Audio compression reduces the size of digital audio files without sacrificing sound quality, making it easier to store and transmit audio data. Compression algorithms use mathematical techniques to remove redundant or irrelevant audio data from the file while preserving the essential parts, resulting in a smaller file size.
Audio compression is a crucial component of digital audio technology that has revolutionized the way we store, share, and transmit audio data. With compression, we can store a vast library of music on a portable device or stream high-quality audio over the internet in real-time.
We’ll explore the fundamentals of audio compression, the different compression algorithms commonly used in the industry, and the pros and cons of compression on audio quality. We’ll also answer common questions about compression, such as how it works, the impact of compression on file size and sound quality, and how to choose the right compression settings for your audio needs.
What Is Audio Compression?
Audio compression is the process of reducing the dynamic range of an audio signal. This allows for more consistent levels and saves storage space. By compressing a recording, you can make sure that the quiet parts are audible, and the loud parts are adjusted to a reasonable level, without overloading the audio.
Explaining Audio Compression
Audio compression is a process used to reduce the size of digital audio files, making them easier to store and transmit. It involves compressing the dynamic range and removing unnecessary data from an audio signal. By doing this, audio files can be made smaller without compromising on sound quality. Audio compression can be either lossless or lossy. Lossless compression preserves the quality of the original audio file despite its smaller size. On the other hand, lossy compression achieves smaller file sizes by “throwing away” some of the data in the audio signal, which can result in a slight loss in sound quality.
Benefits Of Audio Compression
There are many benefits to using audio compression, including:
- Smaller file sizes: compressed audio files take up less space on your computer or mobile device.
- Reduced bandwidth usage: compressed audio files can be transmitted more quickly over networks with limited bandwidth.
- Better streaming performance: by reducing the size of audio files, they can be streamed more smoothly.
- Easier to share: compressed audio files can be shared more easily via email, social media, or other online platforms.
- Improved sound quality: while lossy compression may result in a slight reduction in sound quality, most listeners can’t tell the difference.
Audio compression has become an essential tool in the creation and distribution of digital audio content. It allows for more efficient storage, smoother streaming, and easier sharing of audio files. Whether you’re a musician, podcaster, or music lover, audio compression can help you get more out of digital audio technology.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Types Of Audio Compression
Types of audio compression are used in music, film, and other forms of audio productions to control the dynamic range of sound. Lossless and lossy compressions are the two major types of compression techniques. Both help reduce the file size while maintaining sound quality to an extent.
Audio compression is the process of reducing the size of digital audio files so they take up less storage space while still retaining the quality of the original recording. There are two main types of audio compression: Lossless Audio Compression and Lossy Audio Compression. Both types have their own characteristics that make them suitable for different purposes.
Lossless Audio Compression
Lossless audio compression is a method of reducing file size without losing any data from the original recording. In this process, the audio file is compressed and then decompressed, resulting in exactly the same file as the original. This means that the audio quality is not compromised in any way. Lossless compression is widely used in audio recording and editing, where every detail of the original recording is important, and no data loss is acceptable.
Lossy Audio Compression
Lossy audio compression is a method of reducing file size that involves discarding some data from the original file. This process reduces the quality of the audio but typically results in a much smaller file size. Lossy compression is widely used in music streaming services and digital audio distribution, where small file size is essential to reduce bandwidth usage and improve the user experience. The amount of data discarded depends on the level of compression chosen, with higher compression levels resulting in smaller file sizes but lower audio quality. In summary, the choice of audio compression method depends on the intended use of the audio file. If quality is essential, lossless compression is the best choice, whereas lossy compression is more suitable for scenarios where small file sizes are necessary.
How Audio Compression Works
Audio compression is the process of reducing the size of digital audio files while maintaining audio quality. Compression works by removing parts of the audio file that are less important to the listener’s perception of sound. This process allows for faster transmission of the file over the internet and helps reduce storage space. In this section, we will discuss the basics of audio compression algorithms and the difference between hardware and software compression.
Basics Of Audio Compression Algorithms
The purpose of audio compression algorithms is to reduce the size of audio files by removing redundant data while retaining the quality of the sound. There are two types of audio coding algorithms: lossy and lossless. The lossy algorithms remove the audio data that is less important to the listener, while the lossless algorithms only remove the data that is not necessary for reconstructing the original audio signal.
| Lossy Algorithm | Lossless Algorithm |
|---|---|
| MP3 | FLAC |
| AAC | ALAC |
| Ogg Vorbis | Monkey’s Audio |
Lossy algorithms are used more frequently since they produce smaller files that are easier to transmit and download over the Internet. Most popular audio file formats like MP3, AAC, and Ogg Vorbis use lossy algorithms.
Hardware Vs. Software Compression
Hardware-based compressors are dedicated devices that provide real-time processing to control the dynamics of audio signals. Software compressors, on the other hand, work on digital audio signals and can be run on any device capable of running audio software. Software-based compressors are widely used in music production, while hardware compressors are used more in live sound situations.
- Hardware-based compressors can provide analog warmth to audio signals, while software compressors can achieve perfect precision.
- Hardware-based compressors are more expensive, while software compressors are available for free or at a lower cost.
- Hardware-based compressors have physical controls, while software compressors are controlled through a computer interface.
In conclusion, audio compression is an essential tool for reducing the size of digital audio files while maintaining quality. Lossy and lossless compression algorithms are vital in achieving this, and hardware and software compressors each offer their unique advantages in music production and live sound situations.
Common Audio Compression Formats
Audio compression formats are used to reduce the size of digital audio files without compromising sound quality. Some common audio compression formats include MP3, AAC, and Ogg Vorbis. These formats make it easier to store and share music files online.
Audio compression formats are used to reduce the size of audio files, making it easier and faster to transfer and store them. There are several audio compression formats available, each with its own features and uses. In this section, we’ll discuss some of the most common audio compression formats.
Mp3
MP3 is the most widely used audio compression format. It’s a lossy format, which means that some information is lost when the audio is compressed. However, the level of compression can be adjusted, allowing you to balance file size and sound quality. MP3 files can be played on almost any device, making them a popular choice for music distribution.
Aac
AAC is another widely used audio compression format. Like MP3, it’s a lossy format, but it typically provides better sound quality at the same level of compression. AAC files are often used for streaming audio and video content online, as well as for digital music downloads.
Flac
FLAC is a lossless audio compression format, meaning that no information is lost when the audio is compressed. This results in higher-quality sound than lossy formats like MP3 and AAC. FLAC files are significantly larger than other compression formats, but they’re often used by audiophiles and music enthusiasts who demand the highest possible sound quality.
Alac
ALAC is a lossless audio compression format developed by Apple. It’s similar to FLAC in that no information is lost when the audio is compressed. ALAC files are typically used on Apple devices and within the Apple ecosystem, but they can be played on other devices as well.
Wav
WAV is a common uncompressed audio format that doesn’t use compression at all. This results in the highest possible sound quality, but at the cost of file size. WAV files are often used by professionals who need to work with high-quality audio. They’re also a popular choice for music production and mastering. In conclusion, there are several audio compression formats available, each with its own benefits and drawbacks. Whether you’re a music enthusiast, a professional, or just looking to store or transfer audio files, it’s important to choose the right format for your needs.
Factors To Consider When Choosing An Audio Compression Format
When it comes to choosing a compression format for your audio files, it’s important to consider a few factors to ensure that you choose the best option for your needs. The three main factors that you should consider are the quality vs. file size, compatibility, and application.
Quality Vs. File Size
One of the main decisions that you’ll need to make when choosing an audio compression format is whether you prioritize quality or file size. If you want to maintain the highest possible audio quality, you’ll need to choose a format that doesn’t compress the file too much. However, this will result in larger file sizes. On the other hand, if you need smaller file sizes, you’ll need to choose a format that compresses the audio more, but this may result in some loss of quality.
Compatibility
Another important factor to consider when choosing an audio compression format is compatibility. Not all formats are compatible with all devices and software, so if you plan to share your files or use them on multiple devices, it’s important to choose a format that is widely supported. Some popular audio compression formats that are widely supported include MP3, WAV, and AIFF.
Application
The third factor to consider when choosing an audio compression format is application. Depending on how you plan to use your audio files, you may need to choose a specific format to ensure compatibility. For example, if you’re creating audio for a podcast, you may need to choose a format that is optimized for streaming, while if you’re creating audio for a video production, you may need to choose a format that is compatible with the video editing software that you’re using.
Overall, when choosing an audio compression format, it’s important to consider the quality vs. file size, compatibility, and application to ensure that you choose the best option for your needs.
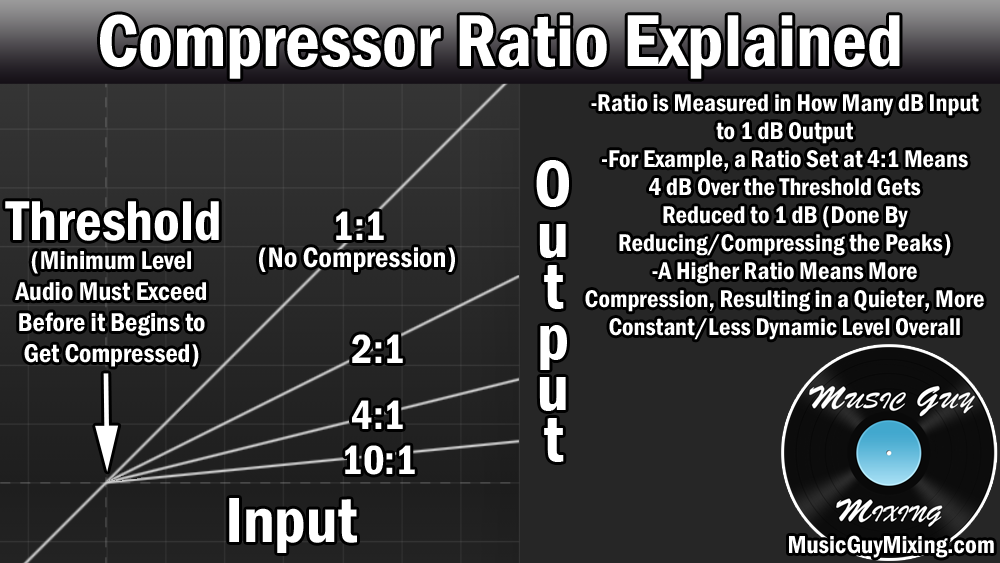
Credit: www.musicguymixing.com
Tools For Audio Compression
When it comes to audio compression, there are a variety of tools available to help you get the job done. Whether you prefer to use an audio editing software or an online compression tool, it’s important to choose the right tool based on your needs and level of expertise. Let’s take a closer look at some of the top tools for audio compression.
Audio Editing Software
If you’re looking to edit your audio files before compressing them, an audio editing software may be the way to go. With an editing software, you can manually adjust the settings to achieve the desired sound quality and compression ratio.
Some popular audio editing software options include:
| Software | Price | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Audacity | Free | – Cross-platform – Open-source – Easy to use |
| Adobe Audition | $20.99/month | – Advanced editing tools – Multi-track mixing – Integration with other Adobe software |
| Logic Pro X | $199.99 | – Professional-grade mixing and mastering – Built-in effects and instruments – Mac-only |
Online Audio Compression Tools
If you’re looking for a quick and easy way to compress your audio files without the need for specialized software, an online audio compression tool may be the right choice for you.
Here are some popular online audio compression tools:
- AudioAlter: Free, easy to use, no need to sign up.
- YouCompress: Free, supports a wide range of audio file types, simple and user-friendly interface.
- Online Audio Converter: Free, supports batch conversion, allows you to adjust audio settings.
Whether you choose an audio editing software or an online compression tool, it’s important to experiment with the settings to find the optimal compression for your audio files. With the right tools and a bit of practice, you can achieve professional-quality results and take your audio projects to the next level.
Best Practices For Audio Compression
Audio compression is the process of reducing the file size of an audio file without losing its quality. However, applying too much compression can cause distortion and artifacts. That’s why applying compression is an art that requires following certain best practices. Here, we have listed some essential guidelines for audio compression that will help you preserve the audio quality while reducing its size.
Choosing The Right Compression Format
Choosing the right compression format is essential for audio compression. Different formats use different algorithms to compress audio. Lossy compression formats like MP3, AAC, and Ogg Vorbis remove some data from the audio file to reduce its size. On the other hand, lossless formats like FLAC and WAV use complex algorithms to compress an audio file without losing any data. While lossy formats sound good, they can cause some loss of quality. Therefore, it is important to choose the right format depending on your requirements.
Applying Compression Settings
After choosing the right compression format, the next step is to apply the compression settings carefully. Compression settings include bit rate, sample rate, and codec type. This is where you can control how much compression is being applied to the audio file. Keep in mind that lower bit rates or sample rates result in smaller file sizes, but they also reduce the audio quality. Therefore, it is crucial to apply the compression settings carefully to get the desired file size without losing the audio quality.
Preserving Audio Quality
While compressing audio files, it’s essential to preserve the audio quality. This can be achieved by avoiding excessive compression, applying the compression settings carefully, and using a high-quality compression codec. You can use some tools like sound editors and dynamic range processors to reduce the peak levels of the audio file before compressing it. This will help maintain the audio quality, making it sound more pleasant to the listeners.
By following these best practices, you can compress your audio files to a smaller size without losing its quality. Keep in mind that proper audio compression requires attention to detail and careful consideration of all the aspects related to it.
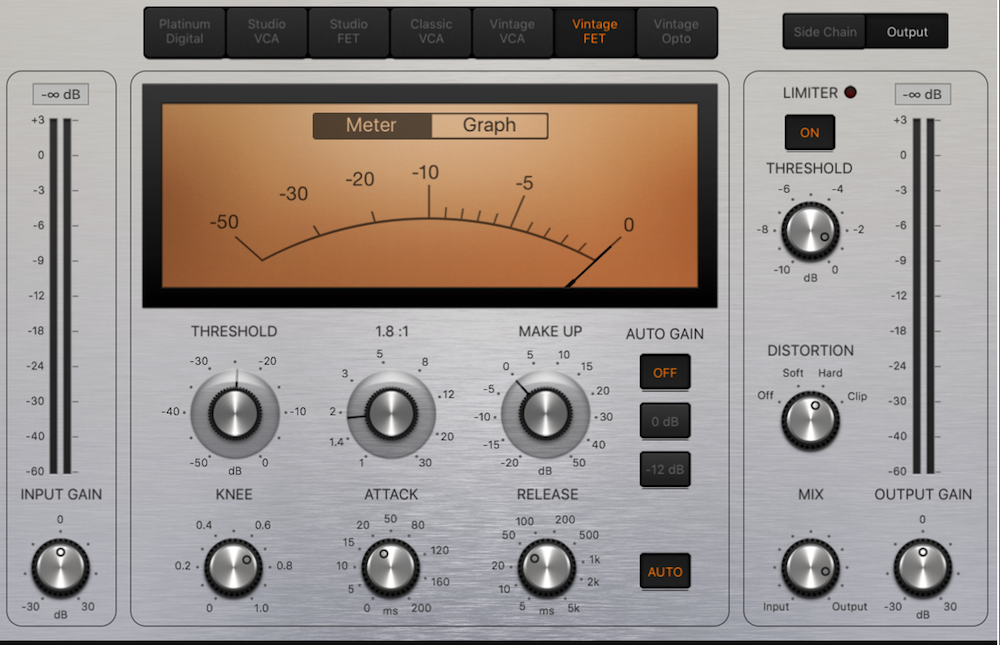
Credit: producelikeapro.com
Frequently Asked Questions Of Audio Compression Easy To Understand
What Is Audio Compression In Simple Terms?
Audio compression is a method of reducing the size of digital audio files without significantly affecting their quality. It is achieved by removing unnecessary data or using algorithms to minimize the amount of information stored. This allows for more efficient storage and faster transmission of audio files.
How Do You Explain Compression?
Compression is the process of reducing the size of a file or data without losing any significant information. It is achieved by removing redundant, irrelevant or unused data from the file or data which results in a smaller size. This makes it easier to transmit or store the file or data, making it faster and more efficient to use.
What Are The Advantages Of Audio Compression?
Audio compression improves data storage, network bandwidth, transmission speed, and enhances sound quality by reducing unnecessary or redundant bits in an audio signal. Compression also allows more audio files to fit into a smaller storage space without losing quality.
What Is The Common Technique To Compress Audio?
The most common technique to compress audio is through the use of lossy algorithms such as MP3 or AAC. These algorithms discard some of the audio data that is perceived as less important by the human ear, resulting in smaller file sizes without significant loss in quality.
Other techniques include lossless compression and dynamic range compression.
Conclusion
Audio compression is an essential tool for any audio engineer or producer. It allows for a better sonic experience and enables the listener to hear all aspects of the music. Understanding the principles of compression and how to use it effectively is key to achieving a high-quality sound.
Experiment with different settings and listen carefully to your results until you find the perfect balance for your project. With this guide, you now have the knowledge to master the art of audio compression and create amazing music.