Audio compression threshold refers to the level at which a compressor begins to reduce the dynamic range of audio signals. Audio compression is an important tool for helping to control the dynamic range of audio recordings, making them sound clearer and more polished.
The threshold is the level at which the compressor begins to activate its gain reduction process, and it determines how much of the dynamic range of the audio signal is affected by the compressor. We’ll take a closer look at audio compression threshold, what it is, and how it works.
We’ll also explore some of the common uses of audio compression, and provide some tips on how to use compression effectively in your own recordings.
Credit: www.iconcollective.edu
What Is Audio Compression?
Audio Compression is a process that reduces the dynamic range of an audio signal. The threshold is the level at which the compression starts to work. Understanding the compression threshold will help you control the loudness of your audio and ensure a balanced mix.
Dynamic Range Compression Threshold
Audio compression can be defined as a process that reduces the dynamic range of an audio signal. It is a crucial and widely-used technique in the field of audio engineering, enabling audio professionals to achieve a more consistent volume level throughout a recording. Compression is particularly useful in cases where the audio content has a wide dynamic range, such as with live recordings or performances where the volume can vary greatly.
Threshold
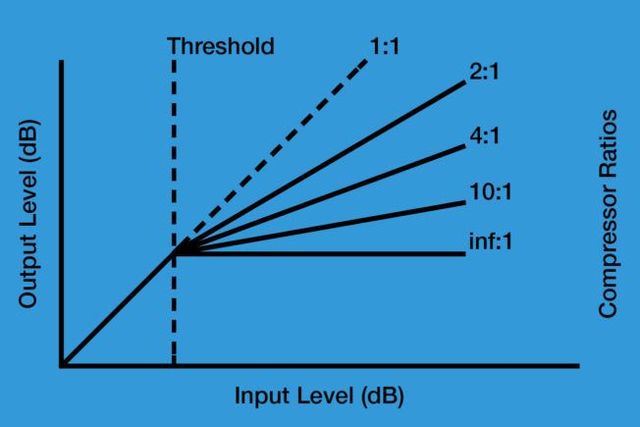
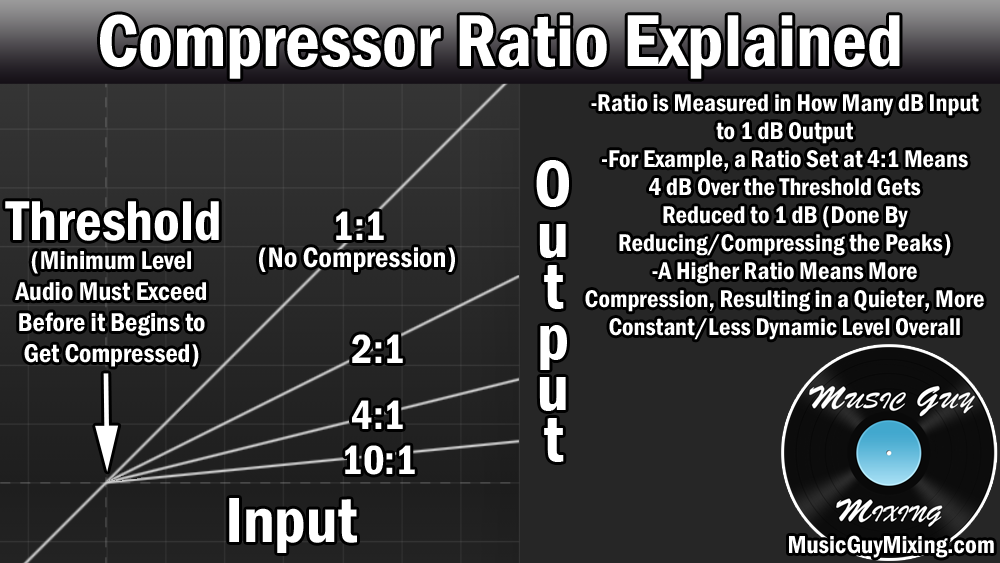
The threshold is one of the most important parameters of audio compression. It determines the point at which the compressor starts to act on the audio signal. Any audio level below the threshold remains uncompressed, while any level above the threshold is attenuated by a certain ratio. The threshold is usually expressed in decibels (dB) and can be adjusted according to the requirements of a particular recording.
Examples Of Thresholds
As a reference, the threshold for vocals is typically set at around -10 dB, while that for drums is around -20 dB. A higher threshold will allow more dynamic range to pass through uncompressed, resulting in a more natural and unprocessed sound. On the other hand, a lower threshold will compress more of the dynamic range, resulting in a more consistent and polished sound.
Final Words
In conclusion, audio compression is a powerful tool for achieving a consistent volume level in audio recordings. The threshold parameter is a crucial aspect of dynamic range compression and can greatly affect the overall sound of a recording. By understanding how the threshold works and experimenting with different settings, audio professionals can achieve a well-balanced and polished sound that meets the requirements of their clients.
Why Is Compression Used In Audio Production?
Audio compression is an essential tool in music production. The process of compression helps to manipulate the dynamics of an audio signal, controlling the levels of both loud and soft sounds in order to achieve a desired sound. It is an integral part of the recording and mixing process, used to ensure that recordings have a balanced and polished sound.
Balance And Clarity
One of the main reasons for using compression in audio production is to achieve a balanced and clear sound. Compression helps to tame the peaks of an audio signal, making the difference between the louder and quieter parts of a track less extreme. This creates a more consistent sound and ensures that no parts of the recording are lost in the mix. By bringing up quieter elements, compression can help to bring out the details and nuances in a song, leading to a more dynamic and exciting final product.
Volume Control
Compression is also often used to control volume and maintain a consistent overall level. By compressing the louder parts of a track, the signal can be brought down to a more manageable level, allowing for more headroom. This means that softer elements of the recording can be brought up without causing distortion or clipping. Compression can also help to prevent individual tracks from getting lost in the mix, making it easier to hear all of the different elements of a song.
Overall, compression is a powerful tool in audio production that helps to create a balanced and polished final product. By controlling the dynamics of an audio signal, compression can help to bring out the details in a recording and make sure that no parts of the mix are lost in the shuffle.
What Is Compression Threshold And How Does It Work?
Audio compression is an important tool for any music producer, sound designer, or audio engineer. Compression threshold is a key element of understanding how audio compression works. It is an important parameter that determines when the audio signal will be compressed, limiting its dynamic range and making the audio sound more consistent.
Definition Of Compression Threshold
The compression threshold is the level at which the compressor begins to work. Once the audio signal reaches the threshold level, the compressor kicks in and starts reducing the volume of the signal. This helps to bring the loudest parts of the audio signal down to a more manageable level, while not affecting the quieter parts of the audio. This can help to even out the overall dynamics of the audio, making it sound more consistent and easier to mix.
Adjusting The Threshold
Adjusting the compression threshold is an important part of using compressors effectively. If the threshold is set too high, the compressor will not engage until the audio signal is too loud, and the dynamic range will not be effectively reduced. On the other hand, if the threshold is set too low, the compressor will be engaged too often, and the audio may sound overly compressed or flattened.
A good starting point for setting the compression threshold is to aim for a gain reduction of around 3-6 dB. This will help to reduce the dynamic range of the signal without overly affecting the audio quality. After setting the threshold, it’s important to monitor the audio output carefully and adjust the settings as necessary.
Conclusion
Understanding compression threshold is an essential part of using compression effectively. By adjusting the threshold and monitoring the output, you can achieve a more even, consistent sound that is easier to mix and master. Keep these tips in mind when working with audio compression to get the most out of your tracks.
Types Of Compression Threshold
Audio compression threshold determines the range above which loud sounds get compressed. The types of compression threshold include hard, soft, and medium, with each type affecting the audio differently.
Understanding the types of compression threshold is crucial for audio engineers and producers. Compression threshold determines the level at which the compressor starts to reduce the dynamic range of an audio signal. There are two types of compression threshold – Soft Knee and Hard Knee.
Soft Knee
Soft Knee compression threshold is achieved gradually. In this case, the amount of gain reduction increases gradually as the input signal level passes the threshold. Soft knee threshold is ideal for situations where a natural, smooth dynamic range reduction is required. It’s perfect for vocals, acoustic guitar, and other instruments that require a smooth transition between quiet and loud parts.
Hard Knee
Hard Knee Compression Threshold is a clear and defined threshold that kicks in abruptly. It starts being effective right from the point when the audio signal hits the threshold. It is best suited for situations that require a more transparent effect, such as drums or percussion. Hard Knee processing is most effective when working with material with a relatively consistent dynamic range.
How Does The Compression Threshold Affect Sound?
The compression threshold refers to the level at which an audio compressor starts to reduce the volume of a signal. Essentially, by setting a compression threshold, you’re telling the compressor to activate only when a certain volume level is exceeded, which can impact the overall sound of your audio.
The compression threshold is a crucial feature in audio recording, mixing, and production. It is the point at which a compressor starts reducing the volume of an audio signal. The compression threshold affects sound in several ways, and it is essential to understand how it impacts audio quality. In this article, we will explore the implications of the compression threshold and how it affects sound.
Reduction Of Dynamic Range
One of the primary ways that the compression threshold affects sound is through the reduction of dynamic range. Dynamic range is the difference between the loudest and softest parts of an audio track, and it is an essential aspect of audio quality. When the compression threshold is low, the dynamic range of the audio signal is reduced. As a result, the loudest parts of the track are quieter, and the softest parts are louder. This can lead to a dull and lifeless sound, which is undesirable in most cases.
Creating A More Consistent Sound
On the other hand, a higher compression threshold results in a more consistent sound. This means that the loudest parts of the track are not significantly louder than the softest parts, and the overall volume is more controlled. A consistent sound can be desirable in some cases, especially when recording vocals, where a consistent volume level is critical.
Impacts On Natural Dynamics
While a consistent sound may be desirable in some cases, it can have significant impacts on natural dynamics. When the compression threshold is high, the natural dynamics of the track are compressed, and the audio can sound unnatural. This is because the compressor is reducing the differences in volume between the loudest and softest parts of the track. This compression can result in a loss of detail and nuance in the audio signal. In conclusion, the compression threshold has a significant impact on audio quality, and it is essential to understand its implications. A low compression threshold can lead to a dull and lifeless sound, while a high compression threshold can result in a loss of detail and nuance. Ultimately, finding the right compression threshold will depend on the specific needs of the audio project, but understanding its impact is crucial to achieving the desired sound.
Tips For Using Compression Threshold
Compression threshold is an essential feature in audio compression that determines the part of a track that needs compressing. Using it effectively can help achieve a balanced and professional sound output. Below are some tips on how to use compression threshold:
Start With A Low Threshold And Ratio
Begin the compression process by setting a low threshold, bagingin at -20db. This ensures that only the louder parts of the track are compressed. The ratio should also be set low, to about 2:1 or 3:1, for a softer compression effect. A lower ratio is necessary, especially when mixing vocals, as it helps to maintain the track’s dynamic range.
Adjust The Threshold To Suit The Track
The nature of the music track dictates the compression threshold that should be used. Use your ears to identify the loudest and quietest parts of the track, and then set the threshold at a level that balances the two. If it’s a drum-heavy track, a higher threshold would be more appropriate, but for a vocal track, a lower compression threshold is required.
Use Your Ears To Determine The Right Balance
After setting the threshold level and the ratio correctly, before hitting the compression button, listen to the track to determine if it sounds balanced. Adjust the compression threshold and ratio accordingly until you achieve the desired result. Remember that every track is unique, and there is no set formula for applying compression. Therefore, it’s essential to trust your ears and experiment to achieve the best sound output.
In conclusion, using compression threshold correctly requires patience and a good ear. Start with a low threshold and ratio, adjust the threshold to suit the track, and use your ears to determine the right balance.
Common Mistakes When Using Compression Threshold
Setting the compression threshold can be a tricky task, and some common mistakes are often made. One of the most common mistakes is setting the threshold too low, resulting in over-compression and a loss of dynamic range. It is important to carefully consider the desired effect and adjust the threshold accordingly.
When it comes to audio compression, setting the threshold is crucial. The threshold determines the level at which the compressor kicks in and starts reducing the volume of the audio signal. However, many people make some common mistakes when using compression threshold. Here are some of them:
Over-compression
One of the most common mistakes people make when using compression threshold is over-compressing the audio signal. Over-compression can result in a lack of dynamics and a loss of natural sound. It can also make the audio sound squashed and lifeless. It’s important to find the right balance when setting the compression threshold, so that the audio remains dynamic and natural-sounding while still being controlled.
Setting The Threshold Too High/low
Another mistake people make when setting compression threshold is setting it too high or too low. If the threshold is set too high, only the loudest parts of the audio will be compressed, while quieter parts will remain untouched. This can result in inconsistent volume levels and an unbalanced mix. On the other hand, if the threshold is set too low, the compressor will kick in too often, compressing almost the entire audio signal. This can result in a lack of dynamics and an unnatural sound. To avoid these mistakes, it’s important to find the sweet spot where the compression is applied consistently across the entire audio signal, while still preserving the natural dynamics of the sound. In conclusion, setting compression threshold correctly is essential to achieving a well-balanced and controlled audio signal. By avoiding these common mistakes, you can ensure that your audio sounds natural, dynamic and professional.
Credit: theproaudiofiles.com
Credit: www.musicguymixing.com
Frequently Asked Questions Of Audio Compression Threshold Explained
What Should My Compression Threshold Be?
Your compression threshold should be set based on the specific needs of your website and its visitors. In general, it is recommended to set it between 60-80% to balance file size and image quality. It’s important to regularly analyze and adjust your compression settings to ensure optimal performance.
What Is The Threshold Of Audio Compression?
The threshold of audio compression is the point at which the compressor begins to affect the volume of the audio being processed. It is the level at which the compressor reacts, reducing the volume of the audio when it exceeds the threshold.
What Is A Good Compressor Setting For Audio?
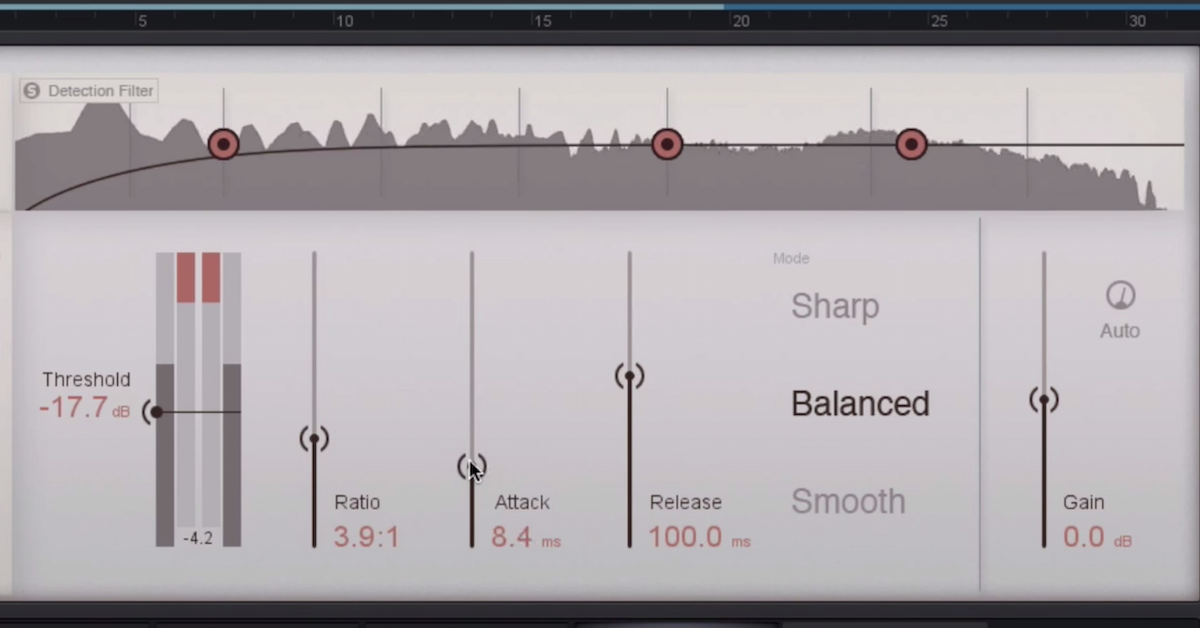
The ideal compressor setting for audio depends on the type of audio you are compressing. Generally, the ratio should be set between 2:1 to 4:1, the threshold should be set just below the peak level of the audio, attack should be set between 5-30ms, and release should be set between 100-300ms.
It’s best to experiment with different settings to find what sounds best for your particular audio.
What Is A Low Threshold Compressor?
A low threshold compressor is a type of compressor that uses a lower starting pressure compared to other types of compressors. This means that the compressor will start working at a lower pressure rather than waiting for a higher pressure to build up.
This makes it useful for applications where there is a requirement for low pressure air.
Conclusion
As we have seen, audio compression thresholds play a crucial role in determining the quality and loudness of a sound. Understanding compression and how it works is essential for any audio enthusiast, musician, or sound engineer. By manipulating the audio compression threshold, you can achieve a balanced and defined sound that is pleasing to the ears.
To truly master the art of compression, it’s essential to study its different parameters and how they interact. Get creative and experiment with different settings to find your unique sound signature. With dedication and practice, you can become an expert in audio compression and take your music to the next level.