To use EQ shelf filters, adjust the gain or attenuation of a selected frequency range. To do this, select the filter type and frequency range, then adjust the gain or attenuation to achieve the desired sound.
EQ shelf filters are an essential tool for audio engineers and producers to make sonic adjustments during the mixing process. They work by adjusting the gain or attenuation of a selected frequency range, helping to sculpt a mix to sound the best it can.
The shelf filter type provides an even gain or attenuation across the selected frequency range, making it an ideal choice for boosting or cutting low or high frequencies. However, for more targeted adjustments, a peak filter may be a better choice. Overall, EQ shelf filters are a powerful tool for achieving the desired sound in any mix.
What Are Eq Shelf Filters?
Equalization (EQ) is an audio-processing technique that allows you to change the tonal balance of an audio signal. To do this, an equalizer applies a set of filters to the signal. Each filter is responsible for adjusting a specific frequency range of the audio signal.
Definition Of Eq Filters
EQ filters are circuits that control the frequency response of an audio signal. They operate by either boosting or cutting selected frequencies to enhance or attenuate a particular tonal quality. EQ filters can be either passive or active, and they come in many different forms, each with unique sonic characteristics and application scenarios.
Types Of Eq Filters
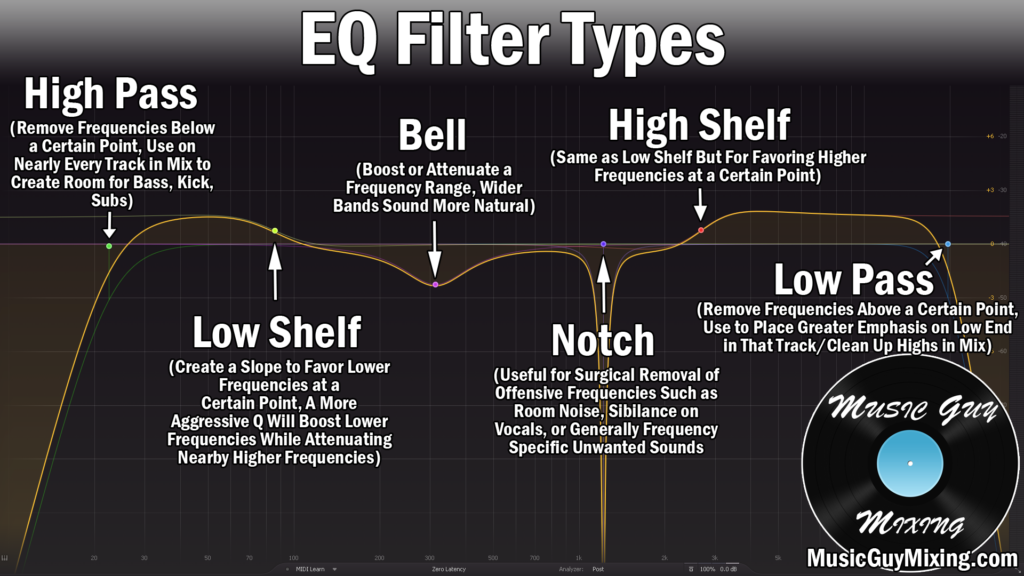
There are various types of EQ filters, including high-pass filters, low-pass filters, band-pass filters, and shelf filters. A shelf filter, also referred to as a “tone control,” is a type of EQ filter that works by attenuating or boosting frequencies above or below a certain cutoff point, creating a “shelf” shape in the frequency response curve.
There are two types of shelf filters: high-shelf and low-shelf. A high-shelf filter attenuates or boosts frequencies above the shelf point, while a low-shelf filter does the same for frequencies below the shelf point.
Credit: www.musicguymixing.com
How Eq Shelf Filters Work
Eq shelf filters are critical audio tools that allow you to adjust specific frequency ranges in a sound signal. These filters work by boosting or attenuating frequency ranges around a particular frequency to achieve your desired tonal balance. With the flexibility to fine-tune sound, EQ shelf filters are a valuable asset in any sound engineer’s toolkit.
Frequency Range
EQ Shelf Filters are used to make changes to the frequency response of an audio signal. They work by allowing selection of a frequency range and altering the amplitude of all frequencies above or below that range.
For instance, if you boost frequencies above the chosen range, you enhance the high frequencies. If you cut frequencies below the selected range, you lower the low frequencies.
Shelving Points
Shelf filters have two shelving points: one is the frequency at which the shelving starts, and the other is the amount of boost or cut applied to the signal.
The shelving points act like a shelf that lets frequencies pass unchanged below the shelf and boosts or cuts frequencies above the shelf.
Types Of Shelving Filters
There are two types of shelf filters: high shelving filters and low shelving filters.
A high shelf filter increases or decreases the level of high frequencies above a particular frequency. Conversely, the low shelf filter boosts or cuts the level of low frequencies below a particular frequency.
In conclusion, EQ shelf filters are a powerful tool that can be used to manipulate the frequency response of an audio signal. By understanding how they work and the different types of shelving filters available, you can enhance the sound quality of your audio recordings.
Understanding The Roles Of Frequency And Gain
Frequency and gain are intricate components in EQ shelf filters, and understanding their roles is crucial in getting your desired sound. By adjusting the gain, you can control the amount of boost or cut in a frequency range, which affects the tone of your music.
Defining Frequency And Gain
Before delving into the use of EQ shelf filters, it is essential first to understand the two fundamental concepts that form the backbone of EQ – frequency and gain. Frequency refers to the pitch of the sound, with high frequencies producing high-pitched sounds, and low frequencies producing low-pitched sounds. Gain, on the other hand, refers to the strength or intensity of the sound. In simpler terms, frequency can be likened to the key on a piano while gain can be compared to how hard the key is pressed. The understanding of these two concepts is critical to using EQ shelf filters effectively.
Relationship Between Frequency And Gain
The relationship between frequency and gain is essential since EQ shelf filters alter both. EQ shelf filters adjust both the frequency and the gain of the audio signal and enable us to boost or reduce the energy levels of specific frequency ranges. For instance, an EQ shelf filter can be used to increase the gain of the high frequencies in a vocal track to make it sound brighter. Conversely, it can be used to reduce the gain of the low frequencies to lessen boomy sounds in a bass guitar track. It’s important to note that the frequency adjustment point must be chosen carefully since boosting or refining too much can result in unnatural or unrealistic outcomes. The art of using EQ shelf filters is finding the perfect balance between frequency and gain adjustments while staying true to the original sound of the audio. In conclusion, understanding the roles of frequency and gain is critical to using EQ shelf filters effectively. The relationship between the two is what enables us to alter the specific frequency ranges that make up the audio signal and can result in high-quality audio output.

Credit: www.mixinglessons.com
How To Use Eq Shelf Filters In Music Production
Learn how to effectively use EQ shelf filters in music production. Adjusting the frequency levels of the high and low end of a sound can help balance and shape the overall mix.
Music production relies heavily on equalization (EQ), a process of manipulating sound frequencies. EQ Shelf Filters are one of the commonly used types of EQs that allow you to alter everything from bass to treble frequencies. By boosting or cutting frequencies with EQ Shelf Filters, you can improve the overall balance and clarity of your tracks. In this post, we will discuss how to use EQ Shelf Filters in music production, including identifying problem frequencies, choosing the right EQ Shelving Filter, and applying EQ Shelving filters to tracks.
Identifying Problem Frequencies
Before applying EQ Shelf Filters to a track, it is essential to identify the problem frequencies that you want to address. These problem frequencies could be resonant frequencies that lead to harsh, unpleasant sounds or muddiness in the tracks. Identifying these frequencies can be done using an EQ analysis tool or by listening carefully to your tracks. It is crucial to identify these frequencies to prevent over-EQing that may lead to music tracks sounding unnatural or hollow.
Choosing The Right Eq Shelving Filter
Once you have identified the problem frequencies, the next step is to choose the right EQ Shelving Filter. EQ Shelf Filters come in two categories: High-Shelf and Low-Shelf. High-Shelf is used to tame treble frequencies, while Low-Shelf helps in controlling bass frequencies. The best practice is to use the same type of EQ Shelving Filter to set a consistent tonal balance in your tracks.
How To Apply Eq Shelving Filters To Tracks
After identifying the problem frequencies and choosing the right EQ Shelving Filter, the final step is to apply the EQ Shelving Filters to tracks. Before applying the EQ Shelving, ensure that your volume levels are balanced. Boost or cut specific frequencies using the chosen EQ Shelving Filter. It is worth noting that EQ adjustments can affect other aspects of your mix, such as dynamics, so it’s essential to monitor how the changes sound together. In conclusion, EQ Shelf Filters are handy tools in music production. Identifying problem frequencies, choosing the right EQ Shelving Filter, and properly applying them to tracks can help improve audio quality. Remember to be mindful of the overall mix as you make EQ adjustments to ensure that your tracks sound cohesive and balanced.
Best Practices For Using Shelving Eq Filters
Eq shelf filters are useful tools for controlling the tonal balance of a mix. Best practices for using shelving eq filters include choosing the appropriate frequency range, setting the filter to the correct slope, and using multiple filters to achieve the desired effect.
It is important to approach equalization with a purpose and a clear understanding of how the tools work to avoid negatively impacting the mix.
Shelving EQ filters are an essential tool for any audio engineer. They allow you to adjust the EQ of a track, boosting or cutting frequencies as needed. However, like any tool, you must use them correctly to achieve the best results. In this section, we will discuss the best practices for using shelving EQ filters, including how to avoid overuse, creative ways to use them, and the benefits of experimenting with shelving vs non-shelving filters.
Avoiding Overuse Of Eq Shelving Filters
EQ shelving filters can be incredibly useful when used correctly, but it’s easy to overuse them. The most common issue is when they are used to fix problems instead of using targeted EQ adjustments. When you apply a shelving filter, you are affecting all frequencies in a particular range, not just the problematic ones. As a result, overuse can muddle the sound and make it less clear. To avoid overuse, it’s essential to use EQ shelving filters sparingly. Consider the overall mix, and try to identify which particular frequencies need boosting or cutting. The best approach is to use a series of targeted EQ adjustments to eliminate specific issues and then use shelving filters to further adjust the overall tone.
Using Eq Shelving Filters In Creative Ways
Shelving EQ filters are not just for correcting problems. They can also be used creatively to shape the sound of a track and add interest to the mix. One way to use them is to create a “smile” or “frown” EQ curve, which shapes the low, mid, and high frequencies in a particular way. Another creative way to use shelving EQ filters is to create a sense of depth and space in the mix. By cutting the low frequencies of a track, you can make it sound like it’s farther away. Conversely, boosting the high frequencies can make a track sound closer.
Experimentation With Shelving Vs Non-shelving Filters
Finally, it’s essential to experiment with shelving vs non-shelving filters to understand their specific benefits. A shelving filter affects all frequencies above or below the cutoff point, while a non-shelving filter affects only a particular frequency or range. Understanding the differences between them will help you make better decisions about when to use each type of filter. To wrap up, using EQ shelving filters can significantly improve the sound of your mix. However, it’s crucial to use them sparingly, creatively, and with a clear understanding of their benefits and drawbacks. With these best practices in mind, you can achieve the results you desire and create a professional-sounding mix that stands out.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Advanced Eq Filtering
Advanced EQ filtering involves using EQ shelving filters to shape the frequency response of specific audio signals in more precise and granular ways. These techniques can be especially useful for special use cases, such as enhancing the sound of a specific instrument or voice, or fixing issues with room acoustics. To get the most out of EQ shelving filters, it is important to use the right tools and plugins that enable you to fine-tune the frequency response to your desired specification.
Eq Shelving Filter Techniques For Special Use Cases
One way to effectively use EQ shelving filters for special use cases is to target problematic frequencies that need to be raised or lowered. For example, if you are working with a vocal recording with too much low-end resonance, a low-shelf filter with a sharp cutoff can help to reduce the unwanted frequencies in a specific range while keeping the rest of the frequency spectrum intact. On the other hand, if you are dealing with a recording that lacks depth, a high-frequency shelf filter can help to boost the upper frequencies and add more presence to the sound.
Another way to use EQ shelving filters is to shape the frequency response of individual instruments so they sit better in the mix. For instance, let’s say that you have a bass guitar track that is competing with the kick drum for space in the lower frequencies – by cutting the bass frequencies with a high-pass filter and boosting the midrange with a low-shelf filter, you can essentially “carve out” a space for the bass guitar that gives it more clarity and definition.
Advanced Tools And Plugins For Eq Filtering
If you want to take your EQ filtering skills to the next level, you can also consider using advanced tools and plugins that offer more precision and flexibility. One popular plugin is FabFilter Pro-Q 3, which provides a range of EQ filtering options, including per-band mid/side processing, dynamic EQ, and EQ matching. Another plugin worth checking out is Waves F6 Floating-Band Dynamic EQ, which allows you to dynamically adjust the frequency response of individual audio bands based on the level of the signal.
When using advanced EQ tools and plugins, it is important to keep in mind that less is often more. Over-processing can lead to a compromised sound that lacks clarity and focus, so use EQ filtering techniques sparingly and only when needed.
Frequently Asked Questions On How To Use Eq Shelf Filters
How Does Shelf Eq Work?
Shelf EQ works by adjusting the tonal balance of audio material, typically for enhancing the sound of music. By adjusting the levels of low, mid, and high frequencies, shelf EQ can alter the overall sound character, helping to add depth and clarity to the music.
How Do Eq Filters Work?
EQ filters work by adjusting the amount of specific frequencies in an audio signal. They can boost or cut specific frequencies, allowing you to adjust the sound of a recording to your liking. EQ filters can be applied to individual tracks or the entire mix in order to achieve a desired sound.
What Is The Difference Between High Shelf And Low Shelf Eq?
High shelf EQ boosts or cuts high frequencies, while low shelf EQ boosts or cuts low frequencies. High shelf EQ is used to add brightness and clarity to audio, while low shelf is used to add warmth and body. Both affect the overall tonal balance of the audio signal.
What Is The Difference Between Shelf Filter And Notch Filter?
Shelf filter and notch filter are both used in audio processing. The main difference is that a shelf filter adjusts all frequencies above or below a certain point, while a notch filter only affects a specific frequency.
Conclusion
EQ shelf filters serve as a powerful tool for enhancing the overall quality of your audio mix. By selectively reducing or boosting specific frequency ranges, you can significantly improve the clarity and balance of your tracks. Whether you’re a seasoned audio professional or a beginner, mastering EQ shelf filters can help take your audio production to the next level.
So don’t hesitate to experiment and fine-tune your sound until you achieve your desired results. Happy mixing!