keep your compression settings to a maximum of 4:1. You can also use the output gain control to balance the overall sound.
Using Sidechain Compression For Vocal Clarity
sidechain compression. This technique helps to reduce competing frequencies and brings clarity to the vocal. You can do this by routing a copy of the vocal track to the compressor’s sidechain input. From there, set the compressor’s threshold to the competing frequency’s level to achieve optimal clarity. In conclusion, vocal compression is a crucial technique for enhancing the quality of your recordings. By following these tips, you can effectively control the dynamics, avoid over-compression, and use sidechain compression to bring clarity to your vocals.
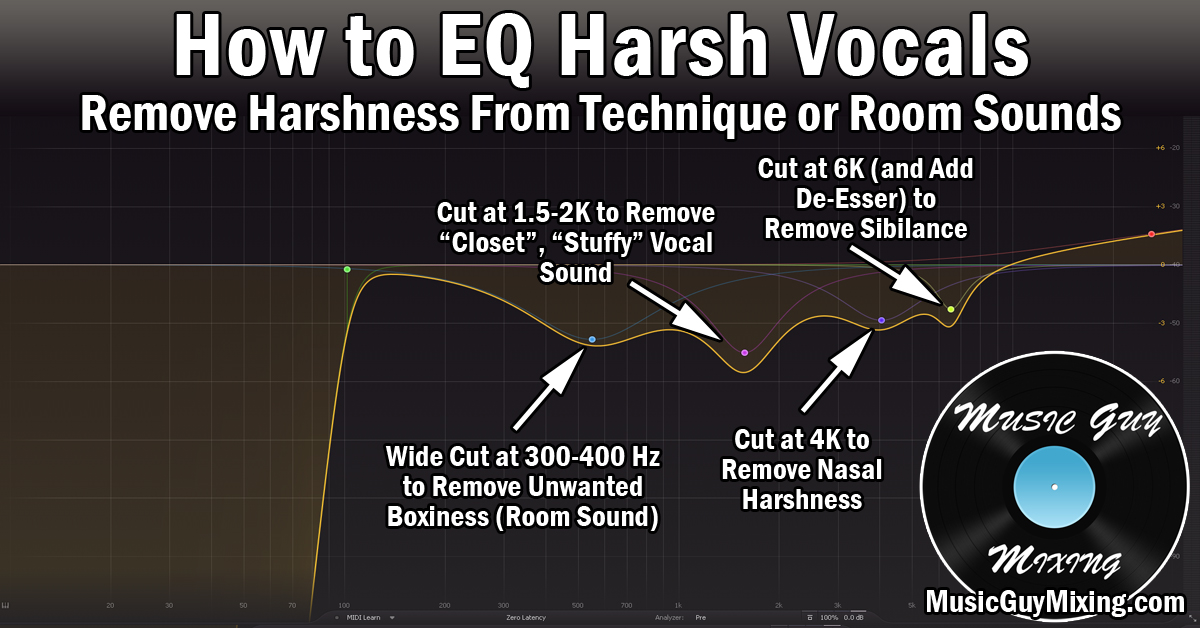
Credit: www.musicguymixing.com

Credit: www.youtube.com
Frequently Asked Questions On Vocal Eq Compression
How Do I Compress And Eq Vocals?
To compress and EQ vocals, use a dynamic processor and an equalizer. First, use compression to reduce the dynamic range and even out the volume. Then, use EQ to shape the frequency response and smooth out any harshness or sibilance.
Experiment until you find the right settings for the desired effect.
Should You Eq Vocals Before Compression?
Yes, it is recommended to EQ vocals before compression. This helps to eliminate unwanted frequencies and enhance the desired ones, resulting in a cleaner and more professional sound. EQing after compression can alter the overall balance and affect the dynamic range of the vocals.
What Is The Best Setting For Vocal Compression?
The best setting for vocal compression depends on the recording quality, desired sound, and genre of music. Generally, a ratio of 2:1 to 4:1, attack time of 5-10ms, and release time of 80-100ms work well. Adjust the threshold until the vocal sounds consistent and clear in the mix.
How Much Compression Should I Use On Vocals?
The amount of compression to use on vocals depends on the song and desired effect. Generally, gentle compression is recommended to deal with minor fluctuations in vocal volume. More compression can be used for a “squashed” effect, but be careful not to overdo it and lose the natural dynamic range of the singer’s performance.
It’s important to experiment and find a balance that works for each specific track.
Conclusion
Achieving the perfect vocal sound is a complex art to master, but utilizing the right vocal EQ compression techniques can make all the difference. By using the correct settings and experimenting with different techniques, you can help to enhance the clarity, depth, and overall quality of vocals in your recording.
It’s important to remember that every voice is unique, so it’s essential to tailor your vocal EQ compression to the individual artist to maximize their vocal potential. With dedication and practice, you can unlock the full potential of your vocal tracks.