Sample rates determine the number of times that audio is sampled per second, while bit depth represents the number of bits used to express each sample. In other words, sample rates and bit depth define the quality of digital audio recordings.
Digital audio is ubiquitous in our media-driven world, from music streaming to video game sound effects, and accurate reproduction of sound is a crucial aspect of audio production. The specific settings for sample rates and bit depths can impact the final product, influencing factors such as the size of the audio files, the level of detail in the recordings, and the compatibility with different playback devices.
Understanding these settings is vital for audio professionals and enthusiasts alike, as they work to create high-quality digital audio productions. We will explore the basics of sample rates and bit depth, and how they play a crucial role in digital audio recording and reproduction.

Credit: fifinemicrophone.com
Sample Rate
When it comes to digital audio, there are two important technical concepts to understand: sample rate and bit depth. The sample rate determines how many times per second the audio is measured, while the bit depth determines how many bits are used to represent each sample. In this article, we will focus on the sample rate.
Definition Of Sample Rate
The sample rate, also known as the sampling frequency, is the number of times per second that a sound is digitally recorded. It is measured in Hertz (Hz), which is the equivalent of cycles per second. A higher sample rate means more samples per second, which results in more accurate audio reproduction.
How Sample Rate Affects Audio Quality
The sample rate has a direct impact on the quality of your audio. If the sample rate is too low, the audio will sound distorted and you may experience a loss of detail and clarity. On the other hand, a higher sample rate will result in better sound quality and a more realistic representation of the original audio.
Here is how different sample rates affect the quality of audio:
| Sample Rate | Quality |
|---|---|
| 22.05 kHz | Low quality, suitable for speech recordings and telephony |
| 44.1 kHz | CD-quality, suitable for music production |
| 48 kHz | DVD-quality, suitable for video production |
| 96 kHz | High definition, suitable for professional audio production |
It is important to note that a higher sample rate also means a larger file size, which may be a concern if you are working with limited storage space. Ultimately, the sample rate you choose will depend on your specific needs and intended use.

Credit: www.izotope.com
Common Sample Rates
Sample rates in digital audio refer to the number of times per second that the analog sound wave is measured and recorded. Common sample rates include 44. 1 kHz, 48 kHz, and 192 kHz. The higher the sample rate, the more accurately the digital representation of the audio resembles the original analog signal.
Common Sample Rates: Sample rate and bit depth are the two fundamental concepts that determine the audio quality of a recorded sound. Sample rate refers to the number of audio samples per second, and bit depth refers to the number of bits used to represent each sample of audio data. The higher the sample rate, the more accurately the audio waveform is captured. The higher the bit depth, the more accurately the captured waveform is represented in digital form. In this article, we’ll explore common sample rates, including CD sample rate and high-resolution audio sample rates. CD Sample Rate: The most common sample rate used in the music industry is CD quality, which has a sample rate of 44.1 kHz and a bit depth of 16 bits. CD quality is the most widely used sample rate and bit depth for music production and distribution because it provides excellent sound quality and is compatible with most consumer-grade equipment. High-Resolution Audio Sample Rates: In recent years, high-resolution audio has gained popularity among audiophiles. High-resolution audio is an umbrella term used to describe formats that provide higher audio quality than CD-quality audio. High-resolution audio commonly has a sample rate of 96 kHz or 192 kHz and a bit depth of 24 bits. These higher sample rates and bit depths provide much greater detail and more accurate representation of the original sound recording. High-resolution audio formats are commonly used in professional audio production and mastering. Overall, the choice of sample rate and bit depth depends on the application and the desired audio quality. For most consumers listening to music on consumer-grade equipment, CD-quality audio is more than sufficient. However, for professional audio production and audiophiles, high-resolution audio with sample rates of 96 kHz or 192 kHz and bit depths of 24 bits is a must-have.
Bit Depth
Bit depth refers to the number of bits of information recorded for each sample in digital audio. Higher bit depth means more accurate representation of audio, resulting in better sound quality. It is important to consider both bit depth and sample rate when working with digital audio.
Definition Of Bit Depth
In a nutshell, bit depth refers to the number of bits of information that are recorded for each sample in a digital audio recording. Bit depth is measured in bits, and it determines the dynamic range of a recording. To put it simply, a higher bit depth means that more information is recorded for each sample. This results in a recording with a greater dynamic range and less noise.
How Bit Depth Affects Audio Quality
The bit depth of a recording has a direct impact on its audio quality. The higher the bit depth, the more accurate and faithful the recording will be to the original source. In general, 16-bit audio is considered to be CD quality, while 24-bit audio is considered to be high-resolution. This is because 16-bit audio has a limited dynamic range, which can result in clipping and distortion. On the other hand, 24-bit audio has a much wider dynamic range, which allows for a much more natural and lifelike sound. It is important to note that increasing the bit depth of a recording also increases the size of the audio file. This is because more information is being recorded for each sample, resulting in a larger amount of data being stored. However, the increase in quality that comes with a higher bit depth is generally considered to be worth the extra space required. In summary, bit depth is a critical factor in determining the quality of a digital audio recording. A higher bit depth allows for a greater dynamic range and more accurate representation of the original source, resulting in a superior recording overall.
Common Bit Depths
When it comes to recording audio, understanding the concept of bit depth is crucial. Bit depth refers to the number of bits of information captured for each sample. A larger bit depth means that there is more information captured, which results in higher overall sound quality.
16-bit Audio
16-bit audio is the most common bit depth used in audio recording and is the standard for CDs. This means that each sample is represented by 16 bits of data, resulting in a total of 65,536 possible values. While 16-bit audio is suitable for most recordings, it may not be sufficient for more complex projects.
24-bit Audio
24-bit audio is becoming increasingly popular, as it offers superior sound quality compared to 16-bit audio. With each sample represented by 24 bits of data, there are 16,777,216 possible values, resulting in clearer and more detailed recordings. 24-bit audio is ideal for recording high-quality music, sound effects, and voice-overs that require a higher level of detail.
32-bit Audio
32-bit audio is a relatively new addition to the audio recording world, and it offers the highest level of detail and sound quality. With 32 bits of data representing each sample, there are an enormous 4,294,967,296 possible values, resulting in incredibly accurate, high-fidelity recordings. 32-bit audio is typically used in professional studios for recording and mastering music.
Choosing Sample Rates And Bit Depths
Choosing the right sample rates and bit depths is crucial in recording and producing high-quality audio. The sample rate is the number of audio samples captured per second, while bit depth is the number of bits of information stored in each sample. In a nutshell, the higher the sample rate and bit depth, the better the audio quality.
Matching Sample Rate And Bit Depth To Recording
Matching the sample rate and bit depth to your recording equipment is the first step in producing high-quality audio. Setting a high sample rate and bit depth will capture more accurate audio and give you more flexibility during the editing process. Keep in mind that choosing too high of a sample rate and bit depth can lead to large file sizes and require more processing power.
| Sample Rate | Bit Depth | Best Use |
|---|---|---|
| 44.1 kHz | 16-bit | CD-quality audio |
| 48 kHz | 24-bit | Professional recording |
| 96 kHz | 24-bit | Mastering and high-quality productions |
Matching Sample Rate And Bit Depth To Playback Equipment
Matching the sample rate and bit depth to your playback equipment is just as important as matching it to your recording equipment. For example, if you’re producing music for CD release, it’s best to record in 16-bit/44.1 kHz because that’s the standard for CD audio. However, if you’re producing music for digital distribution, you may want to consider recording in a higher sample rate and bit depth to ensure the best possible sound quality.
Unordered List: Tips for Choosing Sample Rates and Bit Depths
- Consider your recording and playback equipment
- Choose the right sample rate and bit depth for your project
- Be mindful of file size and processing power
- Test your audio on different playback devices to ensure optimal sound quality
Overall, choosing the right sample rates and bit depths is an essential aspect of audio production. Keeping in mind your recording and playback equipment, choosing the right sample rate and bit depth for your project, and being mindful of file size and processing power will ensure that you produce high-quality audio that’s optimized for your intended audience.
Pros And Cons Of Higher Sample Rates And Bit Depths
In audio recording, sample rates and bit depths refer to the quality and resolution of the recorded sound. When it comes to professional audio recording, the higher the sample rates and bit depths, the better the audio quality will be. However, this comes with certain pros and cons that should be considered before choosing which sample rate and bit depth to use.
Improved Audio Fidelity
The primary advantage of using higher sample rates and bit depths is improved audio fidelity. When you record at a higher sampling rate, the resulting audio has more detail and nuance. The same is true for bit depth; the more bits you use, the more dynamic range the audio will have. This improved fidelity is especially important for recording music or sound effects that will be heard on high-end playback systems or in professional audio environments.
Increased Storage And Processing Requirements
One of the main disadvantages of using higher sample rates and bit depths is that they require more storage and processing power. The higher the sample rate and bit depth, the more memory and processing power required to record, edit, and mix the audio. This is a major concern for anyone recording on a budget or using a less powerful computer or recording device.
In conclusion, it is important to consider the pros and cons of using different sample rates and bit depths when recording audio. While higher sample rates and bit depths offer improved audio fidelity, they also require more storage and processing power. It’s important to strike a balance between quality and practicality based on your specific recording needs.
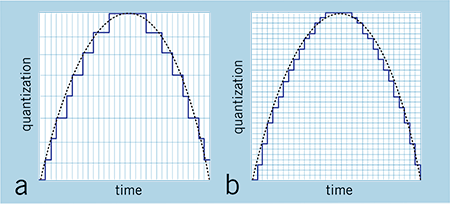
Credit: legacy.presonus.com
Frequently Asked Questions On Sample Rates And Bit Depth In A Nutshell
What Is Bit Depth And Sample Rate?
Bit depth refers to the number of bits used to represent each sample in a digital audio file, while sample rate is the number of samples taken per second. A higher bit depth means more accurate representation of sound, while a higher sample rate means more samples per second and therefore higher frequency range.
How Do You Explain Sample Rate?
Sample rate is the number of samples of audio taken per second. Higher sample rates produce better quality sound, but require more storage space. It is measured in Hertz (Hz) and generally ranges from 44. 1 kHz to 192 kHz for audio.
What Does Bit Depth Of A Sample Mean?
The bit depth of a sample refers to the amount of data used to represent each audio sample. It determines how fine the audio resolution is and the dynamic range of the audio signal. The higher the bit depth, the more accurately the original audio can be reproduced.
What Is The Effect Of Sample Rate Duration And Bit Depth?
Sample rate duration and bit depth affect the quality of digital audio. Higher sample rates capture more detail and produce clearer sound. Bit depth determines the dynamic range and accuracy of sound reproduction. Higher bit depths result in more detailed and accurate sound, while lower bit depths lead to potential distortion and loss of information.
Conclusion
To wrap things up, understanding sample rates and bit depth is crucial in producing high-quality audio. While higher sample rates and bit depths do result in better sound quality, they also require more storage and processing power. It’s important to strike a balance between quality and practicality.
When choosing your desired sample rate and bit depth, consider your project’s specific needs and budget. With these factors in mind, you can create audio that truly shines.