The main distinction between Mix Bus and Master Bus is that Mix Bus applies to individual tracks, while Master Bus affects the overall mix. The Mix Bus is a collection of audio sent from individual tracks to a mix bus channel that is affected by plugins.
Master Bus, on the other hand, is the final destination of the mix, where plugins like EQ, compression, and saturation are applied. Understanding these two terms is crucial as it will affect the overall sound quality of the mix. Mix Bus and Master Bus represent two essential parts of digital mixing that work together to create a better end result.
The difference can be subtle, but it’s integral to understanding how to mix a track or master a song. This article explores the differences between Mix Bus and Master Bus and how to use them effectively.
Mix Bus Vs Master Bus
Mix bus and master bus are important components of audio mixing, but they serve different purposes. The mix bus is typically used to combine channels and send them to the master bus, which is responsible for the final output. Understanding the differences can help you achieve a better overall sound for your mixes.
Introductory Paragraph: When it comes to mixing and mastering a track, it’s important to understand the difference between the mix bus and master bus. Both are essential tools in achieving a balanced and polished final mix. In this article, we’ll explain the primary functions and key differences between these two buses so you can use them effectively in your music production. H3: What is Mix Bus? The mix bus, also known as the stereo bus or 2-bus, is the main output channel of your mixer. It’s where all the individual tracks in your mix converge to create a stereo mix. The mix bus can be thought of as a final mixing stage where you can process your entire mix using various plugins and processors. This can help glue your mix together and add a sense of cohesion to your track. H3: What is Master Bus? The master bus is the final step in the mixing process, and it’s where the entire mix is processed before being exported. All the processing you do on the mix bus, including EQ, compression, and other effects, is applied to the master bus as well. This means that any adjustments you make to the master bus will affect the entire mix. The master bus is where you can add the final touches to your mix, bringing out certain elements while taming others. H3: Primary Function of Mix Bus The primary function of the mix bus is to process the entire mix as a whole and apply processing that influences the overall sound. Typically, you’ll use a combination of EQ, compression, and other processors to give your mix a cohesive and balanced sound. You might also use saturation or other distortion effects to add warmth and character to your mix. By processing the mix as a whole, you can ensure that each element is sitting well in the mix and not clashing with other elements. H3: Primary Function of Master Bus The primary function of the master bus is to put the finishing touches on your mix and prepare it for export. This can include making final adjustments to the mix elements, such as EQ and compression. The master bus is also where you’ll typically apply limiting, which can help increase the overall loudness of your mix and make sure it’s competitive against other tracks in the same genre. However, it’s important to be careful with limiting and not overdo it, as it can result in undesirable artifacts such as distortion and pumping. Conclusion: In summary, the mix bus and master bus are two key components of the mixing and mastering process. The mix bus is where you can process your entire mix to achieve a balanced and cohesive sound, while the master bus is where you can add the final polish to your mix and prepare it for export. Understanding the differences between the two will help you make informed decisions about how to process your mix and ultimately achieve the desired sound for your music.
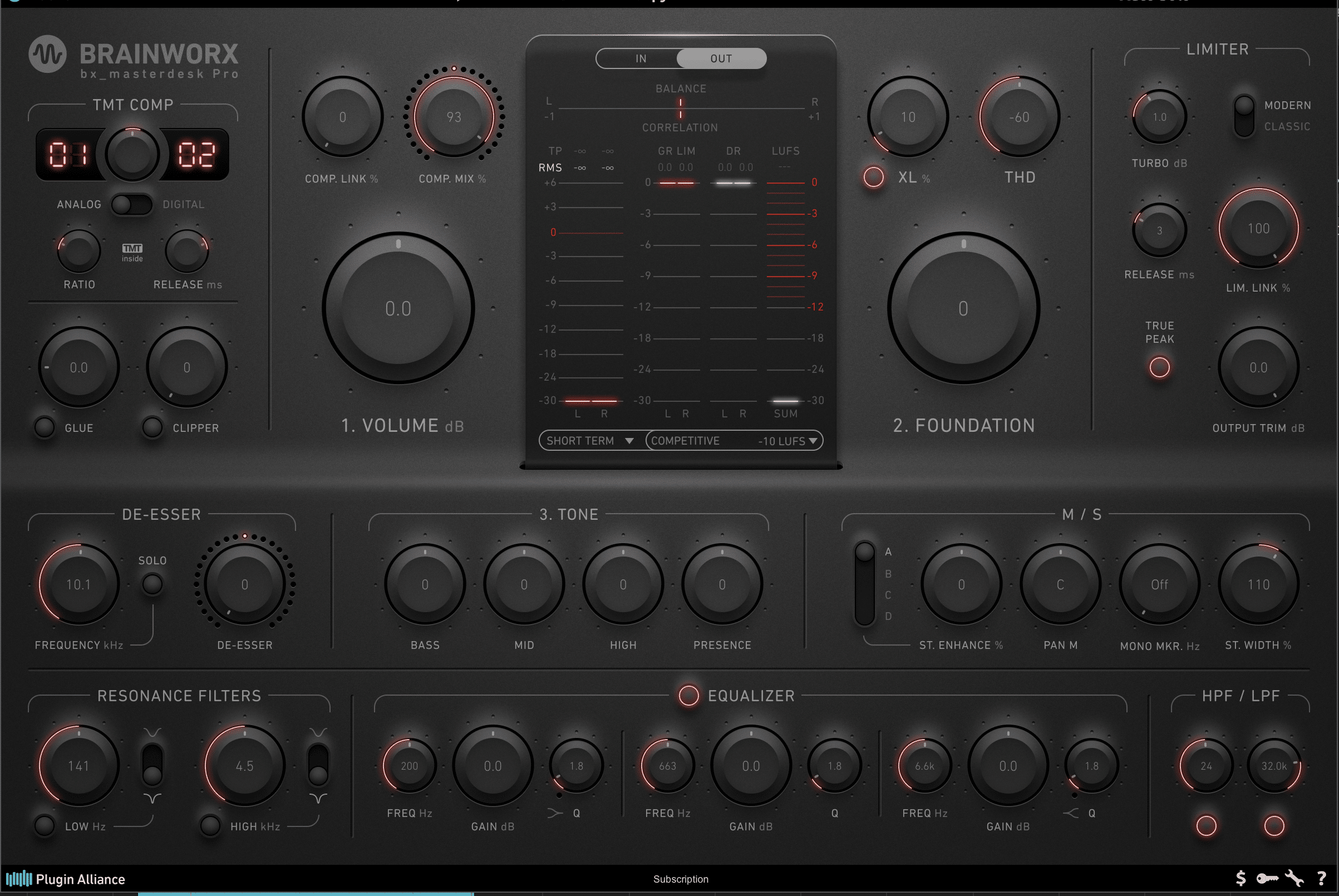
Credit: mixandmastermysong.com
Key Differences
The key differences between mix bus and master bus are multifaceted. Mix bus processes signals on individual tracks, while master bus controls the overall mix of signals on all tracks. Understanding these differences is integral to optimizing your audio production.
Mix Bus and Master Bus are essential components of any mix, but they work differently to achieve different results. Mix Bus is primarily responsible for grouping and signal processing, while Master Bus is for overall control and processing. Understanding these differences is crucial to achieve a well-balanced and polished mix. In this article, we’ll explain how Mix Bus and Master Bus work together and their key differences. We’ll also provide actionable tips to help you improve your mixes.
How Mix Bus And Master Bus Work Together
Mix Bus and Master Bus are closely related and work hand-in-hand to produce a cohesive and balanced mix. The Mix Bus processes the individual tracks and channels, while the Master Bus is responsible for processing the sum of all those tracks. The Mix Bus is usually placed before the Master Bus, and it acts as a preliminary stage of processing before the final mix processing on the Master Bus. By processing each track first, the Mix Bus ensures that each sound is balanced, EQed, and compressed correctly before they are combined on the Master Bus.
Mix Bus Is For Grouping And Signal Processing
Mix Bus is an essential tool for grouping and processing individual tracks to achieve a cohesive sound. It allows you to group similar tracks, such as drums or backing vocals, and process them together. This process results in a more cohesive sound and helps glue the individual tracks together. Mix Bus processing can include EQ, compression, reverb, and other effects.
Master Bus Is For Overall Control And Processing
The Master Bus is the final step of the mixing process and is responsible for processing the overall mix. This includes processing the final stereo mixdown, including EQ, compression, limiting, and other mastering effects. The Master Bus usually includes a limiter to prevent clipping and ensure that the mix remains at a consistent volume level. It’s crucial to use the Master Bus sparingly and not to over-process the mix, resulting in an overtly processed sound. In conclusion, understanding the differences between Mix Bus and Master Bus is crucial to achieve a well-balanced and polished mix. By processing each track separately, the Mix Bus ensures that every sound is balanced before they are combined on the Master Bus for final processing. Remember to use the Master Bus sparingly and not over-process the mix, resulting in an overtly processed sound.
Advantages Of Mix Bus
Mix bus and master bus are crucial for fine-tuning audio in a mix. By using a mix bus, sound engineers can achieve better control over the mix while preserving individual track dynamics. In contrast, mastering is done on the master bus, which helps produce a polished final product for listeners.
Advantages of Mix Bus When it comes to mixing music, the mix bus and master bus are two crucial components that need to be understood. The mix bus is where most of the audio mixing takes place, while the master bus is where the final output is produced. In this article, we will be discussing the advantages of mix bus and how it can help you achieve a better sound quality for your music.
Better Control And Flexibility
Mix bus offers better control and flexibility as compared to the master bus. This is because, in the mix bus, you can easily manipulate the individual tracks by adding different processing effects to each one of them, like reverb, delay, compression, and EQ. This gives you complete control over your music mix, and you can experiment with different settings to bring out the perfect mix for your audio.
More Focused Sound
Another advantage of using the mix bus is that it enables you to achieve a more focused sound. This is because, when you use the mix bus, you can apply effects to individual tracks that help bring out their unique characteristics. For instance, if you want to fix the low-frequency buildup in your music, you can use EQ on the bass to eliminate that problem. Likewise, you can make other adjustments to other tracks to achieve a more balanced and focused sound.
Easier To Manage Levels
Managing levels is an extremely important aspect of audio mixing. You want to ensure that each track is leveled, so they all sound good with each other. This is where the mix bus performs better than the master bus. With the mix bus, you have full control over the levels of each track, and you can quickly adjust them if needed. This ensures that every track is audible and balanced with each other, and you get an overall better sound quality. In conclusion, the mix bus offers better control and flexibility in achieving the desired sound quality for your audio. It ensures that you have complete control over the levels, and you can easily fix any imbalance issues, resulting in a more focused sound. Therefore, it’s worth understanding how to use the mix bus effectively to get the most out of your music mixes.
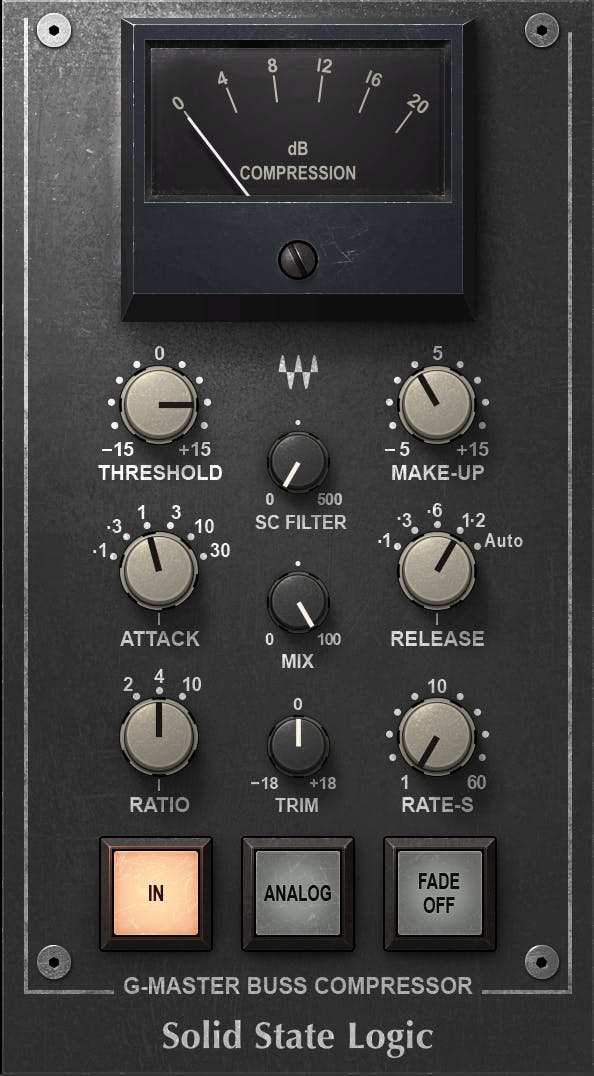
Credit: www.waves.com
Advantages Of Master Bus
When it comes to mixing music productions, the master bus is a vital component in achieving a polished final product. Here are some advantages of using a master bus:
Application Of Overall Dynamics Processing
The master bus allows for overall dynamics processing to be applied to the mix as a whole. This means that any adjustments made on the dynamics, such as compression or limiting, will affect the entire mix, adding essential cohesion and uniformity to the final product. With the application of overall dynamics processing, the listener will experience a consistent volume level, avoiding any drastic spikes or dips in volume.
Application Of Global Eq
Another advantage of a master bus is the application of global EQ. Adding EQ to the master bus allows for a cohesive sound. This ensures that no frequency range is unrepresented, and no instruments sound overly bright or muddy. Additionally, the overall tonal balance of the mix can be tweaked to achieve presence and clarity.
Coherence Of Mix As A Whole
Using a master bus can provide coherence to the mix as a whole. The master bus allows for better control of the stereo image, establishing a consistent location of instruments across the soundstage. This also means that the listener can perceive instruments and vocals without any overlapping elements that distract from the focus of the music. The coherence of the mix ensures that each track contributes to the overall production, contributing to the musicality and impact of every component.
When To Use Mix Bus
To achieve a well-balanced and cohesive mix, it’s important to understand the differences between the mix bus and master bus. The mix bus combines all the individual instrument and vocal tracks, while the master bus processes the final mix before sending it to the mastering stage.
Knowing when to use each can greatly improve the overall quality of your music production.
Mix bus and master bus are essential for mixing and mastering audio. Understanding the key differences between the two can help you make informed decisions when working on your music production. In this post, we’ll focus on the use of mix bus and its significance in pre-mastering and processing single instruments or groups.
For Pre-mastering
Mix bus is essential to use in pre-mastering to create a cohesive sound. You can use mix bus to enhance the stereo image and control the dynamics of your overall mix. By doing so, you can ensure that your mix sounds consistent across different playback systems. You can add some glue to the individual tracks in your mix by processing them through a mix bus. Additionally, you can use plugins like compressors, EQs, and limiters on the mix bus to achieve that desired sound you’re after.
Processing Single Instruments/groups
Mix bus can also be useful when processing single instruments or groups. If you’re working on a multi-track project, it can be challenging to manage the levels of each instrument or group. One way to make it easier is to group them together and process them through a mix bus. This way, you can apply similar effects and processing to different tracks and control the overall sound of the group. In conclusion, using a mix bus can significantly enhance your mixing and mastering processes. It’s critical to manage levels and apply processing to create a cohesive sound. Whether you’re processing single instruments or groups or pre-mastering, using a mix bus should be a crucial part of your workflow.
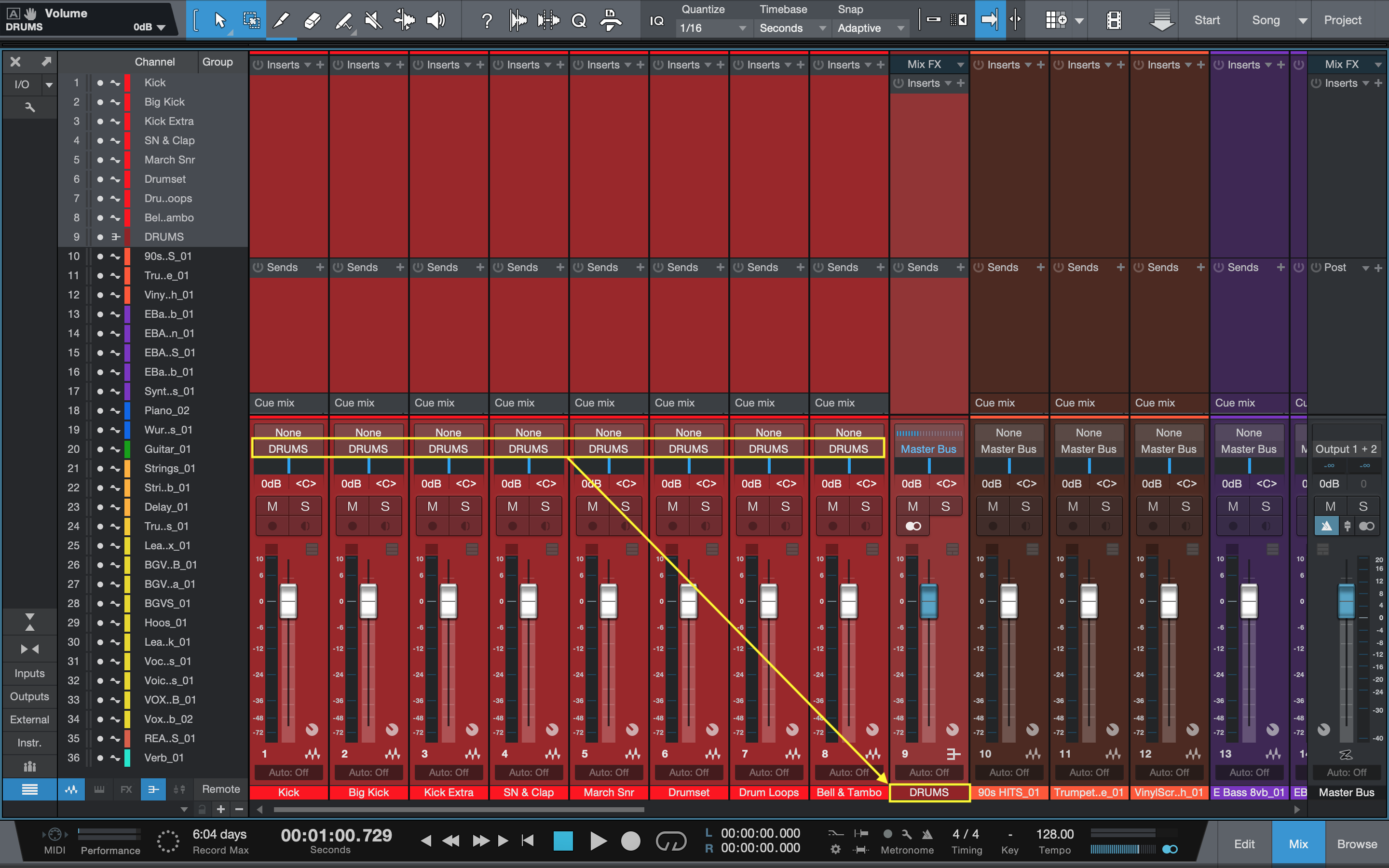
Credit: www.izotope.com
When To Use Master Bus
Understanding the difference between Mix Bus and Master Bus is essential to achieve the desired sound quality in your music production. Often, in the mixing process, you might think of Mix Bus as the starting point and Master Bus as the endpoint. Mix Bus is where individual component tracks are combined to make a single mix, while Master Bus is where the final mix output is conveyed. In this post, we’ll discuss the key differences between Mix and Master Bus and explore the situations when using Master Bus is appropriate.
For Final Mix Control
The Master Bus provides complete control over the final mix, which affects the overall balance and coherence of the song. At this stage, all the tracks have already been mixed, and the output sound is passed through the Master Bus. Here, you can make subtle adjustments to enhance and polish the mix. Using compression, EQ, and other mastering plugins, you can shape the final output to ensure that it’s consistent with the genre and style of music. Master Bus processing helps bring all elements of the mix together, resulting in a cohesive and engaging sound.
Adjusting Overall Tone
Master Bus is also an excellent tool to adjust the overall tone of the mix. As you know, different frequency ranges produce different emotions, and the right tone can evoke the desired reaction in the listener. Here, you can add or remove frequencies to level out the mix. For instance, if the mix sounds too bass-heavy, you can reduce the low-end frequency to produce a more balanced sound. Similarly, if the cymbals are piercing, you can dampen the high-end frequency. Overall, Master Bus processing is crucial for creating a well-balanced and tonally-rich mix.
In conclusion, Master Bus processing is crucial for achieving the desired sound quality in music production. By providing complete control over the final mix, it helps create a cohesive and engaging sound. Whether you’re adjusting the overall tone of the mix or making subtle enhancements, Master Bus is an excellent tool to ensure that your mix sounds its best.
Best Practices For Mix And Master Buses
Understanding the differences between the mix and master bus is crucial for achieving the best sound quality in your music production. The mix bus refers to the processing chain applied to all tracks before summing to a stereo image, while the master bus is where the final processing is done before exporting the track.
Best Practices for Mix and Master Buses: Mix bus and master bus are two significant elements in the audio mixing process. The mix bus connects all tracks, while the master bus gives the final output for the mix. It is crucial to know the differences between these two buses to create high-quality audio. Here are the best practices for mix and master buses that you should keep in mind: Keeping Levels in Check: It is crucial to keep the track levels in check to prevent any distortion or clipping. While mixing audio, the levels must be appropriate on each track, and the mix bus should be peaking at approximately -6db. This practice will ensure that you will have enough headroom while mastering the track and prevent clipping or distortion caused by overloaded levels. Avoiding Over-Processing: Over-processing on the mix or master bus can lead to poor-quality audio. Applying too much compression, EQ, or saturation can ruin your mix and create an unpleasant sound. It is essential to use light compression, EQ, and saturation, especially in the early stages of the mixing process. You may need more drastic processing at a later stage, but it is essential to keep it balanced and subtle. A/B Testing for Comparison: Comparing your mix and master with similar tracks is a crucial practice to perfect your mix. A/B testing is an effective way to compare your mix with commercial tracks close to your mix’s genre. Doing this can give you more of an understanding of what sonic characteristics are found in your track and how it differs from professional tracks. It is helpful to use a reference track to understand the frequency balance and the overall sound that you are trying to achieve. Implementing these best practices into your mix and master process will lead to high-quality audio tracks that meet professional standards. Remember to keep the levels in check, avoid over-processing, and perform A/B testing for comparison.
Frequently Asked Questions For Mix Bus Vs Master Bus Key Differences Explained
What Is The Purpose Of A Mix Bus?
A mix bus is a component in audio mixing consoles that combines and processes multiple audio signals into a unified output. Its main purpose is to control the overall sound and level of the mix, while maintaining the tonal balance and clarity of the individual tracks.
It is an essential tool in professional audio production, allowing engineers to sculpt the final sound of the recorded music or dialogue.
What Is The Difference Between Master Bus And 2 Bus?
The master bus is the main output bus that carries all mixed signals from different tracks and channels before it goes to the master fader. On the other hand, 2 bus refers to the stereo output of the mix that typically consists of left and right channels.
The main difference is that the master bus is an internal routing function while the 2 bus is an external output that feeds the final mix.
What Is A Master Bus Used For?
A master bus is used to combine and route multiple audio signals to an output source, such as speakers or recording equipment. It allows for mixing and control of various audio channels, and is commonly used in music production and live sound settings.
What Is A Mix Bus On Sound Board?
A mix bus on a sound board is a group of channels that are combined to form a single audio output. This allows the sound engineer to control the overall levels and tone of multiple channels at once, and send them to speakers or recording devices as a single mix.
Conclusion
Ultimately, understanding the differences between mix bus and master bus can greatly improve the sound quality of your music productions. Mix bus processing can enhance individual tracks, while master bus processing can add a final polish to the overall mix.
It’s important to experiment with both techniques and find what works best for your particular mix and style. By doing so, you can elevate your music to a professional level and stand out in a crowded industry.