Understanding and mastering EQ balancing involves carefully adjusting the frequency spectrum to achieve a well-rounded sound. In other words, it’s finding the perfect balance between bass, mid-range, and treble to create a pleasant listening experience.
EQ balancing is crucial for any music producer or sound engineer, as it can make or break a song’s overall sound quality. A balanced frequency spectrum can improve the clarity, depth, and overall tonality of any piece of music. We’ll take a closer look at mastering EQ balancing and explore some techniques to help you achieve a balanced sound in your productions.

Credit: www.masteringthemix.com
The Basics Of Eq
The Basics of EQ are crucial to mastering audio mixing. EQ, or equalization, is the process of adjusting the balance between frequencies within an audio signal. This process is essential in achieving a balanced and well-rounded sound for your audio project. Proper EQing offers a distinct advantage in making your music, podcast, or video production sound more polished and professional.
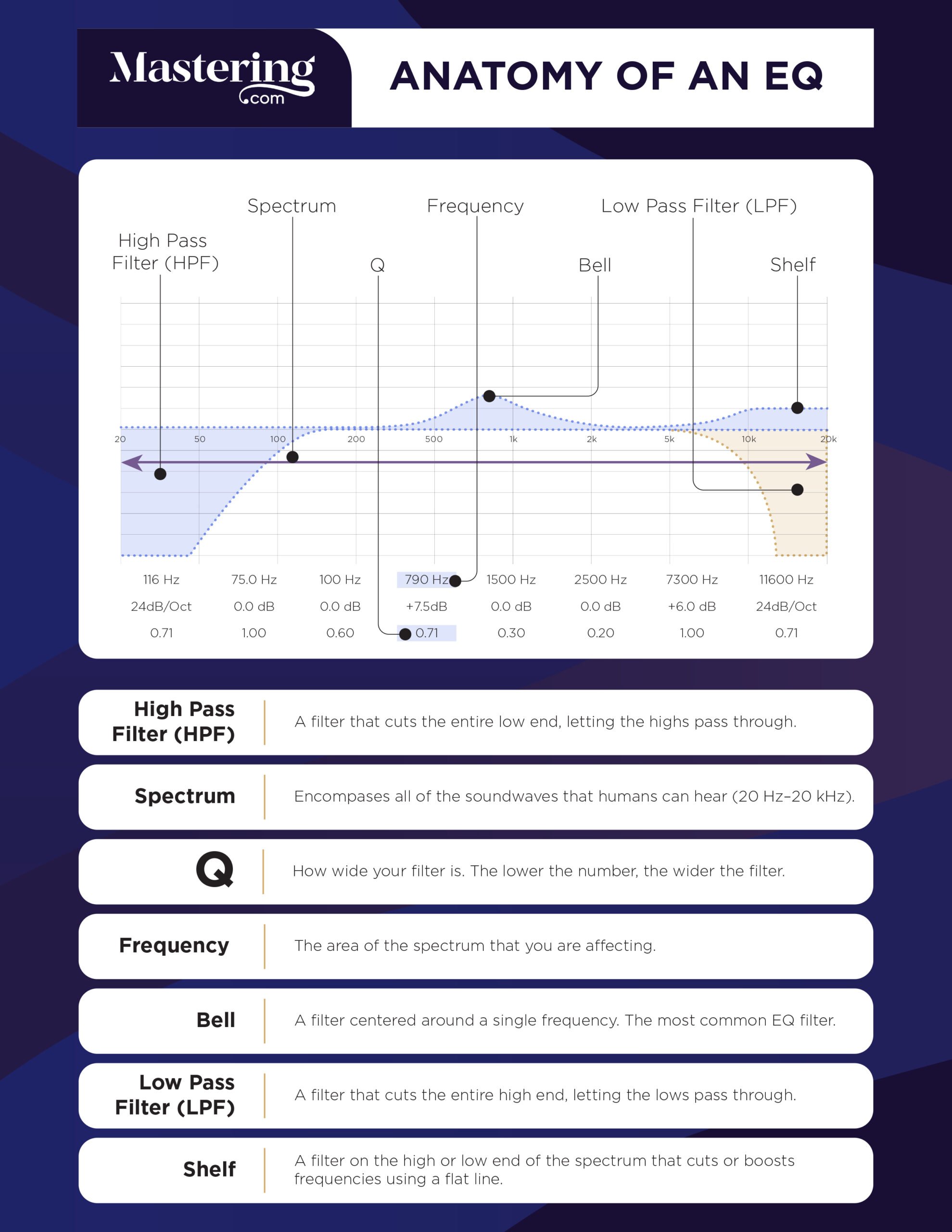
Frequency Spectrum
The Frequency Spectrum is a range of frequencies that are audible or perceptible to the human ear. The audible frequency spectrum ranges from 20Hz to 20kHz. Understanding this spectrum is essential in mastering musical production and being able to create balanced sound profiles for any project. A standard EQ interface provides you with the visual representation of these frequencies split into bands, each with its own range of frequencies.
Types Of Eqs
When it comes to EQs, there are two fundamental types – graphic EQ and parametric EQ. Graphic EQ works by providing preset frequency bands that can be raised or lowered. On the other hand, a parametric EQ allows you to change different aspects of the EQ, such as center frequency and bandwidth.
Common Frequency Ranges
One of the most important aspects of understanding EQ is being able to recognize common frequency ranges. Here are some of the most used frequency ranges:
| Frequency (Hz) | Range | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 20Hz – 100Hz | Sub-bass | Lowest bass notes present in music, felt more than heard. |
| 100Hz – 250Hz | Bass | Low-end frequencies; the bass notes that provide a foundation. |
| 250Hz – 500Hz | Low mids | The range where instruments with low midrange tones sit. |
| 500Hz – 2kHz | Mids | The frequency range in which clarity and presence lie. |
| 2kHz – 4kHz | Upper mids | The part of the spectrum where sounds become more clear and sharp. |
| 4kHz – 6kHz | Presence | The range in which vocals and melodic instruments naturally sit. |
| 6kHz – 20kHz | Brilliance | High-end frequencies, responsible for sparkle and clarity. |
Understanding the basics of EQing and how to balance the frequency spectrum is critical to creating a well-rounded and professional-sounding audio project. Mastering EQing is an ongoing process and an art form that requires a lot of practice and dedication. But, once you gain a deep understanding of how EQ works, you’ll be able to create audio that’s not only well-balanced but also has a particularly distinctive sound.
Credit: mastering.com
Mastering Eq Techniques
Boost your music production skills with mastering EQ techniques, which involve understanding how to balance the sound spectrum. From boosting individual frequencies to taming harsh sounds, mastering EQ techniques are essential for achieving a polished and professional sound.
Gain Staging
Gain staging is an essential technique in mastering EQ. It involves setting the input levels of each plugin in the signal chain to avoid distortion and optimize the signal-to-noise ratio. Proper gain staging ensures the volume levels are consistent throughout the mixing process, enabling a clear understanding of the EQ balance and preserving the integrity of the audio signal.
Filters
Using filters is a practical mastering EQ technique for removing unwanted frequencies from audio signals. Different types of filters, including low-pass, high-pass, and bandpass filters, can be used to adjust tonal balance better. Mastering engineers can remove unwanted artifacts resulting from the mixing process and other noise with these filters. It’s essential to use filters carefully when mastering; otherwise, you risk removing too many frequencies from the signal, resulting in a dull or lifeless sound.
Multi-band Eqs
Multi-band EQs are tools that can be used to control specific frequencies. They divide the sound spectrum into various frequency ranges, allowing the mastering engineer to adjust each band separately. By doing so, multi-band EQs enable more precise control over the tonal balance of a mix, which can help to bring out specific elements in the music. When using multi-band EQs, it’s crucial to avoid overdoing it as it may change the feel of the original mix.
Putting It All Together
Mastering EQ techniques come together to balance the spectrum of sound. Proper gain staging, filter application, and multi-band EQ adjustments can help to optimize the overall sound quality, adding clarity, and helping individual instruments cut through the mix. By using each technique correctly in mastering, you can take a mix to a professional standard that sounds great across different systems.
Tips For Mastering Eq
Balancing the spectrum with mastering EQ is essential for professional audio production. Understanding the different frequencies and how to adjust them is key to achieving a balanced sound. With practice and experimentation, you can master EQ and enhance the overall quality of your audio.
Mastering EQ (equalization) is one of the most crucial steps in music production, responsible for balancing the different frequencies of a track. While it can seem daunting for beginners, with the right approach, mastering EQ can be a breeze. Below are a few tips to help you master EQ balancing the spectrum effectively.
Using Reference Tracks
Using reference tracks is a great way to learn EQ balancing. A reference track is a professional track in the same genre as the track you’re working on. By comparing your mix to the reference track, you can identify areas where your mix may need some EQ adjustments. It helps you to improve your EQ balancing and achieve a clean, balanced mix.
Avoiding Over-eqing
One common mistake that beginners make is over-EQing. While EQ is an essential tool to bring out the best in your mix, overusing it can quickly ruin your track. When you use too much EQ, it can create phase problems and distort the sound. EQ is meant to be used sparingly, you should only cut or boost frequencies that need adjusting. Always take breaks while working on your track to avoid ear fatigue that leads to over-EQing.
Working In Context
Another crucial tip when mastering EQ is to work in context. Working in context means EQ’ing your track within the context of the whole song. You should EQ while listening to the entire track instead of an individual instrument. You’ll need to be aware of the different parts of the song and how they interact. This way, you can make informed decisions about where to make cuts and boosts with EQ to improve the sound of your mix. In conclusion, mastering EQ is critical to achieving a well-balanced mix. Using reference tracks, avoiding over-EQing, and working in context are essential tips to help you master EQ balancing the spectrum. With practice, you’ll develop a keen ear for EQ, and balancing the different frequencies of your mix will become second nature.
Eq Balancing In Different Genres
Achieving EQ balance is crucial when mastering audio in different music genres. Understanding how to balance the spectrum for each genre ensures that every instrument and vocal is heard clearly, resulting in a professional and polished finish.
When it comes to mastering the art of EQ balancing, it’s important to note that different music genres require different approaches. Rock/metal, hip hop/R&B, and electronic music all have distinct sound characteristics that should be considered when balancing the spectrum. Let us explore each genre’s specific EQ nuances to get a better understanding.
Rock/metal
Rock and metal music are characterized by heavy bass, guitar riffs, and powerful drums. When balancing the EQ for these genres, it’s crucial to have a clear mix. EQ can help to bring out the unique sound of each instrument without overloading the mix. In general, the guitar and bass should occupy the low-end spectrum, while the vocals and cymbals should occupy the high-end spectrum. For example:
- Bass guitar: 100-800Hz
- Electric guitar: 800Hz-6kHz
- Vocals: 800Hz-6kHz
- Cymbals: 6kHz-20kHz
Hip Hop/rb
When balancing EQ in hip hop and R&B, it’s essential to achieve a full, warm sound. The bass and drums play a crucial role in defining the overall sound of the genre, along with vocals. Hip hop and R&B vocals generally occupy the lower spectrum, with the kick and bass occupying the low-end frequencies. For example:
- Bass: 20-60Hz
- Kick drum: 80-150Hz
- Snare drum: 100-250Hz
- Vocals: 100-250Hz
Electronic Music
Electronic music is all about creating a unique sonic experience, with a mix of synthesized sounds and samples. When EQ balancing electronic music, it is crucial to remember that a heavy, overpowering bass can quickly overwhelm the mix. The key is to balance the kick and bass with the high-end spectrum, which includes lead sounds, pads, and vocals. For example:
- Bass: 60-250Hz
- Kick drum: 80-150Hz
- Snare drum: 100-250Hz
- Lead sound: 800Hz-6kHz
- Pads: 1kHz-6kHz
- Vocals: 1kHz-6kHz
In conclusion, mastering the art of EQ balancing requires a good understanding of the sound characteristics of each genre. EQ balancing is all about ensuring that each instrument has its space in the mix, and nothing is overpowered. With careful consideration of each genre’s unique sound nuances, you can achieve a well-rounded, polished mix that sounds great in any context.
Advanced Eq Techniques
Advanced EQ techniques are essential when it comes to balancing the spectrum of your audio mix. These techniques can help you fine-tune your music and bring out the best in your audio, leaving you with a clean and professional-sounding track. Here are some advanced EQ techniques you can use to take your audio to the next level:
Mid-side Eqing
Mid-side EQing is a powerful technique that allows you to control the stereo image of your mix. By separating the mid (center) and side (periphery) frequency information of a stereo track, you can adjust the stereo image to make it wider or narrower depending on your preference. For example, boosting the high frequencies in the side channel can create a wider sound. On the other hand, cutting the low frequencies in the mid channel can help enhance the clarity of the vocals or other instruments that are panned to the center of the stereo field.
Parallel Processing
Parallel processing is when you duplicate a track, apply a certain effect or EQ, and mix it back into the original track. This technique can help you add more color and depth to your audio by compressing or EQing only a portion of the track without affecting the entire mix. For example, you can use parallel processing to add more punch to the drums by applying a heavy EQ and compression to only the drum track.
Dynamic Eqs
Dynamic EQs are like standard EQs, except they have the added ability to dynamically adjust the frequency boost or cut based on the input signal. This can help you achieve a more natural-sounding result and eliminate the need for additional compression or other processing. For example, you can use a dynamic EQ to tame harsh frequencies in a vocal recording without affecting the overall clarity of the track.
In conclusion, mastering the art of EQ balancing with advanced techniques like mid-side EQing, parallel processing, and dynamic EQs can help you create a radio-ready mix with a professional-sounding finish. By applying these techniques wisely and with attention to detail, you can take your audio to the highest level possible.
Using Eq In The Mixing Process
Mastering EQ balancing is an essential process in mixing music. Focusing on the full spectrum, including lows, mids, and highs, allows for a well-rounded and polished sound. Utilizing EQ techniques can bring clarity and depth to a mix, creating a more enjoyable listening experience.
Using EQ in the Mixing Process: EQ is a crucial tool in the mixing process. Understanding and mastering EQ balancing the spectrum is essential for any musician or music producer. EQ can help you solve problems in your mix, as well as create a unique and compelling sound. In this article, we will dive deeper into using EQ as a problem solver and a creative tool, as well as exploring different EQ techniques for different instruments. H3: EQ as a problem solver EQ can solve a myriad of problems in a mix. For example, if your mix sounds muddy, you can use EQ to cut out some of the low end to make it clearer. Likewise, if your mix lacks clarity, you can boost the higher frequencies to make it more defined. EQ can also be used to fix harsh or dull sounding vocals by cutting or boosting the mid frequencies. Here are a few situations where you can use EQ as a problem solver:
- Reduce harshness in cymbals by cutting high frequencies
- Reduce boomy bass by cutting low frequencies
- Reduce nasal vocals by cutting mid frequencies
H3: EQ as a creative tool EQ can also be used as a creative tool to shape a unique and compelling sound. By boosting or cutting certain frequencies, you can create a specific tone or sound. For example, boosting the bass frequencies can create a deep and powerful sound, while cutting the same frequencies can produce a thin and weak sound. EQ can also be used to create space in a mix by cutting frequencies of one instrument that interferes with another. Here are some creative ways to use EQ:
- Use EQ to create a telephone effect by cutting high and low frequencies
- Use EQ to create a lo-fi sound by cutting high frequencies and boosting lower ones
- Use EQ to create a distant sound by cutting high and boosting mid frequencies of a reverb effect
H3: EQ techniques for different instruments Different instruments require different EQ techniques to sound their best in a mix. For example, a bass guitar may need to be boosted in the low frequencies to create a full and rich sound, while a piano may need to be cut in the same range to avoid muddiness. Here are some EQ techniques for various instruments:
| Instrument | Technique |
|---|---|
| Electric guitar | Boosting mid frequencies for a cutting sound |
| Drums | Cutting low frequencies for a tighter sound |
| Vocals | Boosting high mid frequencies for clarity |
In conclusion, understanding and mastering EQ balancing the spectrum is essential for any musician or music producer. EQ can be used as a problem solver to fix issues in a mix, as well as a creative tool to shape a unique and compelling sound. By using different EQ techniques for different instruments, you can ensure that each element of your mix is well-defined and sounds its best.

Credit: www.groove3.com
Frequently Asked Questions For Understanding Mastering Eq Balancing The Spectrum
What Is The Best Eq Curve For Mastering?
The best EQ curve for mastering varies depending on the specific track and its intended outcome. There is no one-size-fits-all answer, as each track has its unique attributes. Skilled mastering engineers select EQ curves based on their training and experience, always prioritizing what sounds and feels best for the track and target audience.
What Is An Ideal Eq Type To Use During Mastering?
The ideal EQ type for mastering varies depending on the mix. It’s important to listen carefully and make adjustments accordingly to best enhance the overall sound. A combination of EQ types, such as shelving and parametric, may be necessary to achieve the desired results.
How Should We Approach Equalization During Mastering?
When approaching equalization during mastering, follow these 5 guidelines: 1) listen carefully and make small adjustments, 2) prioritize fixing frequency problems first, 3) use high-quality EQ tools, 4) use reference tracks to achieve a balanced sound, and 5) trust your ears and make subjective decisions.
How Do You Balance Frequencies?
Balancing frequencies involves adjusting the levels of different frequency bands in an audio mix to achieve a pleasing balance. This can be done through the use of EQ (equalization) and other audio processing tools. It’s important to pay attention to the overall balance of the mix and not overemphasize any particular frequency range.
Conclusion
To sum up, mastering EQ balancing is an essential skill for audio engineers and producers. It allows for a dynamic and well-rounded sound that enhances the overall listening experience. By understanding and manipulating the frequency spectrum, one can create a more defined and polished mix.
Remember to take your time and approach EQ balancing with intention and careful consideration of the individual track and the overall mix. With practice and attention to detail, you can master the art of EQ balancing and take your music to the next level.