To mix the bass, adjust the EQ settings and compression levels to enhance the clarity and impact of low frequencies. The key is to find the right balance between the bass and other elements in the mix.
As an audio engineer or music producer, you know that mixing is a crucial process, and the bass is one of the most important elements in shaping the overall sound. A well-mixed bass not only provides depth and warmth but also creates a strong foundation for the entire track.
However, finding the perfect balance between the bass and other instruments can be challenging. The bass frequency range tends to overlap with the kick drum and other instruments. Therefore, you need to apply different techniques to make the bass sit perfectly in the mix. We will discuss some effective tips and tricks to help you mix the bass like a pro.
Importance Of Mixing The Bass
The bass forms the foundation of any song or music piece. It holds everything together, provides the rhythm, and creates a unique atmosphere. Thus, mixing the bass correctly is crucial to achieve the desired quality and balance in the final audio production. Mixing the bass requires a careful approach as the bass response of every system varies. In this blog post, we’ll give you a detailed insight into the importance of mixing the bass properly and how it can enhance the overall sound.
Enhances Clarity
Mixing the bass is essential to improve the clarity of the music piece. If the bass is not mixed correctly, it may overpower other elements of the track, making it difficult for the listener to discern them. By mixing the bass appropriately, you can create a clear separation between different elements of the song. This ensures that each part of the track is distinct, audible, and contributes to the overall quality of the music.
Adds Depth And Warmth
Mixing the bass adds warmth to the music piece while providing depth to it. A well-mixed bass fills up the low end of the frequency range, making the overall sound richer and more complex. It also offers the listener a sense of depth and space. Mixing the bass allows the other instruments to shine and have their unique moments in the mix without losing their impact or getting lost in the track’s low-frequency spectrum. Properly mixing the bass creates balance in the song by emphasizing every instrument in the mix, creating better dynamics, and presenting quality sound.
Pre-mixing Preparations
Before you start mixing the bass, there are some important pre-mixing preparations that you need to do. These preparations will ensure that your mixing process goes smoothly and you achieve the best bass mix possible. In this section, we will go over the key pre-mixing preparations to take before mixing the bass.
Tune Bass Guitar Properly
The first step in preparing for mixing the bass is to tune the bass guitar properly. Tuning the bass guitar will ensure that all the notes played on the instrument are in tune. If you have an out of tune bass guitar, it will make it harder to get the right sound when mixing the bass. You can use a tuner to help you make sure that each string is tuned to the correct pitch.
Clean Up Track
Another important pre-mixing preparation to take is to clean up the track. This means that you need to make sure that there are no unwanted sounds or noises in the bass track. You can use EQ to clean up any unwanted frequencies and remove any noise from the track. This will help to create a clean and clear bass sound that is easy to mix into your final track.
Adjust Levels
Adjusting the levels of the bass track is an essential pre-mixing preparation. You need to ensure that the bass track is at the right level and not too loud or too quiet in the mix. Adjusting the levels also means making sure that the other tracks in the mix are balanced with the bass track. You can use a meter to help you adjust the levels and ensure that all the tracks in the mix are at the right volume.
In Conclusion
In conclusion, these pre-mixing preparations are essential if you want to achieve a great bass mix. Tuning the bass guitar, cleaning up the track, and adjusting the levels are all important steps to take before mixing the bass. By taking these preparations, you will be able to achieve a clear, balanced, and powerful bass sound that fits perfectly into your final mix.
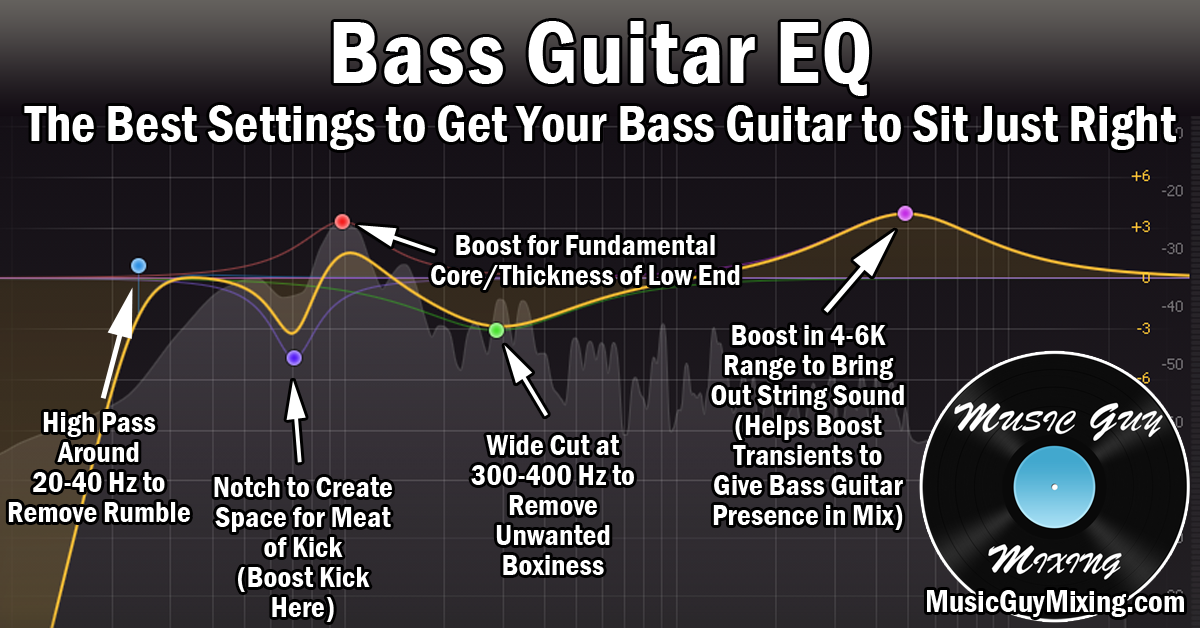
Assigning Eq To Bass
Enhancing the mix of the bass is essential in producing good quality sound. Assigning EQ to the bass can help create a clean and distinct bass sound in your mix. Properly mixing the bass can improve the overall quality of your music production.
Mixing a song requires a balance between all elements, with bass being a critical one. With the help of EQ, you can assign different frequencies to your bass and improve the overall sound quality. In this post, we’ll discuss how to assign EQ to the bass effectively and make the most of it.
Finding Problematic Frequencies
Before assigning EQ to your bass, it’s important to identify any problematic frequencies. These frequencies cause distortion or muddiness in the sound and need to be addressed. To find these frequencies, start by isolating the bass in your mix. Use a narrow Q with a boost to highlight specific frequencies. Slowly sweep through the spectrum to identify any frequencies that sound harsh or unbalanced. Once you have identified these frequencies, lower them using a cut.
Cutting Unwanted Frequencies
Cutting unwanted frequencies is critical to achieving a balanced and clear bass sound. When cutting, it’s important to be precise. Use a narrow Q to target specific frequencies and make sure to lower them enough to make a difference in the sound. Begin by cutting the problematic frequencies that you identified earlier. Then move on to other frequencies that aren’t adding any value to the sound. Cutting these frequencies will help to clean up the low-end and give room for other instruments in the mix.
Boost Low-end Frequencies
Boosting the low-end frequencies can add warmth and depth to your track. This technique is used to improve the bass’s presence in the mix and make it more prominent. To boost low-end frequencies, start with a broad Q and a small boost. Sweep through the low-end spectrum to identify which frequencies to boost. The amount of boost will depend on the overall mix, so use your ears to find the right balance.
Wrapping Up
Assigning EQ to bass is a necessary step in mixing a track. Finding problematic frequencies and cutting unwanted frequencies will help to clean up the bass, giving room for other instruments to shine. Boosting the low-end frequencies can add warmth and depth to your mix, but be careful not to overdo it. With these techniques, you can achieve a balanced and clear bass sound in your mix.
Credit: www.musicguymixing.com
Adding Compression To The Bass
Enhance the bass in your mix by adding compression. By compressing the bass, you’ll level out its dynamic range and make it easier to hear in the mix, without overpowering other elements like the drums or vocals.
When it comes to mixing bass, adding compression is a crucial step. Compression helps to even out the dynamics of the bass, making it more consistent and easier to fit into the mix. In this post, we will cover the basics of adding compression to the bass, including setting compression threshold, adjusting attack and release times, and using parallel compression.
Setting Compression Threshold
The first step in adding compression to the bass is to set the compression threshold. The threshold determines when the compressor will kick in and start reducing the level of the bass. A lower threshold means the compressor will start working sooner, while a higher threshold means the compressor will only kick in when the bass goes above a certain level. When setting the compression threshold, it’s essential to listen carefully to the bass and adjust the threshold accordingly. You want to find a balance between reducing the dynamic range of the bass while still allowing it to breathe and sound natural.
Adjusting Attack And Release Times
Once you’ve set the compression threshold, it’s time to adjust the attack and release times. The attack time determines how quickly the compressor starts reducing the level of the bass, while the release time determines how quickly the compressor stops compressing after the bass falls below the threshold. When adjusting attack and release times, it’s crucial to listen to how the bass sounds in the mix and make adjustments accordingly. A faster attack time will result in a more aggressive sound, while a slower attack time will allow more of the bass’s natural transients to come through. Similarly, a faster release time will result in a more natural sound, while a slower release time can result in a pumping effect.
Using Parallel Compression
Finally, you may want to try using parallel compression when mixing the bass. Parallel compression involves duplicating the bass track, adding compression to one of the tracks, and blending the uncompressed and compressed tracks together to get the best of both worlds. When using parallel compression, it’s essential to experiment with the levels of the compressed and uncompressed tracks to get the desired sound. You may also want to adjust the attack and release times of the compressed track to fine-tune the sound. In conclusion, adding compression to the bass is a crucial step in the mixing process. By setting the compression threshold, adjusting attack and release times, and using parallel compression, you can get the bass to sit perfectly in the mix and bring out the best in your music.
Applying Other Effects To The Bass
When it comes to mixing bass, applying effects can make a huge difference in the final sound. While EQ and compression are essential tools, adding other effects such as saturation and modulation can help bring out the warmth and motion in the bass.
Using Saturation To Add Warmth
Saturation is a type of distortion that can add warmth, harmonics, and character to the sound. When used on the bass, it can help bring out the low-end frequencies, making it sound fuller and richer. Saturation plugins come in many different varieties and can be used subtly or aggressively, depending on the desired effect.
Here are some tips for using saturation on the bass:
- Use a tape emulation plugin for a vintage, analog sound.
- Try using a parallel processing technique, where you blend the dry and saturated signals together for a more controlled effect.
- Don’t overdo it. Too much saturation can make the bass sound muddy and undefined.
Using Modulation Effects To Add Motion
Modulation effects such as chorus, flanger, and phaser can add movement and depth to the bass sound. These effects work by creating a copy of the original signal, altering its pitch and timing, and then blending it back in with the dry signal.
Here are some tips for using modulation effects on the bass:
- Use a chorus effect to add width and dimension to the bass.
- Try using a phaser effect to create a swirling, psychedelic sound.
- Use modulation effects sparingly. Too much modulation can make the bass sound unnatural and distracting.
Mixing The Bass With Other Instruments
Mixing the bass guitar is a crucial aspect of music production. The bass provides the foundation for all the other instruments to build upon. However, it’s not always easy to mix the bass with other instruments. In this section, we’ll explore some tips and techniques for mixing the bass with other instruments.
Setting Levels Properly
The first step in mixing the bass guitar with other instruments is setting the levels properly. The bass should be balanced with the other instruments in the mix. If the bass is too loud, it will overpower the other instruments. If it’s too quiet, it will get lost in the mix. A good rule of thumb is to start with the bass at around -10 dB and adjust from there.
Panning Positions
The panning position of the bass guitar is also important when mixing with other instruments. In most cases, the bass should be panned in the center. However, if there are two or more bass guitars or if the bass is played differently in different sections of the song, panning can be adjusted to create separation between the different parts.
Using Eq To Avoid Frequency Conflicts
One of the biggest challenges when mixing the bass with other instruments is frequency conflicts. The bass guitar and the kick drum, for example, both occupy the low end of the frequency spectrum. To avoid muddiness or masking of frequencies, it’s important to use EQ to carve out a space for each instrument. A high-pass filter can be used to remove unnecessary low frequencies from the other instruments, while a low-pass filter can be applied to the bass guitar to remove unwanted higher frequencies. Additionally, cutting certain frequencies on other instruments can help make space for the bass guitar to sit better in the mix.
Final Touches On Bass Mixing
Achieving the perfect balance of bass in a mix is crucial for any song. When mixing the bass, pay attention to the EQ, compression, and stereo imaging to ensure that it complements the rest of the track without overpowering it.
Use these tips to give your bass that final touch and make it sound just right.
After leveling the bass to perfection, it’s time to add final touches to ensure a professional-sounding mix. Double-checking bass levels, adding effects to the bass bus, and A/B testing the mix are crucial steps to take when mixing bass.
Double Checking Bass Levels
It’s easy to overlook certain sounds while mixing, especially the bass. Double-checking the bass levels ensures that it’s audible without drowning out other instruments. This step involves listening to the mix with fresh ears, and adjusting the levels as needed. Here are some tips:
- Use a spectrum analyzer to detect frequency ranges that lack bass.
- Compare the bass levels to a reference mix.
- Experiment with different speaker systems to determine if the bass levels still sound good.
Adding Effects To The Bass Bus
Adding effects to the bass bus enhances the overall sound of the bass. Some popular effects used in bass mixing include compression, equalization, and saturation. Here’s what to keep in mind while adding effects:
- Use effects sparingly to avoid over-processing the bass.
- Try using a parallel compression technique to add more body to the bass.
- Experiment with different plugins to find the best sound for the track.
A/b Testing The Mix
A/B testing involves comparing the mixed track to a reference track. This step ensures that the bass levels and effects added sound good in the context of the mix. Here are some tips for A/B testing:
- Choose a reference track that’s similar to the mixed track.
- Compare the tracks at similar volume levels to ensure accurate comparisons.
- Listen to the mix in various environments, such as on headphones and speakers, to ensure its quality is consistent.
Remember, the final touches are crucial when mixing bass. Double-checking bass levels, adding effects to the bass bus, and A/B testing the mix all contribute to a professional-sounding mix that’ll make your listeners nod their heads in approval.

Credit: www.soundonsound.com

Credit: m.youtube.com
Frequently Asked Questions On How To Mix The Bass
Where Should The Bass Be In The Mix?
The bass should sit at an appropriate level in the mix to maintain a balance between all the instruments. It should be audible enough to add depth and power to the sound but not overpowering to the point where it dominates the other instruments.
It’s advisable to use high-quality studio monitors or headphones to accurately judge the bass levels in a mix.
How Do You Get The Bass To Cut Through The Mix?
To get the bass to cut through the mix, you can use EQ to reduce other frequencies competing with the bass, enhance the harmonics to increase clarity, and adjust the level of the bass to achieve balance. Compression can also help to add sustain and punch.
Experiment with these techniques to find the best approach for your mix.
How Do You Mix Bassline Music?
To mix bassline music, use EQ to boost or cut frequencies, compression to balance levels, and use effects like delay or reverb to add texture. Use a limiter to prevent distortion and listen to the mix on different speakers. Practice and experiment with different techniques to find what works best for you.
How Do You Mix Smooth Bass?
To mix smooth bass, you need to use EQ to cut out any unwanted frequencies and boost the desired ones. Balance the bass with the rest of the mix, and don’t let it overpower other instruments. Use a compressor to control the bass’s dynamics, and make sure it is consistent throughout the song.
Lastly, listen to the mix on different devices to ensure it sounds good on all of them.
Conclusion
To sum it up, mixing the bass may seem like a challenging task for a beginner, but it’s crucial to achieve a well-balanced and professional-sounding track. Following the steps discussed, such as starting with good recording techniques, focusing on EQ, and experimenting with compression, reverb, and stereo imaging, can help you achieve a well-rounded low-end mix.
Keep in mind that practice makes perfect and don’t be afraid to try different methods to find what works best for you. With persistence and dedication, you’ll be on your way to achieving an impressive mix.