RMS, or Root Mean Square, is a key metric in audio that quantifies the average power output of an amplifier or the power handling capability of a speaker. It indicates the continuous power level that audio equipment can handle or produce while maintaining quality sound.
Understanding RMS (Root Mean Square) is essential for anyone involved in audio production or sound systems. It serves as a reliable indicator of performance, helping users compare and select audio components based on their power output and quality. As RMS describes the average power an audio device can manage without distortion, it’s a critical factor in achieving optimal sound reproduction.
A speaker or an amplifier with a high RMS rating typically delivers more consistent performance at varying sound levels, ensuring a clearer audio experience. RMS values offer a more realistic understanding of audio equipment potential compared to peak power ratings, which can sometimes be misleading. By focusing on RMS, you are better equipped to make knowledgeable decisions about your audio system for sustained quality and durability.
Rms Audio Power: Why It Matters
RMS (Root Mean Square) audio power is crucial in the world of sound. It tells you how powerful an audio system is. Think of RMS as the muscle of your speakers or amplifier. It can help you pick the best audio system for your needs. An amplifier with a higher RMS rating will deliver more consistent power to your speakers. This means better and clearer sound over time. Let’s dive into why this matter.
Decibels And Perceptions
Understanding decibels, or dB, is key to knowing why RMS matters. Decibels measure the intensity of the sound. Here’s how RMS power and decibels link:
- More RMS power means the potential for louder volumes.
- Higher decibels mean a sound is louder to our ears.
- A sound system’s RMS rating can help predict its maximum decibel output.
Steady State Vs. Peaks
Sound isn’t just about loudness; it’s about consistency and quality. RMS deals with steady state power – the power an audio system can handle continuously. This is different from peak power, which is the maximum power it can handle in short bursts.
Steady state power affects how your music feels. It’s like running a marathon at a steady pace instead of sprints. For audio, this means:
| RMS Power | Effect |
|---|---|
| High RMS | Smooth, consistent quality |
| Low RMS | Potential for distortion at high volumes |
Root Mean Square Explained
When talking about audio, RMS explains how powerful a sound is. It measures this power over time. The RMS value helps us compare different audio systems. It shows how loud and clear they can play music or sounds.
Math Behind The Magic
RMS isn’t just about audio; it’s a math formula. First, we square all the sound waves’ heights. Next, we find the average of those squares. Last, we get the square root of that average. This final number is the RMS.
Here’s a simple step-by-step:
- Square each sound wave height.
- Average these squares.
- Take the square root of that average.
This math tells us the sound wave’s steady strength.
From Electrical To Acoustic Energy
RMS helps us know how speakers change electric signals into sound. The RMS value says how good a speaker is at this job.
Sound systems turn electrical energy into sounds. This energy moves the speaker parts to make the air move. That moving air reaches our ears as sound. RMS shows how well this change happens.
- Higher RMS – Louder and clearer sound.
- Lower RMS – Softer and maybe unclear sound.
The higher the RMS value, the more powerful the output. This means the speaker can play sounds louder without harm.
Gauging Audio Equipment
When choosing audio equipment, understanding RMS (Root Mean Square) is key. It tells you how much power a speaker can handle. Let’s explore what specs to look for and clear up some marketing misconceptions.
Specifications To Look For
To gauge audio equipment properly, focus on these specifications:
- Power Output: Measured in watts, it indicates the speaker’s volume capacity.
- RMS Rating: This tells you the continuous power it can handle, not just peak moments.
- Frequency Response: Shows the range of sound a speaker can reproduce.
- Sensitivity: Measures how loudly a speaker plays per watt of power.
- Impedance: Lower impedance means more power draw from the amplifier.
Misconceptions In Marketing
Audio equipment marketing can be misleading. Here’s what to watch out for:
| Misconception | Truth |
|---|---|
| “More watts means louder.” | RMS is a better loudness indicator. |
| “Bass boost equals good sound.” | True quality comes from balanced audio, not just bass. |
| “Higher Peak Power is better.” | RMS value is more reliable for sustained performance. |
Measuring Sound: Tools And Techniques
Understanding the power of sound is key in many industries. It helps audio engineers, musicians, and even hobbyists improve the quality of their work. The process involves the use of specialized tools and techniques. Let’s dive into some popular methods for measuring the intensity and clarity of sound.
Common Devices Used
Professionals rely on certain devices to capture sound data accurately. These tools provide clear insights into audio quality. Let’s look at some of the most trusted ones.
- Sound Level Meters – Portable gadgets that measure sound pressure levels.
- Audio Analyzers – Provides in-depth analysis of sound frequency and distortion.
- Decibel Meters – Handy for quick checks on volume intensity.
Diy Measurement Approaches
Creative and cost-effective methods can also yield useful sound measurements. These approaches can be fun and educational.
- Using smartphone apps to approximate sound levels can be a great start.
- Building a simple decibel meter with a microcontroller for hands-on learning.
- Setting up a home-based audio testing lab using computers and software.
Implications For Audio Engineers
The concept of RMS in audio is paramount for audio engineers. RMS, or Root Mean Square, is a measure of the continuous power of an audio signal. It represents the average level of audio and helps engineers maintain consistent sound quality. With this in mind, let’s delve into how audio engineers apply RMS in different settings.
Recording Studio Standards
In a studio environment, RMS levels guide the recording process. Engineers use RMS to ensure recordings meet industry standards for loudness. Table 1 illustrates standard RMS values used in professional recording studios:
| Genre | RMS Level (dB) |
|---|---|
| Rock | -9 to -12 |
| Pop | -8 to -11 |
| Classical | -14 to -20 |
Adhering to these levels ensures recordings play back properly on most devices, avoiding distortions or inaudible sections in the final product.
Live Performance Applications
During live performances, RMS is equally influential. Setting appropriate RMS levels ensures the sound is powerful and immersive to the audience. For live settings, see the bullet points below detailing the significance of RMS:
- Avoiding speaker damage from excessively high levels
- Balancing the sound in different areas of the venue
- Ensuring vocal clarity throughout the performance
- Minimizing ear fatigue for the audience
RMS levels are adjusted in real-time to adapt to the dynamics of the live music and the audience’s response. An optimal RMS level balances intensity with clarity, a critical aspect for a memorable live audio experience.
Comparing Rms To Other Audio Metrics
Understanding how different audio metrics work is crucial for anyone interested in high-quality sound. Root Mean Square, or RMS, is one metric used to help listeners gauge a speaker’s average power output. Compare RMS with other audio measures to get a clearer picture of a speaker’s true sound quality.
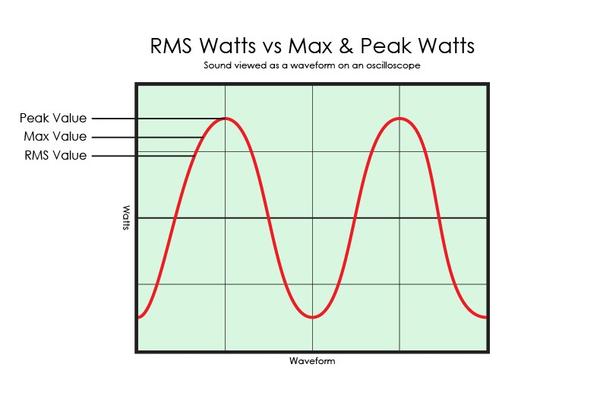
Peak Power Vs. Rms Power
Peak power and RMS power are both ways to measure a speaker’s abilities. Peak power shows the highest level of power a speaker can handle in short bursts. RMS power represents the average power a speaker can handle continuously. RMS is often seen as more reliable because it reflects normal usage over time.
- Peak Power – Maximum power during short spikes
- RMS Power – Average continuous power
Choose speakers with a high RMS rating for everyday use. A high peak power is less important for sound quality and more about withstanding power spikes.
Total Harmonic Distortion And Rms
Total Harmonic Distortion, or THD, measures how much a speaker’s output differs from the original audio source. A lower THD means a clearer, more accurate sound. When paired with RMS, these two metrics paint a full picture of a speaker’s performance.
| THD Rating | Sound Quality |
|---|---|
| Lower than 1% | High-quality sound |
| 1% – 10% | Decent sound quality |
| Higher than 10% | Poor sound quality |
Speakers with low THD and high RMS are ideal. Always look at RMS values when considering a speaker’s power. Together with THD, RMS helps determine audio clarity and quality.
Impact Of Rms On Listening Experience
Root Mean Square (RMS) is key in audio quality. It measures speaker power. High RMS means louder, clearer sound. It shapes how we hear music and movies. Good RMS creates unforgettable listening.
Speaker Selection
Picking speakers is more than just size or brand. RMS value matters greatly. It shows the speaker’s continuous power handling. This is not about short bursts but consistent sound quality.
Better RMS, better sound. Listeners want clear, distortion-free audio. Speakers with high RMS ratings deliver this. They produce powerful sound for any room size. This leads to a more impressive listening experience.
Room Acoustics And Rms
The room’s shape and size affect sound. High RMS doesn’t mean every room benefits. Rooms with poor acoustics can lead to bad sound even with good speakers. Match RMS to room acoustics for the best effect.
- Large rooms need high RMS for full sound.
- Small rooms with too much power can cause echo.
- Soft furnishings absorb sound, so adjust RMS accordingly.
RMS and acoustics work together. Balance is critical for perfect audio. This combination guides us to a better listening journey.
Credit: www.soundlabsgroup.com.au
Advancements In Sound Wave Technology
Sound wave technology has leaped forward. Today’s groundbreaking audio innovations transform how we experience sound. From the sharp tick of a hi-hat to the deep rumble of a bass, RMS (Root Mean Square) in audio has been pivotal in measuring sound quality. Let’s unlock the wonders of these advancements together.
Innovation In Audio Electronics
Refinements in audio electronics have brought stunning clarity and fidelity to our ears. High-resolution audio formats have raised the bar. They turn ordinary listening into an extraordinarily vivid sonic journey.
Advances like Class-D amplifiers now offer efficiency and precision. These amplifiers use innovative RMS calculations to deliver cleaner sound, with less power wastage.
- Smart amplifiers tailor audio performance in real-time.
- Digital Signal Processing (DSP) tweaks sound to near-perfection.
- High-resolution converters detail every audio nuance.
Future Trends And Research
Audio’s future shines with possibility. Researchers are now exploring quantum acoustics, aiming to revolutionize RMS in audio. This could mean even deeper insights into sound wave behavior.
Exciting developments such as 3D audio and immersive soundscapes are on the horizon. The table below highlights the trends to watch:
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| 3D Audio | Sound that moves around you in three dimensions. |
| Immersive Soundscapes | A full sensory experience resembling real-life environments. |
| AI in Audio | Smart algorithms shaping sound based on listening habits. |
Voice-control interfaces are becoming sleeker. They are taking user interactivity to new levels. With advances in machine learning, audio devices learn and adapt to personal preferences.
- Smarter noise-cancellation technologies.
- Audio equipment with built-in health tracking.
- Inductive charging for wireless audio devices.
As we push the boundaries, tomorrow’s RMS in audio will likely be unrecognizable. It will be precision-engineered to provide experiences that are more authentic and enveloping than ever before. Stay tuned for a symphony of innovation that will resonate with each one of us.
Frequently Asked Questions On Rms In Audio
What Does Rms Stand For In Audio?
RMS stands for Root Mean Square. It’s a statistical measure used to denote the continuous power that an audio amplifier can output, or a speaker can handle. It reflects the average level of power over time, providing a realistic indication of audio performance.
How Does Rms Power Affect Sound Quality?
RMS power influences the maximum volume a system can sustain without distortion. Higher RMS ratings generally mean louder, clearer sound at peak volumes. However, RMS alone doesn’t guarantee sound quality, which also depends on factors like the signal source and speaker design.
Can Rms Value Predict Audio Loudness?
RMS value gives a rough estimate of an audio system’s potential loudness but isn’t the sole determinant. Sensitivity, enclosure, and total harmonic distortion also play crucial roles. Loudness perception varies with frequency and human hearing sensitivity as well.
Is Higher Rms Better For Subwoofers?
A higher RMS rating for subwoofers implies greater power handling capability, which can lead to increased output and better performance. However, optimal listening depends on matching the RMS to the amplifier’s output and considering the subwoofer’s build quality.
Conclusion
Understanding RMS in audio allows for a clearer grasp of sound quality and equipment performance. By considering RMS values, you make informed choices for your audio setup. Let this guide empower your audio decisions, ensuring a superior listening experience. Seek clarity in sound?
Remember, RMS is key.