To use parametric EQ, select a frequency band and adjust the gain. Parametric EQ is a versatile tool that allows you to fine-tune the frequency response of an audio signal.
With its ability to adjust the level of specific frequencies, parametric EQ is popular among audio professionals and enthusiasts alike. Although it can seem intimidating at first, learning how to use parametric EQ can greatly enhance your audio mixing skills.
We will cover the basics of parametric EQ, including its main components and how to use them effectively. We will also provide some tips on how to optimize your use of parametric EQ to achieve the desired sound for your audio project.

Credit: flypaper.soundfly.com
Understanding The Frequency Spectrum
Parametric Equalizer or Parametric EQ is used to adjust the frequency of the sound to achieve a clean and balanced output. Without understanding the frequency spectrum, it is impossible to make the necessary adjustments using a Parametric EQ. In this section, we will dive into the basics of sound waves and frequency ranges in the spectrum to get a better understanding of how a Parametric EQ works.
The Basics Of Sound Waves
Before diving into the frequency spectrum, let’s first understand the basics of sound waves. All types of sound waves have the same basic characteristics – frequency, amplitude, and phase. The frequency of a wave determines the pitch of the sound, while the amplitude determines the volume. The phase of the wave determines the synchronicity of the sound wave with another wave- this is something we don’t often adjust, leaving it as default.
Frequency Ranges In The Spectrum
When it comes to sound, the human ear can detect frequencies ranging from 20Hz to 20,000Hz. This range is referred to as the audible frequency spectrum. However, Parametric EQs often cover a wider range, making it important to understand the entire spectrum. The frequency spectrum can be divided into different ranges, including sub-bass, bass, low-mid, mid, upper-mid, presence, and brilliance.
| Frequency Range in the Spectrum | |
| Frequency Range | Frequency in Hz |
|---|---|
| Sub-bass | 20-60 |
| Bass | 60-250 |
| Low-mid | 250-500 |
| Mid | 500-2,000 |
| Upper-mid | 2,000-4,000 |
| Presence | 4,000-6,000 |
| Brilliance | 6,000-20,000 |
Each of these ranges represents a different part of the sound, and a Parametric EQ can be used to adjust each range to achieve a more balanced output. For example, if you have a track where the bass is too high, you can use a Parametric EQ to reduce the frequencies in the bass range for a more balanced sound.

Credit: legacy.presonus.com
Different Types Of Parametric Eqs
Parametric EQs come in different types that offer varying control over sound frequency. To use them effectively, it’s important to understand which type suits your audio needs best. Whether it’s a graphic or a semi-parametric equalizer, the key is to adjust the right bands to achieve your desired sound.
Different types of parametric EQs are used to shape the frequency response of an audio signal. They allow you to selectively boost or cut specific frequencies to achieve the desired tonal balance. There are three main types of parametric EQs: minimum-phase EQs, linear-phase EQs, and analog emulation EQs. Each type has its unique characteristics and benefits, making it suitable for specific applications. Let’s take a closer look at each one. Minimum-Phase EQs Minimum-phase EQs are the most common type of parametric EQs, and they are used in almost every audio mixing and mastering application. They work by altering the amplitude and phase of the audio signal, which affects the frequency response. Minimum-phase EQs introduce minimal phase shift and latency, making them ideal for live sound and real-time applications. They are also more CPU-efficient than other EQ types, making them suitable for use in digital audio workstations (DAWs). Linear-Phase EQs Linear-phase EQs are designed to eliminate phase distortion, which can occur when using a minimum-phase EQ. They work by applying a phase shift that is opposite to the phase shift caused by the minimum-phase EQ. This cancels out the phase distortion and results in a more transparent sound. Linear-phase EQs are ideal for mastering and other critical applications where sound quality is of utmost importance, but they are more CPU-intensive than minimum-phase EQs. Analog Emulation EQs Analog emulation EQs are designed to replicate the sound of vintage hardware EQs, such as the Pultec and SSL EQs. They use sophisticated modelling algorithms to mimic the unique frequency response and harmonic distortion characteristics of analog hardware. Analog emulation EQs are ideal for adding warmth, character, and color to digital recordings, but they are less precise than minimum-phase and linear-phase EQs due to their inherent nonlinearities. To summarize, parametric EQs are a powerful tool for shaping the tonal balance of an audio signal. The choice of EQ type depends on the specific application and desired sound quality. Minimum-phase EQs are CPU-efficient and suitable for real-time applications, while linear-phase EQs offer transparent sound but require more processing power. Analog emulation EQs provide vintage character and warmth, but at the expense of precision.
Steps For Using Parametric Eq
Using parametric EQ involves understanding the three main parameters – frequency, bandwidth, and gain – and adjusting them to achieve the desired sound. By identifying problematic frequencies and using EQ to reduce them, you can improve the overall clarity and balance of your audio.
If you’re a music producer or sound engineer, you know that equalization is crucial for finding and fixing problems in your audio. One type of equalization, parametric EQ, gives you the ability to adjust specific frequencies in your audio signal. Below are the steps on how to use parametric EQ effectively.
Identify Problem Frequencies
Firstly, you need to identify the frequencies in your audio that need adjustment. Listen to your audio through a good pair of headphones or speakers and try to pinpoint the problematic frequencies. You can also use a spectrum analyzer to visualize the frequencies in your audio. Once you have identified the problem frequencies, move onto the next step.
Adjust Frequency Bands
Next, you need to adjust the frequency bands in your parametric EQ to target the problem frequencies. Each frequency band typically has parameters for frequency selection, gain, and bandwidth. Adjust the frequency knobs until you are targeting the problematic frequency ranges.
Adjust Q Factor
The Q factor, or the bandwidth, determines how wide or narrow the band of frequencies you are adjusting will be. A higher Q factor narrows the band, and a lower Q factor widens the band. Adjust the Q factor to fine-tune your adjustments and help minimize any unwanted changes to adjacent frequencies.
Cut Or Boost Frequencies
Lastly, it’s time to cut or boost the frequencies you have targeted by adjusting the gain knob. If the targeted frequencies are too loud, reduce the gain, or cut the frequencies. If the targeted frequencies are too soft, increase the gain, or boost the frequencies. In conclusion, using parametric EQ is not difficult once you understand the process. Identify the problematic frequencies, adjust the frequency bands, adjust the Q factor, and cut/boost frequencies. With a bit of practice, you’ll be able to create ideal-sounding audio.
Tips For Using Parametric Eq
To effectively use parametric EQ, start by identifying the problem frequency ranges, then boost or cut those specific frequencies accordingly. Use a narrow Q value for precise adjustments, and remember to listen to the results in context with the whole mix.
Tips for Using Parametric EQ Parametric EQ is a powerful tool in audio production, allowing you to make precise adjustments to the frequency spectrum of your audio signals. When used correctly, it can enhance the clarity and balance of your mix. However, as with any tool, improper use can cause more harm than good. In this segment, we’ll discuss some tips for using parametric EQ effectively. Don’t Overdo It One common mistake when using parametric EQ is trying to fix every issue with your audio using EQ. While it can be tempting to keep adjusting the frequencies until everything sounds perfect, this approach can lead to an unnatural sound that lacks dynamics and depth. Instead, focus on the most critical issues and make gradual adjustments until you’re happy with the result. Use High-Q Filters Sparingly High-Q filters are great for precisely targeting specific frequencies, but they can cause more harm than good when used excessively. High-Q filters can result in an unnatural or “surgical” sound if used too prominently, especially in the midrange frequencies. As a general rule, use high-Q filters sparingly and reserve for troublesome frequencies that require precision. Make Small Adjustments When using parametric EQ, it’s crucial to make small adjustments instead of drastic changes. A minor change in frequency or gain can have a significant impact on the overall sound of your mix. So it’s essential to listen carefully and make gradual adjustments until you achieve the desired result. Use Your Ears Lastly, trust your ears when using parametric EQ. While it’s necessary to understand the theory of EQ and follow general principles, ultimately, your ears will tell you what sounds right. Let your ears guide you, and use your understanding of EQ to make informed decisions. In conclusion, using parametric EQ can significantly improve the overall quality of your mix, but only if used correctly. By keeping these tips in mind, you can make better decisions and bring out the best in your sound.
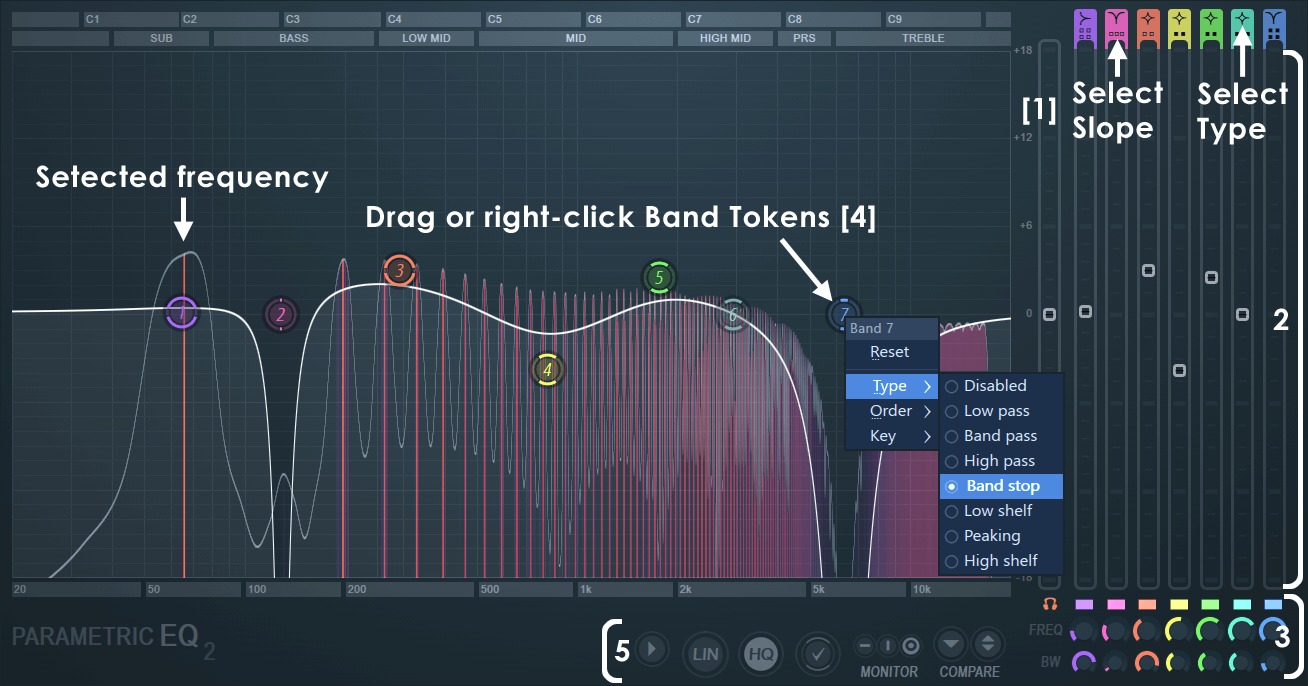
Credit: www.image-line.com
Frequently Asked Questions For How To Use Parametric Eq
How Do You Use Parametric Eq?
Parametric EQ is used to adjust the frequency level of individual audio bands. To use it, select a band, choose a frequency range, and adjust the gain or attenuation. Repeat this process for each band until you achieve the desired sound.
Remember to use it sparingly and avoid over-processing the audio.
What Are The 3 Parameters Of Parametric Eq?
The three parameters of parametric EQ are center frequency, gain, and Q.
What Are The Three Controls For A Fully Parametric Eq?
The three controls for a fully parametric EQ are center frequency, bandwidth, and gain or attenuation.
Is Parametric Eq Good?
Yes, parametric EQ is a good tool for audio professionals for shaping the sound they want. It offers more control and flexibility compared to graphic EQ. By adjusting specific frequency bands, users can fine-tune their audio to achieve the desired sound.
Conclusion
After learning how to use parametric EQ, it can make a significant difference in the quality of your audio output. By taking the time and effort to fine-tune each frequency band, you can create a well-balanced and professional sounding mix.
Keep in mind that adjusting the EQ is a delicate process, and it may take time to perfect. With practice and patience, you can become skilled at using parametric EQ and elevate your audio productions to the next level. Remember, EQ is just one tool in your audio toolkit, but when used correctly, it can greatly enhance your sound.