Soft clipping is a technique used to control the level of distortion in audio recordings. Soft clipping is a form of distortion that occurs when a signal exceeds the maximum level that a system can handle.
It is a subtle form of distortion that preserves the tonal character of the original sound while reducing the overall level of the recording. Soft clipping is particularly useful in music production, where it is often used to add warmth and character to recordings.
We will explore the concept of soft clipping in more detail, discussing its uses, benefits, and how it can be applied in various recording contexts. We will also provide tips for achieving optimal results when using soft clipping in your music production.
Credit: sound-au.com
Soft Clipping Explained
Soft clipping is a type of distortion used in music production to create a warmer, more natural sound. Unlike hard clipping, which produces a harsh distortion when levels exceed a certain threshold, soft clipping allows for more subtle distortion and can enhance the character of audio signals.
What Is Soft Clipping?
Soft clipping is a technique used in audio processing that is applied to prevent distortion of audio signals especially when audio levels surpass the maximum allowed level. Soft clipping works by intentionally distorting the audio waveform gradually, reducing amplitude instead of cutting off the waveform entirely.
Importance Of Soft Clipping In Audio Processing
The importance of soft clipping in audio processing cannot be overstated. Soft clipping is crucial in audio production as it helps produce a more natural and warm sound that is pleasant to the ear. Soft clipping protects speakers and headphones from blowing out especially when the audio levels surge beyond their maximum threshold. It also makes the audio sound fuller in the mix and controls the harshness that comes with high amplitudes that cause distortion, preventing fatigue to the listener’s ear. In conclusion, soft clipping is an essential tool in audio processing that helps produce high-quality sound without the harshness that comes with high amplitudes. Whether you’re a music producer, audio engineer or musician, comprehending the importance of soft clipping in audio processing is an excellent way to elevate your audio production and create a unique sound that’s both natural and enjoyable to the listener.
Credit: www.abletonprivatelessons.com
Different Types Of Clipping
Soft clipping is a type of audio signal processing that can be used to limit distortion in music recordings. It works by rounding off the peaks of the waveform more gradually than hard clipping, resulting in a smoother, more natural sound.
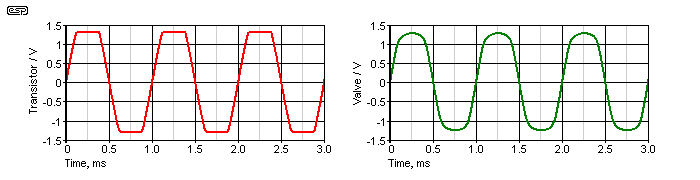
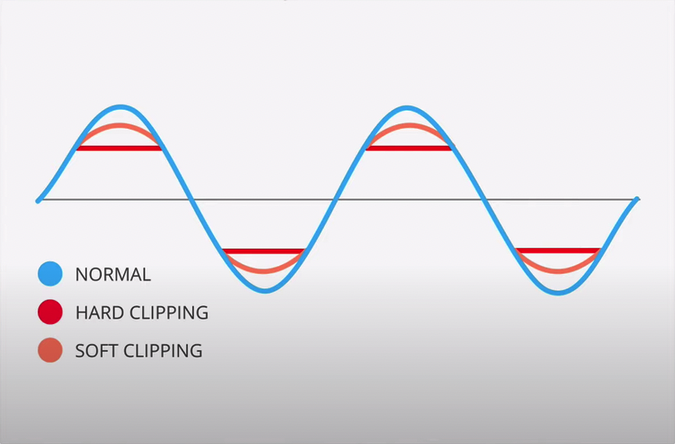
Different Types Of Clipping When it comes to audio processing, clipping refers to a type of distortion that occurs when the amplitude of a signal exceeds the maximum capabilities of the processing system. Clipping is a common occurrence in digital audio processing and can result in unwanted distortion or even damage to audio equipment. There are two types of clipping, Hard Clipping and Soft Clipping. H3: Hard Clipping Hard Clipping is a type of clipping that occurs when the amplitude of a signal exceeds the clipping threshold and the signal is completely clipped at that threshold. This results in a square waveform with sharp edges and is often heard as a harsh, distorted sound. Hard Clipping is often used in guitar distortion pedals and other audio effects to achieve a gritty, distorted sound. H3: Soft Clipping Soft Clipping, on the other hand, is a type of clipping that occurs when the amplitude of a signal exceeds the clipping threshold and is gradually clipped at that threshold. This results in a more rounded waveform and a softer, more natural distortion. Soft Clipping is often used in audio processing to add harmonic distortion to a signal, which can enhance the warmth and richness of the sound. In addition to Hard Clipping and Soft Clipping, there are also other types of clipping such as Analog Clipping and Digital Clipping. Analog clipping occurs when the input signal exceeds the maximum output level of the analog circuitry, while digital clipping occurs when the signal exceeds the maximum bit depth of the digital audio processing system. Understanding the different types of clipping is important for audio engineers and content creators looking to achieve a specific sound or effect. By using the right type of clipping, it’s possible to add character, warmth, and depth to audio recordings, while avoiding unwanted distortion or damage to equipment.
Why Soft Clipping Is Preferred Over Hard Clipping
Soft clipping is preferred over hard clipping because it offers more natural and subtle distortion to audio signals, whereas hard clipping creates a harsh, digital distortion. Soft clipping produces a more pleasing sound by only slightly distorting the loudest parts of the signal.
Soft Clipping Vs. Hard Clipping
When it comes to audio production, clipping is a common problem. Clipping happens when the signal level exceeds the maximum level that the system can handle. If left unmanaged, it results in poor sound quality or even damage to the equipment. Clipping can be solved using two methods: soft clipping and hard clipping. Hard clipping is the process of limiting the signal once it reaches the maximum level, resulting in a sharp change in the waveform and a distorted sound. On the other hand, soft clipping is a more gentle limiting process, which gradually distorts the waveform, resulting in a more pleasant sound.
Benefits Of Soft Clipping
Soft clipping is preferred over hard clipping for several reasons. Firstly, soft clipping produces a more natural and pleasant sound than hard clipping. It allows for a warmer, more atmospheric sound to be produced, which is desirable in many genres of music. Additionally, soft clipping is easier to manage and control, as it produces fewer artifacts and less distortion than hard clipping. One of the other benefits of soft clipping is that it protects speakers and other audio equipment from damage. Hard clipping can produce an excessive amount of distortion that can cause physical damage to speakers and other audio equipment. Soft clipping, on the other hand, gradually distorts the waveform and avoids causing any physical damage, thus making it a more suitable option for long-term use. In conclusion, soft clipping is a preferred method of limiting audio signals because it produces a more natural, pleasant sound, is easier to manage, and protects equipment from damage. Consider soft clipping if you want to produce a high-quality, distortion-free sound for your audio productions.
Applications Of Soft Clipping
Soft clipping is a technique used in digital audio processing that rounds off the peaks of sound waves as they approach the maximum level, which prevents harsh distortion. Soft clipping is commonly used in music production to give sounds a warmer, more natural sound.
Soft clipping is a crucial technique to prevent any digital distortion or damage to audio. It helps to optimize the performance of electronic devices that process audio signals. Soft Clipping is an easy and preferred method to reduce distortion in digital audio applications such as broadcasting, music concerts, and studios. Let’s delve into how soft clipping is used in the music and broadcast industries.
In Music Industry:
Soft clipping, also known as saturation or overdrive, is extensively used in the music industry. It helps to attain a unique sound that is ideal for some genres. The common applications of soft clipping in music are distortion guitars, kick drums, and bass. A distorted guitar sound is perhaps the most emblematic example of soft clipping. Distorted guitars can produce a unique sound that rock and metal artists prefer. It takes the audio signal and increases the amplitude until it starts to distort or clip. This distortion creates a unique tone, and soft clipping helps to control this distortion. For example, the band Nirvana, famous for their unique sound, extensively used soft clipping in their music production. The crunching sound of guitars was achieved with soft clipping, which created a high harmonic distortion in the soft clipping stage.
In Broadcast Industry:
Soft clipping is also used in the broadcast industry to ensure that the audience receives high-quality sound. The audio that is broadcasted to the listeners might contain high-level signals that can cause digital distortion in low-quality speakers or earphones. In such cases, soft clipping comes in handy. It ensures that audio signals do not exceed a certain threshold level to prevent distortion in low-quality devices. For example, FM radio stations use soft clipping to prevent overdriving of their transmitters and maintain quality sound throughout their broadcast. Soft clipping limits the maximum level of the audio signals, thereby protecting the speakers and amplifiers from distortion. In conclusion, Soft clipping is an essential tool for audio engineers and professionals in the music and broadcast industry. It allows them to modify and shape the audio signals to create high-quality sound without distortion or damage. Its applications are not limited to these two industries; any audio-processing device can make use of soft clipping.

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Frequently Asked Questions For What Is Soft Clipping
Is Soft Clipping Good?
Soft clipping can be good depending on the desired effect. Soft clipping is a type of distortion that produces a more gentle and warmer effect than harsh clipping. It can be used to add character and warmth to a sound, but it may not be appropriate for all types of audio content.
What Is Soft Clipping Vs Hard Clipping?
Soft clipping and hard clipping are techniques used in audio signal processing to prevent distortion caused by excessive amplitude. Soft clipping gradually reduces the amplitude of the signal, resulting in a rounded or softer distortion, while hard clipping is an abrupt cut-off of the signal, resulting in a harsher distortion.
What Does Soft Clipping Sound Like?
Soft clipping is a distortion effect used in music production. It involves rounding off the peaks of an audio signal to create a warmer, more saturated sound. It adds a subtle crunchiness to the mix without drastically changing the dynamics.
Soft clipping is commonly used on bass and drums to give them more presence and drive.
What Is The Difference Between Hard And Soft Clipping Pedals?
Hard clipping pedals produce a square wave sound by limiting the voltage output. Soft clipping pedals create a smooth distortion by gently rounding off the peaks of the waveform. The choice between the two depends on the type of distortion desired.
Conclusion
Soft clipping is a technique used in music production to prevent audio signal distortion. It applies a subtle form of distortion to the peaks of the signal, creating a more natural and pleasant sound. Soft clipping is a powerful tool that can help you achieve a high-quality sound, but it should be used with care.
Remember to always experiment, test, and trust your ears to make the best decisions. Ultimately, the goal is to create music that sounds great both in headphones and on a speaker system.