Audio compression is the process of reducing the dynamic range of an audio signal. It helps to keep the overall volume of a recording consistent and prevent distortion.
Audio compression is an essential element of music production, podcasting, and broadcasting. It is the process of reducing the dynamic range of an audio signal by decreasing the volume of loud sounds and increasing the volume of quiet ones. The dynamic range is the difference between the loudest and quietest parts of an audio recording, and compression helps to keep it in check.
Compression can also help to improve the clarity and punchiness of a recording, and to prevent distortion caused by overly loud signals. This article will explain the basics of audio compression, including how it works, why it is important, and how it is used in various contexts.

Credit: splice.com
What Is Audio Compression?
If you are new to audio engineering, you might have heard the term “compression” without knowing what it is. Compression is an important tool that audio engineers use to help smooth out levels and ensure that dynamics are consistent. Here is a closer look at what audio compression is, how it works, and why it is important.
Dynamic Range
When it comes to music, dynamic range is defined as the difference between the quietest and loudest parts of a track. Dynamic range provides the necessary contrast in a recording and can make the difference between an engaging listening experience and a monotonous one.
However, if dynamic range is too wide, it can make it difficult to hear certain parts of a track. This is where audio compression comes in. Audio compression helps to balance the dynamics of a track, bringing quieter sounds up and limiting the highest peak volumes. This results in a more consistent listening experience and makes it easier to hear each individual part of a track.
Why Is It Important?
Simply put, audio compression is important for two main reasons: level control and tone shaping. Compression allows engineers to control the levels of individual tracks, reducing the dynamic range and ensuring that each part is audible. Compression can also be used for tone shaping, highlighting certain frequencies while compressing others to achieve a specific sound.
Compression is particularly useful when working with vocals or drums, as these tracks can have a lot of dynamic range. By carefully compressing these tracks, engineers can bring out the best in the performance and help it sit better in the mix.
Overall, audio compression is an essential tool for any audio engineer. By providing level control and tone shaping, it ensures that tracks have a consistent, enjoyable sound that engages listeners and highlights the best parts of the performance.
Credit: www.musicguymixing.com
Different Types Of Audio Compression
Audio compression is a technique used to reduce the size of audio files without compromising the quality. There are two main types of audio compression: lossless and lossy. The former retains all the original data while the latter diminishes the quality in order to decrease the file size.
When it comes to audio compression, there are two main types: analog and digital compression. Analog compression dates back to the early days of recording, while digital compression is a more modern technique that has gained popularity in recent years. Let’s take a closer look at each type and how they work.
Analog Compression
Analog compression involves using a physical device, such as a compressor or limiter, to control the dynamic range of a recorded audio signal. The device applies a varying amount of gain reduction to the audio signal based on the input level, resulting in a more consistent output level. This type of compression is often used to add warmth and character to recordings, particularly in genres like rock, blues, and jazz.
Digital Compression
Digital compression, on the other hand, uses mathematical algorithms to reduce the dynamic range of an audio signal. Unlike analog compression, which can add coloration and texture to a recording, digital compression is designed to be transparent and minimize any audible artifacts. There are various types of digital compression, including peak, RMS, and multi-band compression, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. Overall, both analog and digital compression are important techniques used in audio recording and mixing. By understanding the different types of compression available, you can choose the right tools and settings to achieve the desired sound for your project.
Understanding The Audio Compression Process
Understanding the audio compression process is essential to achieve professional-quality audio productions. Audio compression is the most commonly used audio processing technique and has been an essential tool in music production for many decades. It has played a pivotal role in making radio and television broadcasts sound even better. Understanding the various aspects of audio compression, including the threshold, ratio, attack, and release, is crucial to achieving high-quality audio production.
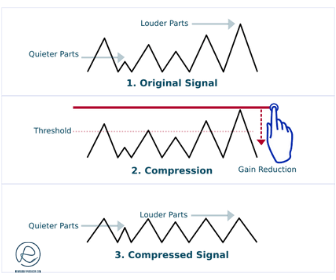
Threshold
The threshold is the level at which the audio compressor starts working. It is the point where the signal is too loud. A compressor only works when the input signal exceeds a certain threshold level. The threshold control typically ranges from -60 dB to 0 dB. The lower the threshold, the more the compressor will be applied to the signal. If the threshold is set too high, the compressor will not work, and the sound will not be compressed.
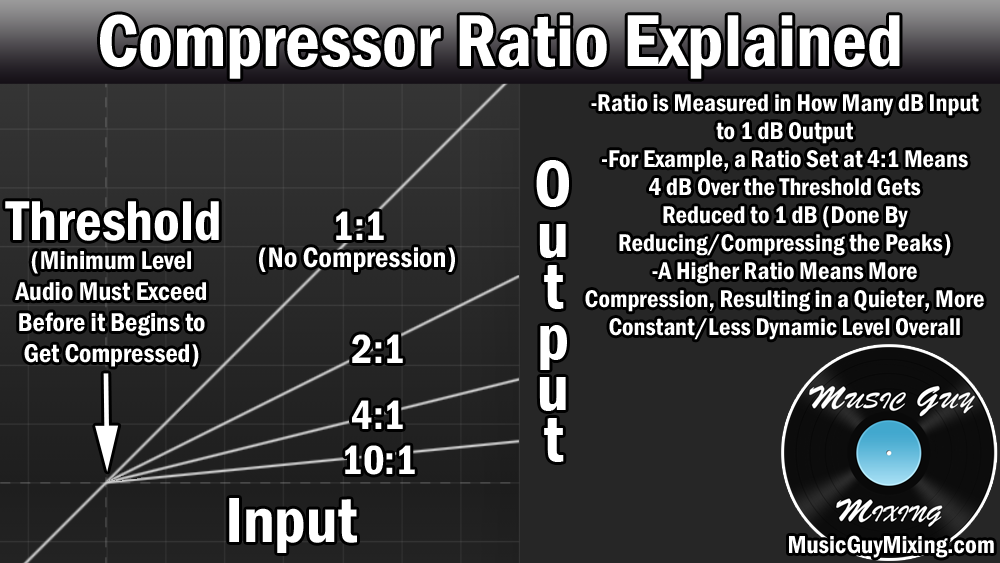
Ratio
The ratio determines the amount of sound compression applied when the signal exceeds the threshold level. The ratio is usually set as a decimal, such as 2:1, 4:1, or 10:1, with the first number indicating the level of input sound, while the second number indicates the level of output sound. For example, a 2:1 ratio means that if the input signal is 2 dB above the threshold, the output signal will be only 1 dB above the threshold.
Attack And Release
The attack and release are two essential parameters of an audio compressor. The attack controls how quickly the compressor starts working once the threshold is exceeded, while the release determines how long it takes for the compressor to stop working when the signal goes below the threshold level. The attack and release times are expressed in milliseconds, and setting them correctly can make a significant difference in the audio quality.
Understanding the different aspects of audio compression is crucial in achieving professional-quality audio. The threshold, ratio, attack, and release controls are all essential in achieving the desired compression effect. Therefore, choose the right settings of these controls based on your audio requirements.
Common Audio Compression Techniques
Audio compression is one of the most critical aspects of sound engineering. Audio compression techniques are often used to improve the quality of an audio track or mix. It helps in reducing the dynamic range of sound in a recording. This process involves decreasing the volume of the loud sounds and increasing the volume of the quiet sounds. Several audio compression techniques are used in the music production industry to achieve this.
Parallel Compression
Parallel compression is a technique where the compressed signal is mixed with the original signal. It is used to create an audio effect that would not have been possible by merely using traditional compression techniques. The process involves creating a compressed copy of the original track and blending it with the original signal. The mix is adjusted to the desired tonal balance, which results in a more natural-sounding mix.
Multi-band Compression
Multi-band compression is a technique that involves dividing an audio signal into several frequency bands, compressing each band separately, and then recombining the bands. This technique allows for more specific control over the compression process, making it possible to apply different compressors to different frequency ranges. Multi-band compression is used to solve issues related to uneven dynamics or frequency response in a recording. It is particularly helpful in mastering a mix where every frequency range requires specific attention.
Applications Of Audio Compression
Audio compression is a key technique which reduces the size of digital audio files while maintaining sound quality. It can be implemented in various applications such as music streaming, podcasting, radio broadcasting, and more. The compression is done by adjusting the dynamic range of audio, resulting in a more efficient and streamlined experience for both producers and consumers.
Audio compression is a technique used to reduce the dynamic range of audio signals. It has numerous applications in various industries where high-quality audio is required. In this article, we will discuss the most common applications of audio compression, including music production and broadcasting.
Music Production
Audio compression is an essential tool in music production. It helps to ensure that all parts of a track are audible and balanced. For example, when recording a bass guitar, the notes played on the lower frets can be much quieter than those on the higher frets. Applying compression to the bass track evens out the volume, making every note audible. Audio compression is also used during the mixing and mastering stages of music production. During mastering, the final mix is compressed to ensure that it sounds consistent across different playback devices and environments. Without compression, some elements of the mix may be too quiet or too loud, making the final product sound unprofessional.
Broadcasting
Audio compression is crucial in broadcasting because it ensures that the sound stays within a specific loudness range. This is important because if there are sudden increases or decreases in volume, it can be jarring for the listener. Compression is applied to all audio that is broadcast, whether it’s music, speech, or sound effects. This ensures that everything sounds balanced, and the listener doesn’t have to constantly adjust the volume. Furthermore, different types of broadcasting require different levels of compression. For example, radio broadcasters use more compression than television broadcasters because the listener is usually further away from the speakers. In conclusion, audio compression is an integral part of music production and broadcasting. It helps to balance and even out the audio, ensuring that every part of the mix is heard clearly and consistently. Whether you are a musician, broadcaster, or sound engineer, understanding audio compression is essential for producing high-quality audio.
Credit: www.renegadeproducer.com
How To Use Audio Compression
Audio compression is a technique used to reduce dynamic range, making quieter sounds louder and louder sounds quieter. This helps to create a more consistent audio level and prevent distortion in recordings. Compression settings can vary depending on the desired effect and the specific audio source.
Audio compression is an essential tool to help level and enhance the quality of a recording. Proper use of audio compression can make all the difference in the final outcome of an audio track. In this section, we will discuss how to use audio compression by setting the threshold, adjusting the ratio, and other important tips and tricks.
Setting The Threshold
Setting the threshold is the first step in using audio compression. The threshold is the level at which the compressor begins to engage, lowering the volume of the audio signal. It is important to set the threshold at the right level to get the desired effect. If the threshold is too low, the compressor will be engaged too often and the audio may sound over-compressed. On the other hand, if the threshold is too high, the compressor may not engage enough, and the audio may sound uneven. A general rule of thumb is to set the threshold around the peak level of the audio track.
Adjusting The Ratio
The ratio is another important setting in audio compression. The ratio determines the amount of volume reduction that occurs when the audio signal exceeds the threshold. A higher ratio will result in more volume reduction, while a lower ratio will provide less reduction. Adjusting the ratio can help level out the audio signal and make it sound more even. However, it is important to use the ratio sparingly, as too much compression can make the audio sound unnatural and squashed.
Other Tips And Tricks
In addition to setting the threshold and adjusting the ratio, there are several other tips and tricks for using audio compression effectively. These include:
- Using a fast attack time to allow the compressor to engage quickly when the audio signal exceeds the threshold.
- Using a slow release time to prevent the compressor from releasing too quickly and reducing the desired effect.
- Using makeup gain to boost the overall level of the audio track after compression.
- Avoiding over-compression by using compression sparingly and making adjustments as needed.
By following these tips and tricks, you can use audio compression to enhance the quality of your recordings and make them sound more professional.
The Pros And Cons Of Audio Compression
Audio compression can improve the overall sound quality of music by reducing file size and providing consistency in volume levels. However, it can also result in loss of dynamic range and clarity in sound. It’s crucial to weigh the pros and cons before using audio compression techniques.
When it comes to audio compression, there are pros and cons that must be considered. Audio compression is often used in music production to even out the levels of different instruments, vocals, and frequencies to make it sound more balanced. Here are some of the benefits and drawbacks of audio compression:
Benefits
- Helps to even out the levels of different instruments and frequencies, making the overall sound more balanced.
- Allows for greater control over dynamics and can make a song sound more polished and professional.
- Improves the overall loudness of the audio, making it more audible.
Drawbacks
- Can result in a loss of sound quality and dynamics if overused.
- May flatten the natural dynamics of the audio, making it sound less expressive and lively.
- Can result in pumping and breathing artifacts, where the audio level jumps up and down unexpectedly.
Overall, audio compression can be a useful tool in music production when used correctly and sparingly. It can help to even out the levels and improve the overall sound quality of the audio. However, it is important to be aware of its drawbacks and use it with caution to avoid negatively affecting the dynamics and natural expression of the music.
Frequently Asked Questions Of Audio Compression Explained
Does Compressed Audio Sound Better?
Compressed audio is not necessarily better in terms of sound quality. While it can save space and bandwidth, it can also result in a loss of audio data and a reduction in sound quality. Higher bit rates and lossless compression can help mitigate this, but ultimately the quality depends on the initial recording and the compression used.
What Is The Explanation Of Audio Compression?
Audio compression is the process of reducing the size of an audio file without significantly compromising its quality. It works by removing data that is not essential to the overall sound, thereby making the file smaller and easier to stream or store.
Audio compression can have a significant impact on the quality of recorded music or voice recordings.
When Should You Compress Audio?
Audio compression should be done when the file is too large to be easily streamed or downloaded, or when certain frequencies are too loud or soft. Compression reduces the file size and makes it easier to handle, but may also result in a loss of audio quality.
What Is The Best Compression Ratio Audio?
The best compression ratio for audio depends on the specific purpose and application. Lossless compression techniques, such as FLAC and ALAC, maintain the original audio quality. For streaming or online distribution, lossy compression such as MP3 or AAC with a compression ratio of 128kbs or higher is commonly used.
Conclusion
Audio compression can make a huge difference to the overall sound quality of your audio files. It reduces the dynamic range, making it easier for listeners to hear all parts of the recording. Types of compression vary depending on the level of compression required, and whether the audio is for live performance or recording.
However, it’s important to remember that compression should be used appropriately and not overdone to avoid compromising on sound quality. Overall, understanding audio compression is an important skill for any audio professional or enthusiast.