Phantom power provides energy to microphones that require electricity to operate. It typically delivers 48 volts through an XLR cable.
Within the world of professional audio, phantom power plays a crucial role in ensuring that condenser microphones and other electronic devices receive the necessary power without needing a dedicated external power source. This feature is a staple in most mixing consoles, audio interfaces, and preamps, enabling them to power a wide array of microphones seamlessly.
It’s activated through a switch that sends a positive voltage to the necessary pins in a balanced XLR cable, allowing sensitive microphone electronics to amplify your sound cleanly. Most modern recording setups accredit their versatility and clutter-free environment to the convenience offered by phantom power technology. It simplifies studio setups and on-stage configurations, allowing for flexibility and ease in various recording situations.

Credit: www.hollyland.com
The Basics Of Phantom Power
Phantom power is a term that sounds mystical, but it’s a staple in audio production.
It allows microphones to function at their fullest without external power supply boxes.
H3 Heading: What is Phantom Power?
What Is Phantom Power?
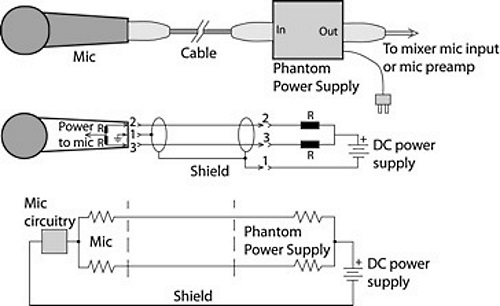
Phantom Power, often labeled as +48V on audio equipment, is a method of providing power to microphones through an audio cable.
- Common in studio and live sound environments.
- Essential for condenser microphones.
Understanding The Technicalities
Here’s a closer look at the technical side of phantom power:
| Voltage Provided | +48 Volts DC (Direct Current) |
|---|---|
| Transmission Method | Through balanced XLR microphone cable |
| Standard Practice | Industry-standard for professional audio gear |
- Balanced audio cable carries both signal and power.
- Power does not affect audio signal quality.
This system simplifies setup and ensures reliable performance across various microphones and audio interfaces.
Historical Context And Evolution
The concept of Phantom Power takes us back years in the realm of audio engineering. Understanding its historical context unravels how it became a pivotal asset in professional audio setups.
Early Uses Of Phantom Power
In the 1960s, phantom power began to illuminate the audio world. Engineers needed a way to power microphones without bulky external batteries. They devised a clever method to send power through microphone cables.
- The power was ‘invisible’, hence the name ‘phantom’.
- Initially used in television studios.
- It gained popularity for its convenience and efficiency.
The Development Of Modern Standards
Over time, a need arose for a standardized system. Consensus emerged among manufacturers and professionals.
| Year | Standard | Voltage |
|---|---|---|
| 1960s | Early Adaptation | 12-48V |
| 1980s | IEC 61938 | 48V ±4V |
Today, 48V is the universal standard for phantom power. This standard ensures compatibility across devices for seamless audio production.
Myths And Misconceptions
Phantom power often becomes shrouded in myths and misconceptions. It creates confusion. People think their electricity bills are higher because of devices not in use. Let’s explore and debunk some common myths associated with phantom power.
Addressing Phantom Power Myths
Many believe that phantom power is a significant expense. However, its impact varies. It is important to understand what devices are actual culprits. Not all contribute equally to phantom power consumption.
- Myth: All chargers consume power when plugged in, even if they’re not connected to their devices.
- Fact: Modern chargers are often designed to minimize energy use when not actively charging.
- Myth: Turning off a device stops it from using power.
- Fact: Some gadgets, like TVs and cable boxes, use standby power for updates and quick start-ups.
- Myth: Phantom power consumption is too small to worry about.
- Fact: While it might be a small percentage, accumulated over time and across multiple devices, it adds up.
Separating Fact From Fiction
Distinguishing between what’s true and false can reduce wastage and bills. Educating oneself is key. Here are facts to understand phantom power better.
| Statement | Myth/Fact |
|---|---|
| Standby mode consumes zero energy | Myth |
| Unplugging unused devices saves energy | Fact |
| Phantom power usage is negligible | Myth |
| Power strips can reduce phantom power drain | Fact |
Remember, awareness and small actions can lead to savings. Start by identifying which devices in your space contribute to phantom power. Unplug appliances that are rarely used. Use power strips with switches for convenience and energy conservation. By separating facts from fiction, we can all do our part to save energy and money.
Key Uses In Audio Engineering
Phantom power is essential in audio engineering, providing a 48-volt electrical supply to condenser microphones and DI boxes. This feature enables these devices to function optimally without an external power source, ensuring high-quality sound capture in various recording settings.
Phantom Power In Microphone Technology
The magic behind many microphones is phantom power. What does it do? Imagine a microphone that needs a little boost. Phantom power is like a superhero, providing the energy needed for microphones to catch sounds clearly. Most condenser microphones use it. Without phantom power, these mics would be asleep, missing the sounds that fill our ears with music, stories, and emotions.
- Condenser microphones get clarity from phantom power.
- It allows active DI boxes to function well.
- Signal refinement happens here, reducing noise.
The Role In Professional Recording Studios
Walk into any recording studio and you’ll find phantom power hard at work. It’s like the heart pumping blood, but here, it pumps life into the sound. In these studios, sound is king. The perfect take means clear, crisp audio.
| Equipment | Need for Phantom Power |
|---|---|
| Microphones | Essential for detailed sound capture |
| Audio Interfaces | Roles in connectivity and power delivery |
| Mixers | Crucial for blending multiple sounds |
Phantom power ensures every performance is caught in detail. No sound is too low or too weak. With its help, artists give their best, knowing the studio captures their art in highest quality.
Tips For Optimizing Phantom Power
Understanding how to optimize Phantom Power can be crucial for anyone using professional audio equipment. Phantom Power is a method of providing power to microphones that require electricity to operate. Through careful management and practical know-how, users can enhance their recording setups’ efficiency and audio quality. Here are some tips to optimize Phantom Power use.
Best Practices For Users
- Check Compatibility: Ensure your mic requires Phantom Power.
- Use Quality Cables: Good cables prevent power loss and interference.
- Power Only When Needed: Turn on Phantom Power after connecting mics.
- Disconnect Properly: Turn off Phantom Power before unplugging mics.
Avoiding Common Mistakes
Many users encounter issues by not adhering to Phantom Power guidelines. Here’s how to steer clear of common errors:
| Mistake | Optimization Tip |
|---|---|
| Leaving Phantom Power on | Always switch off when not in use to save energy. |
| Using for non-compatible devices | Check device requirements to avoid damage. |
| Failing to monitor sound quality | Regularly test and adjust to maintain clarity. |
Credit: www.prosoundweb.com
Phantom Power Benefits
Phantom power sparks life into various microphones and devices. It provides a hidden energy source.
Improving Audio Quality
Improving Audio Quality
Clear sound is crucial for recordings and performances. Phantom power helps achieve this. It offers a reliable power supply to condenser microphones. These mics capture sound details well. They need consistent power to work best. Phantom power delivers just that, reducing noise for professional audio.
- Better signal-to-noise ratio
- High-fidelity recordings
- Minimal interference
Enabling Versatility in Equipment Use
Enabling Versatility In Equipment Use
Equipment versatility is a must for creators. Phantom power allows for flexibility across devices. It powers different mics without extra cables. Live sound or studio setups stay tidy and safe. Users can switch mics with ease.
| Without Phantom Power | With Phantom Power |
|---|---|
| Limited microphone choice | Broad microphone compatibility |
| Cluttered setup with more cables | Clean setup with fewer cables |
| Fixed to specific locations | Flexible and mobile designs |
Choosing The Right Equipment
When diving into the world of audio recording, the right gear is crucial. Whether setting up a home studio or going pro, understanding phantom power is essential. Choosing the best equipment ensures crisp and clear audio. Let’s explore selecting the right microphones and interfaces with phantom power capabilities.
Purchasing Microphones And Interfaces
Quality audio starts with the right microphone. Condenser mics often need phantom power. Look for mics with balanced XLR connections.
Consider these tips:
- Match the mic to the recording task.
- Check mic sensitivity and noise levels.
- Ensure the interface offers clean phantom power.
| Feature | Mic | Interface |
|---|---|---|
| Phantom Power Support | 48V Required | 48V Provided |
| Connection Type | XLR | XLR |
| Price Range | Varies | Varies |
Evaluating Phantom Power Specifications
Knowing the specs helps ensure compatibility and performance. Common phantom power is 48 volts, but some gear may vary.
Check these specs:
- Voltage: Typically 48V, but verify.
- Current: Ensure sufficient mA for the mic.
- Preamps: High-quality preamps reduce noise.
Use the manufacturer’s spec sheet to verify details. Match power needs of mics with the output from interfaces.
Case Studies And Real-world Applications
Case Studies and Real-World Applications shine a spotlight on how Phantom Power revolutionizes the world of audio technology. By examining particular instances of its use, we grasp its significance and versatility. Professionals across industries rely on this innovative tool to amplify sound without the need for bulky batteries or external power sources.
Notable Industry Examples
Phantom Power has become an industry staple for its efficiency and reliability. Here are powerful instances of how this technology has been utilized:
- Broadcast studios use it to power microphones for clear audio capture.
- Recording artists in studios rely on it for high-quality sound production.
- Theatres employ wireless lapel mics using Phantom Power for seamless performances.
Phantom Power In Live Performances
Live performances rely on impeccable sound. Phantom Power plays a critical role here. Let’s look at some cases where it made a difference:
| Event | Use of Phantom Power |
|---|---|
| Concerts | Powering multiple microphones on stage without extra cables. |
| Theatre Productions | Ensuring actors’ lapel mics are always live. |
| Outdoor Festivals | Delivering quality sound in unpredictable environments. |
Frequently Asked Questions Of Phantom Power
What Is Phantom Power Used For?
Phantom power is used to provide the electrical energy necessary to power condenser microphones and other audio equipment. It typically delivers 48 volts directly through the microphone cable.
How Does Phantom Power Work?
Phantom power works by sending voltage through the balanced microphone cable. It energizes the microphone without affecting the audio signal. This power is supplied either by the mixer or through a separate phantom power supply unit.
Can Dynamic Mics Use Phantom Power?
Most dynamic microphones can be exposed to phantom power without damage. They simply do not use the power. However, it’s always best to check the microphone’s specifications before connecting to phantom power.
Is Phantom Power The Same As A Preamp?
No, phantom power is not the same as a preamp. Phantom power supplies the voltage needed for certain microphones, while a preamp amplifies the signal from the microphone to a usable level for mixing and recording.
Conclusion
Phantom power remains a subtle yet critical aspect of many electronic setups. Understanding its role and management can lead to better audio quality and equipment longevity. Remember to always use it wisely to keep your gear in top condition. Embracing these insights can make a significant impact on your technological endeavors.