The audio sample rate and bit depth define the quality of digital audio recordings. This guide provides an overview of the technical aspects and importance of choosing the right settings for audio production.
Audio production requires a fundamental understanding of digital audio processing and how parameters like sample rate and bit depth can impact the final result. Whether you are a beginner or a seasoned professional, having a comprehensive understanding of these settings can significantly improve your audio quality.
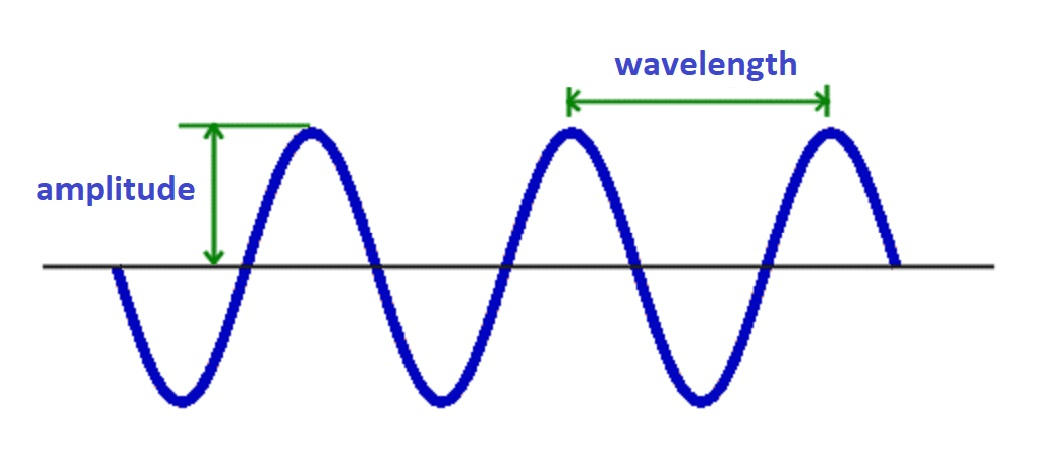
Sample rate refers to the number of digital audio samples captured per second, while bit depth determines the resolution of each sample. Choosing the appropriate audio settings allows for the preservation of audio quality, minimizing distortion and noise in the final product. This guide aims to provide a complete overview of audio sample rate and bit depth, including their technical aspects, and the impact on audio quality.
Credit: majormixing.com
What Is Audio Sample Rate
What Is Audio Sample Rate:
Audio sample rate refers to the number of samples of audio carried per second. In simpler terms, it is the rate at which an audio signal is measured, recorded, or played back. The sample rate determines the quality of an audio recording.
Definition Of Audio Sample Rate
Audio sample rate can be defined as the number of samples of audio carried per second. In digital audio, an analog audio signal is converted into a digital signal by taking several “samples” of the analog signal at regular intervals. These samples are then played back at the same rate to reproduce the original audio signal.
How Audio Sample Rate Is Measured
The audio sample rate is measured in Hertz (Hz). A sample rate of 44.1 kHz is commonly used for consumer audio, while higher sampling rates (e.g., 96 kHz) are used for professional audio applications.
Why Audio Sample Rate Is Important
Audio sample rate is important because it determines the audio quality of a recording or playback. The higher the sampling frequency, the better the quality of the audio recording. This is because higher sampling rates capture more detailed and accurate information about the audio signal.
However, a high sampling frequency also results in larger audio files, which can take up more storage space and may require more processing power to edit or playback.
Credit: www.yololiv.com
Understanding Bit Depth
Understanding bit depth is a crucial aspect of audio sampling rate. It refers to the number of bits of information contained in each audio sample. This complete guide will help you comprehend how to balance bit depth with other aspects of audio quality.
Understanding Bit Depth If you are a budding music producer, engineer, or audio enthusiast, you may have heard the term “bit depth”. Bit depth is an essential aspect of digital audio and is crucial to achieving clarity and precision in your recordings. In this article, we’ll dive into bit depth, what it is, and why it matters. Definition of Bit Depth Bit depth refers to the number of bits of information used to represent each sample in a digital audio file. It basically determines how accurately the recorded waveform conforms to the original sound wave. The more bits used for each sample, the more accurately the digital recording represents the original source. Types of Bit Depth There are two common types of bit depth in digital audio recording, namely 16-bit and 24-bit. 16-bit audio has a total of 65,536 possible values for each sample, while 24-bit audio has 16,777,216 possible values per sample. In other words, 24-bit audio has significantly more resolution and dynamic range since it can represent a broader range of amplitude levels. Why Bit Depth is Important Bit depth is crucial as it determines how much detail and clarity your recordings will have. As you increase the bit depth, your recording becomes more accurate and less susceptible to digital noise. In addition, bit depth affects the overall dynamic range of your recording. A higher bit depth allows for a more prominent dynamic range, resulting in more precise and nuanced recordings. In conclusion, understanding bit depth is vital when it comes to achieving high-quality digital audio recordings. It determines how accurately a waveform conforms to an original sound wave, and it affects the overall clarity, detail, and dynamic range of your recording. Always ensure you use the right bit depth when recording audio; this is crucial to achieving professional-quality recordings.
Choosing The Right Audio Sample Rate
Choosing the appropriate audio sample rate is critical to the quality of your audio recordings. A higher sample rate provides better quality sound, but requires more storage space. A lower sample rate might save storage space, but produces lower quality audio.
When it comes to audio recording, one of the most important decisions you’ll make is selecting the right sample rate. The sample rate determines the quality of your audio, and choosing the right one can make all the difference. In this guide, we’ll explore the factors to consider when choosing audio sample rate, common audio sample rates, and the intended use of audio and sample rate.
Factors To Consider When Choosing Audio Sample Rate
Before choosing an audio sample rate, it’s important to understand the factors that influence your decision. The following are some factors to consider:
- Intended Use: The primary factor to consider is the intended use of your audio. For instance, if you’re recording for podcasts, a sample rate of 44.1 kHz would be suitable. For music production, a higher sample rate of 96 kHz or 192 kHz is preferred.
- Storage Space: Another factor to consider is the size of the audio file. Higher sample rates require more storage space than lower sample rates. Therefore, you need to balance the audio quality you require and the storage space available.
- Computing Power: Higher sample rates require greater computing power to process. If your computer is not powerful enough to handle higher sample rates, you may experience lagging and dropped frames.
Common Audio Sample Rates
The following are some of the most common audio sample rates and their respective uses:
| Sample Rate | Use Case |
|---|---|
| 44.1 kHz | CD Audio, Podcasting, Online Streaming, and Television. |
| 48 kHz | Digital Video, DVD, and Digital Television. |
| 96 kHz | Professional Music Production, Film, and Video Game Sound. |
| 192 kHz | Music and High-Resolution Audio. |
Intended Use Of Audio And Sample Rate
Choosing the right audio sample rate largely depends on your intended use. For instance, if you’re recording audio for YouTube videos or podcasts, a sample rate of 44.1 kHz should suffice. For professional music production or high-resolution audio, a higher sample rate of 96 kHz or 192 kHz is preferred. By understanding the intended use of your audio, you can select the right audio sample rate that guarantees the quality of your audio. In conclusion, choosing the right audio sample rate is crucial in determining the quality of your audio. By understanding the factors to consider when selecting the right audio sample rate, common audio sample rates, and the intended use of the audio, you can make an informed decision.
Credit: www.gumlet.com
Choosing The Right Bit Depth
Selecting the appropriate bit depth is an essential consideration for high-quality audio recordings. The bit depth indicates the precision of the audio’s digital representation and has a significant impact on the overall sound fidelity and dynamic range.
When it comes to choosing the right bit depth, there are a few factors to consider. Bit depth determines the dynamic range and resolution of the audio, which impacts the overall quality. In this section, we’ll go over the common bit depths, factors to consider, and how intended use plays a role.
Factors To Consider When Choosing Bit Depth
There are a few factors to consider when deciding on a bit depth. The intended use, available storage space, and processing power are all important considerations. Intended use: Different types of audio have different bit depth requirements. For example, a podcast may only require a bit depth of 16 bits, while a music project may require a bit depth of 24 bits or higher to capture the full range of the audio. Available storage space: Higher bit depths require more storage space. If you’re working on a project with limited storage, you may want to consider using a lower bit depth. Processing power: Recording and processing audio at higher bit depths requires more processing power. If you’re working on an older or less powerful computer, a lower bit depth may be more suitable.
Common Bit Depths
The most common bit depths used in audio are 16, 24, and 32 bits. Here’s a brief overview of each: 16-bit: CD quality audio is 16-bit, which means it has a dynamic range of 96 dB. This is suitable for most podcast, speech, and other projects where the audio isn’t heavily processed. 24-bit: 24-bit audio captures more dynamic range and resolution than 16-bit audio. It’s commonly used in music production where the audio will be heavily processed, mixed, and mastered. 32-bit: 32-bit audio is the newest professional standard. It captures a massive dynamic range and resolution and is suitable for high-end music production, mastering, and other specialized audio applications.
Intended Use Of Audio And Bit Depth
Ultimately, the intended use of your audio will play the biggest role in choosing the right bit depth. If you’re producing a podcast or speech project, a bit depth of 16 bits is likely sufficient. For music production, a bit depth of 24 bits or higher is recommended to capture the full range of the audio. It’s important to keep in mind that a higher bit depth does not necessarily mean better quality. It’s all about finding the right balance between dynamic range, resolution, and processing power based on your specific project’s needs.
Audio Sample Rate And Bit Depth For Recording
Understanding audio sample rate and bit depth is crucial for recording quality audio. Sample rate measures the number of samples per second which determines the frequency range, while bit depth determines dynamic range and resolution. Choosing higher values improves audio quality.
When it comes to recording audio, choosing the right sample rate and bit depth is crucial for achieving high-quality recordings. Sample rate refers to the number of times per second that audio is sampled and bit depth refers to the number of bits used to represent each sample. In this article, we’ll take a look at how sample rate and bit depth affect recording quality, as well as some common misconceptions about these parameters.
Recommended Audio Sample Rates And Bit Depths For Recording
For most recording applications, a sample rate of 44.1kHz or 48kHz and a bit depth of 24 bits is recommended. However, some professional recording studios may use higher sample rates and bit depths, such as 96kHz or 192kHz and 32 bits, to achieve even higher quality recordings. It’s important to note that higher sample rates and bit depths also require more storage space and processing power.
How Audio Sample Rate And Bit Depth Affect Recording Quality
Sample rate and bit depth have a direct impact on the quality of audio recordings. Higher sample rates capture more detail and nuance in the audio waveform, resulting in a more accurate representation of the original sound. Likewise, higher bit depths allow for a greater dynamic range and more accurate representation of subtle changes in volume.
Common Misconceptions About Audio Sample Rates And Bit Depths In Recording
One common misconception about sample rate and bit depth is that higher is always better. While it’s true that higher sample rates and bit depths can result in higher-quality recordings, there are diminishing returns beyond a certain point. Additionally, it’s important to consider the limitations of the equipment being used, as not all recording devices are capable of capturing and processing higher sample rates and bit depths. Finally, it’s worth noting that the mixdown process typically involves reducing the sample rate and bit depth, so extremely high sample rates and bit depths may not necessarily translate to a better final product. In conclusion, choosing the right sample rate and bit depth for recording is crucial for achieving high-quality audio recordings. By selecting a sample rate and bit depth appropriate for the specific recording application, considering the limitations of the equipment being used and understanding the mixdown process, it’s possible to capture accurate and nuanced audio recordings.
Audio Sample Rate And Bit Depth For Mixing And Mastering
Every music producer knows that mixing and mastering can make or break your final product. One of the most crucial aspects of the mixing and mastering process is setting the audio sample rate and bit depth. Audio sample rate determines how many times per second the audio signal is measured, while bit depth defines the number of bits of information in each sample. Choosing the right sample rate and bit depth can be a daunting task, but in this complete guide, we’ll help you understand how audio sample rate and bit depth affect mixing and mastering quality.
Recommended Audio Sample Rates And Bit Depths For Mixing And Mastering
When it comes to mixing and mastering, it’s essential to use high-quality sample rates and bit depths. Most industry-standard digital audio workstations (DAWs) offer sample rates between 44.1kHz and 192kHz and bit depths of 16, 24, or 32 bits. However, you should choose the right sample rate and bit depth based on your specific needs.
| Sample Rate | Bit Depth | Recommended use |
|---|---|---|
| 44.1kHz | 16-bit | CD-quality audio production |
| 48kHz | 24-bit | High-quality audio production |
| 96kHz or higher | 32-bit floating-point | Professional audio production |
How Audio Sample Rate And Bit Depth Affect Mixing And Mastering Quality
The choice of audio sample rate and bit depth affects the quality of your mix and master. Higher sample rates capture more audio information, resulting in better audio quality. Similarly, using higher bits captures a greater dynamic range, providing more headroom to work with during mixing and mastering. It’s crucial to remember that, although higher sample rates and bit depths provide better quality, they also require more processing power and can increase file sizes.
Common Misconceptions About Audio Sample Rates And Bit Depths In Mixing And Mastering
- Misconception: Higher sample rates always equal better audio quality.
- Reality: Sample rate must match the recording source to achieve optimal sound quality.
- Misconception: Higher bit depths are always better for audio production.
- Reality: It’s essential to strike a balance between bit depth and processing power to avoid excessive file sizes.
- Misconception: There’s no need to use high sample rates and bit depths in modern music production.
- Reality: High-quality audio production requires using high sample rates and bit depths to work with large dynamic ranges and capture more audio information.
Choosing the right audio sample rate and bit depth is crucial to achieve the best audio quality possible during mixing and mastering. Choose the recommended sample rates and bit depths based on your specific needs, and don’t be misled by common misconceptions. Now that you have a complete understanding of audio sample rate and bit depth, you can take your mixing and mastering skills to the next level.
Audio Sample Rate And Bit Depth In Digital Audio
When it comes to digital audio, understanding audio sample rate and bit depth is crucial. These two parameters determine digital audio quality and play a significant role in enhancing the overall audio experience. Audio sample rate and bit depth specify how accurately audio is captured and reproduced. The higher the value, the more precise the audio quality. In this guide, we will discuss how audio sample rate and bit depth affect digital audio quality, the advantages, and limitations of high-resolution audio, and common misconceptions about it.
Advantages And Limitations Of High-resolution Audio
High-resolution audio refers to audio that is recorded at a higher sample rate and bit depth than the standard CD quality, which is 44.1kHz/16-bit. There are several advantages to high-resolution audio, including:
- The ability to reproduce sound more accurately, resulting in better audio quality.
- Higher dynamic range and greater detail in sound reproduction.
- A more realistic listening experience that matches the original recording.
However, high-resolution audio also has its limitations. One of the main downsides is that it requires more storage space than standard CD-quality audio due to the larger file sizes. Additionally, not all audio devices support high-resolution audio playback, and the difference in audio quality may not be noticeable to some listeners.
How Audio Sample Rate And Bit Depth Affect Digital Audio Quality
Audio sample rate and bit depth determine the accuracy and precision of digital audio. Sample rate refers to the number of times per second audio is recorded, and bit depth determines the number of bits of data used to represent each sample. The higher the values of these parameters, the more accurate and detailed the audio will be.
For example, CD-quality audio has a sample rate of 44.1kHz and a bit depth of 16-bit. In contrast, high-resolution audio can have sample rates of up to 192kHz and bit depths of up to 24-bit. The higher values result in better audio quality and more accurate representation of the original sound.
Common Misconceptions About High-resolution Audio
Despite the advantages of high-resolution audio, there are several common misconceptions surrounding it. One misconception is that high-resolution audio always sounds better than standard CD-quality audio. While this may be true in some cases, it largely depends on the quality of recording and the listener’s equipment and ears. Another misconception is that high-resolution audio eliminates the need for proper acoustics and quality speakers, which is incorrect. Good audio quality is a combination of the quality of the recording, the audio equipment, and the room acoustics.
Frequently Asked Questions Of Audio Sample Rate And Bit Depth Complete Guide
What Should I Set My Sample Rate And Bit Depth To?
Set your sample rate to match your project’s requirements and choose the highest bit depth your recording equipment will support. It’s recommended to use at least a 44. 1 kHz sample rate and 16-bit depth for most applications, but higher quality recordings may require 48 kHz or even 96 kHz and 24-bit depth.
What Is The Best Sample Rate And Bit Depth For Audio?
The best sample rate and bit depth for audio depends on the purpose of the recording. For music production and professional purposes, 24-bit depth and 48 kHz or higher sample rate is recommended. For casual listening and streaming, 16-bit depth and 44.
1 kHz sample rate is sufficient.
Should I Record At 44.1 Or 48?
Record at 48 if you’re shooting video and 44. 1 if you’re recording audio. 48 is the standard for digital video, while 44. 1 is the standard for digital audio. You can still record audio at 48 but it will increase the file size.
What Is The Difference Between 44100 And 48000 Sample Rate?
44100 sample rate means capturing 44100 audio samples per second, while 48000 means capturing 48000 samples per second. 48000 provides higher quality audio but consumes more storage space, and 44100 is standard in most devices.
Conclusion
To ensure the best possible audio quality, understanding sample rate and bit depth is crucial for any audio project. By choosing the appropriate settings and keeping in mind the limitations of the equipment, you can produce high-quality recordings with minimal noise and distortion.
Remember to consistently monitor your settings and adjust as necessary to achieve the desired results. Mastering sample rate and bit depth is an essential skill for any serious audio enthusiast or professional.