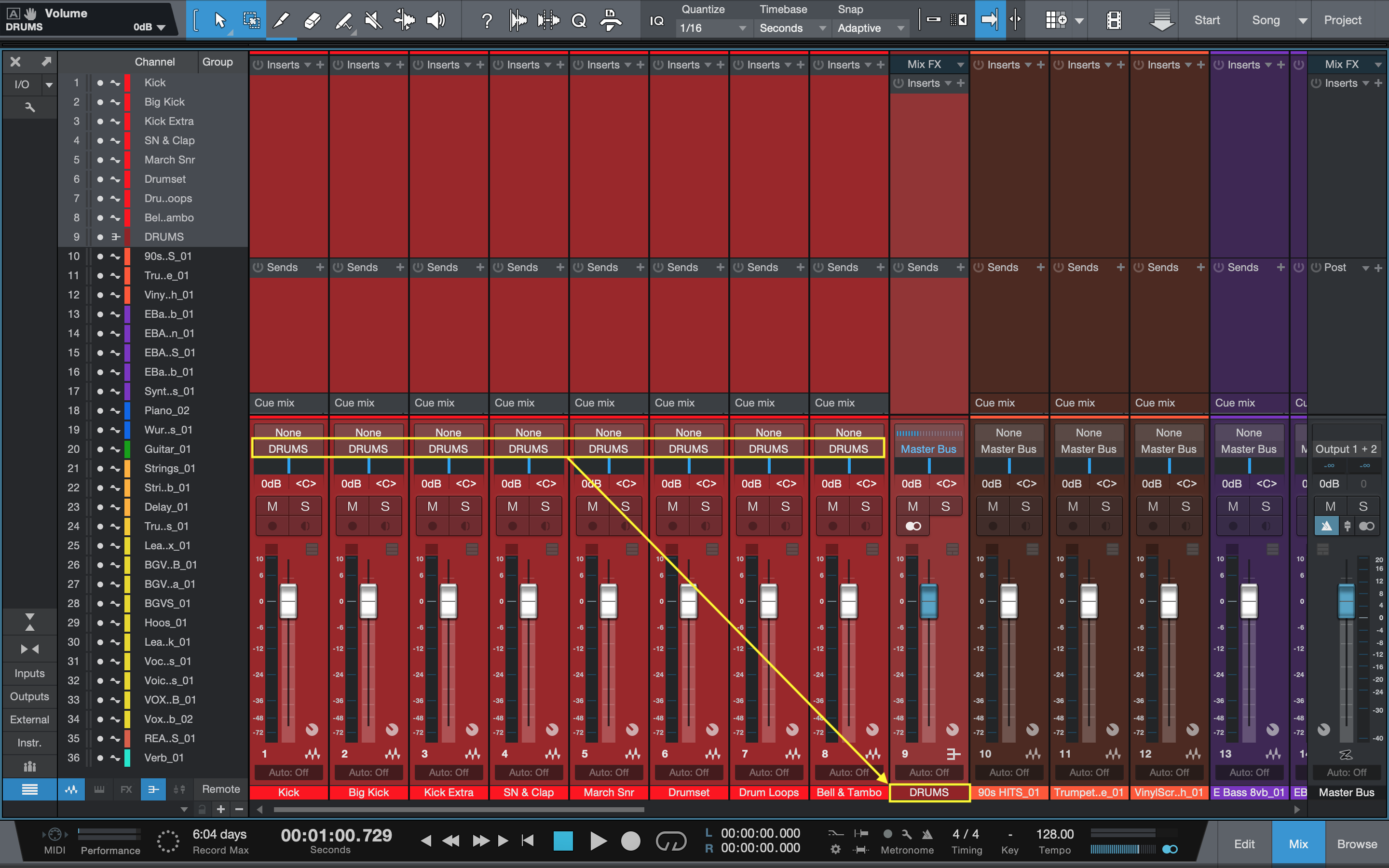
To set up a mix bus, route multiple audio channels into one mix bus track. Then apply effects and processing to the mix bus to enhance the overall sound.
Mix buses are an essential tool for creating polished and professional-sounding mixes. By grouping several audio channels together and processing them as a cohesive unit, you can add depth, width, richness, and clarity to your mixes. The process involves routing the source channels into a single mix bus, where you can then apply various tools and effects such as EQ, compression, and saturation.
Properly setting up a mix bus takes time and experience, but the end result is well worth the effort. In this guide, we will provide you with a step-by-step procedure on how to create an effective mix bus that will elevate your mixes to the next level.
Credit: www.izotope.com
How Does A Mix Bus Work?
A Mix Bus is a channel in a mixing console that brings together multiple audio signals to create a stereo mix. It is where the final signal is summed, processed and enhanced before being sent out to the master output.
A good Mix Bus setup can greatly improve the overall sound quality of a recording.
Mix Bus is an essential part of any mixing console which plays a crucial role in producing high-quality audio output. It is responsible for combining multiple audio signals together and balancing their levels to create a cohesive mix. In this section, we will discuss the basic principles and signal flow of a Mix Bus.
Basic Principles
The Mix Bus is essentially a virtual channel that combines several channels into one output. It applies processing such as equalization, compression, and adds effects in this new combined channel. It’s similar to how an electrical circuit works, where signals from multiple sources are redirected and combined into one destination.
Signal Flow
The signal flow of a Mix Bus can vary depending on the mixing console and the preference of the mixer. Generally, the signal passes through the channel strip first, where individual adjustments can be made for each channel. The signals from all channels are then routed to the Mix Bus, where the mixer can apply overall volume and effects processing. Finally, the signal is adjusted for the master output and sent to the loudspeakers or recording device. To ensure proper signal flow in the Mix Bus, it is essential to maintain proper gain staging. This means adjusting the input gain and output level of each channel to maximize headroom and prevent distortion. In conclusion, understanding how a Mix Bus works and its signal flow is crucial to producing high-quality audio output. Basic principles and proper gain staging are essential components for effective use of a Mix Bus in any mixing setup.
Why Is A Mix Bus Important?
A mix bus is an important element in the mixing process as it helps bring together all the individual tracks in a mix, combining and processing them so they sound cohesive and balanced. A mix bus can make or break the sound of a mix, and it’s a tool that every audio engineer should have in their arsenal.
Balancing Levels
One of the key functions of a mix bus is level balancing. Balancing levels involves adjusting the volume of each track in a mix so they sit well together and don’t overpower each other. When each track is balanced, the mix can sound clean, clear and cohesive. Using a mix bus to balance levels can be an effective way to control and adjust the dynamic range of a mix.
Gluing Mix
Another function of a mix bus is to glue the mix together. Gluing the mix involves processing the mix bus in a way that helps blend the individual tracks together. By adding EQ, compression, saturation, and other processing to the mix bus, the individual tracks can sound more cohesive and unified, creating a professional-sounding mix.
Creating Sonic Space
A mix bus can also be used to create sonic space in a mix. By using reverb, delay and other effects on the mix bus, you can create a sense of depth and width in the mix. This can help create a more immersive and engaging listening experience for the listener.
| Balancing Levels | Gluing Mix | Creating Sonic Space |
| Adjusting volume of each track to sit well together. | Processing mix bus to blend individual tracks. | Using effects to create depth and width in mix. |
| Effective way to control dynamic range. | Creating a professional-sounding mix. | Creating an immersive listening experience. |
Code Example:
function mixBus() {
balanceLevels();
glueMix();
createSonicSpace();
}
mixBus();Summary
A mix bus is a powerful tool that audio engineers can use to balance levels, glue the mix, and create sonic space in a mix. By understanding how a mix bus works and implementing it effectively, you can take your mixes to the next level and create professional-sounding recordings.
Mix Bus Techniques
Discover effective mix bus techniques for getting that polished sound you desire in your mixes. Learn how to use EQ, compression, and saturation on your mix bus to achieve clarity, punch, and warmth in your tracks.
Mix Bus Techniques are essential to the production of high-quality audio mixes. It’s a process that involves several technical aspects of music mixing. Compression, EQ, Saturation/Analog Emulation, and Stereo Techniques are fundamental mix bus techniques that every audio engineer must master. In this post, we will discuss each of these techniques in-depth to provide valuable insights on how to use them effectively.
Compression
Compression is a game-changer in mixing and mastering. It is used to smooth out an audio track’s dynamic range, making the quieter parts louder and the louder parts quieter. A compressor helps to keep the track’s volume level consistent, making it easier to hear every detail of the mix. When applying compression, it’s important to set the threshold and ratio correctly. Using a faster attack and slower release can also help to create a smoother sound. Experimenting with compression settings can help an audio engineer create a unique sound profile for a track.
Eq
Equalization is the process of adjusting the balance of frequencies in an audio track. EQ can be used to boost or cut specific frequencies, allowing an audio engineer to tailor the sound to their liking. When using EQ, it’s crucial to take note of each instrument’s frequency range so that they do not overlap and cause muddiness in the mix. Cutting frequencies can be just as important as boosting them, so it’s essential to have a good understanding of EQ when mixing music.
Saturation/analog Emulation
Saturation and Analog Emulation are two powerful mixing tools that aim to provide warmth, depth, and character to a mix. Saturation can be used to add subtle harmonics to a track, producing a more pleasing sound. Analog Emulation can imitate the sound of vintage equipment, creating a unique and authentic sound profile. Both techniques are great for adding color and depth to a mix without changing its dynamics or balance, which can be beneficial when producing music in a digital environment.
Stereo Techniques
Finally, Stereo Techniques are the use of panning and stereo imaging to give depth and dimension to a mix. Panning is the act of adjusting the stereo field of individual tracks in a mix. Stereo imaging, on the other hand, refers to the process of adjusting the stereo image of a mix as a whole. These techniques help to create a more immersive sound that can help to capture the listener’s attention. Proper use of Stereo Techniques can lead to a more engaging and enjoyable listening experience. In conclusion, Mix Bus Techniques in music production are essential to create high-quality and unique audio mixes. Compression, EQ, Saturation/Analog Emulation, and Stereo Techniques help to bring color, depth, and character to your mixes. A good understanding of these techniques can help elevate your production and establish you as an expert audio engineer.

Credit: store.harrisonaudio.com
Mix Bus Setup
HTML Response:
Setting up a Mix Bus is a crucial part of achieving a polished final mix. It determines how the different audio tracks mix together as a whole. There are two primary types of Mix Buses: Analog Mix Bus and Digital Mix Bus. Let’s discuss the setup of each Mix Bus:
Analog Mix Bus
An Analog Mix Bus involves mixing audio signals using analog hardware. This setup creates warmth and character in the sound, which is missing in digital mixing. Here’s how to set up an Analog Mix Bus:
- Connect the output of your mixer to the input of the Analog Mix Bus processor (a compressor, EQ, or a combination of both).
- Use the bus send feature of your mixer to send each channel to the Analog Mix Bus.
- Adjust the levels of each channel going into the Analog Mix Bus to achieve the perfect balance of sound.
- Apply compression and EQ as desired to enhance the mix.
- Connect the Analog Mix Bus output to a stereo recorder or back to the mixer’s stereo inputs.
Digital Mix Bus
Digital Mix Buses use software and digital processors to mix audio signals, making it much more flexible and repeatable. However, the resulting sound is less warm and more precise. Here’s how to set up a Digital Mix Bus:
- Create a stereo Aux Bus in your DAW (Digital Audio Workstation).
- Use the Bus Send feature to route each channel to the Aux Bus.
- Apply any desired digital processors such as EQ, Compressor, and Limiters to the Aux Bus.
- Adjust the levels of each channel going into the Aux Bus to achieve the perfect balance of sound.
- Connect the Aux Bus output to the main stereo output of your DAW.
By following the above steps, you can set up an Analog or Digital Mix Bus to create a cohesive and polished final mix. Keep experimenting with different processors and settings to find that perfect balance that makes your mix sound amazing.
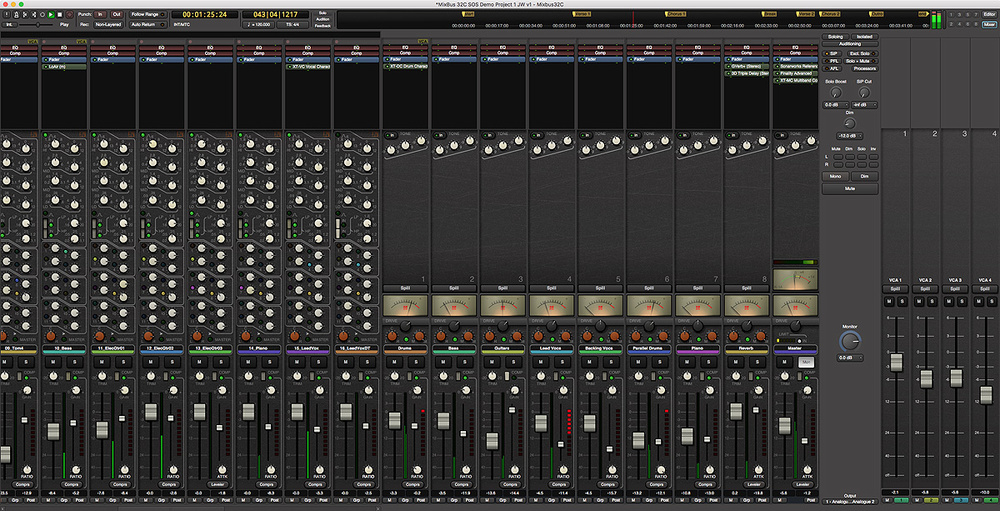
Mix Bus Plugins
Mix bus plugins are essential for achieving a polished and cohesive sound in your mix. These plugins route all your tracks to a single channel where you can apply additional processing and effects to enhance the overall balance and impact of your mix.
Overview
Mix Bus Plugins are essential for every music producer who wants to create high-quality audio productions. In the simplest terms, a mix bus consists of all the audio channels in a mix routed to a single stereo output. This allows you to apply processing to the entire mix as a whole. Mixing is an art, and mix bus plugins play a crucial role in enhancing the sonic characteristics of your mix.
Recommendations
There are a plethora of mix bus plugins available in the market. It can be overwhelming to choose the right one for your project. Here are some highly recommended mix bus plugins that can significantly improve your mix:
| Plugin Name | Description | Price |
|---|---|---|
| FabFilter Pro-L 2 | A top-of-the-line limiter plugin that provides transparent limiting, loudness metering, and various limiting algorithms. | $199 |
| Waves API 2500 | Emulates the sound of the classic API 2500 compressor and offers features like adjustable threshold, attack, and release settings. | $299 |
| Izotope Ozone 9 | A comprehensive mastering suite with a range of tools, including equalization, dynamic processing and much more. | $499 |
These plugins offer different features and functionalities that cater to different types of music. It’s important to experiment with different plugins and find the one that enhances the overall sound of your mix. In conclusion, mix bus plugins are a crucial part of the mixing process, as they allow you to enhance the sonic characteristics of your overall mix. By experimenting with different plugins and understanding how they affect the sound, you can choose the one that best suits your music production needs.
Credit: www.soundonsound.com
Frequently Asked Questions Of Mix Bus How To
How Do You Set Up A Mix Bus?
To set up a mix bus, you need to route your tracks to a designated bus. Then, add any desired plugins and adjust the levels and pan of the tracks to achieve the desired balance. It’s important to reference the mix through different speakers and headphones to ensure it translates well.
What Goes On Mix Bus?
The mix bus is where all recorded tracks come together before being sent to the master output. This is the final stage where various processing is applied to achieve the desired sound of the mix. Equalizers, compressors, and limiters are commonly used on the mix bus to balance and enhance the mix.
It is important to use caution when adding processing to the mix bus as it affects the entire mix.
How To Do Mix Bus Compression?
Mix bus compression is the process of applying compression to the stereo mix bus to glue together the individual tracks of a mix. Start by selecting an appropriate compressor and setting a moderate amount of compression. Adjust the attack and release times to achieve a smooth sound and use a low ratio to avoid over-compression.
Finally, adjust the makeup gain to compensate for the loss of volume caused by compression.
What Is The Compression Ratio For A Mix Bus?
The compression ratio for a mix bus depends on the genre of music and desired outcome. Typically, a ratio of 2:1 to 4:1 is suitable for Pop and Rock genres, while Jazz and Classical may require a lower ratio of 1.
2:1 to 2. 5:1. It’s important to experiment with different ratios to achieve the desired sound.
Conclusion
To sum up, the mix bus is a vital component of the audio mixing process that can make or break the success of a recording. Understanding how to properly configure and process your mix bus is crucial for achieving a professional and cohesive sound.
By taking into account the tips and techniques we’ve discussed, you’ll be well on your way to mastering the mix bus and creating outstanding mixes that stand out from the competition. Remember, practice makes perfect, so keep experimenting and refining your techniques to take your music to the next level.